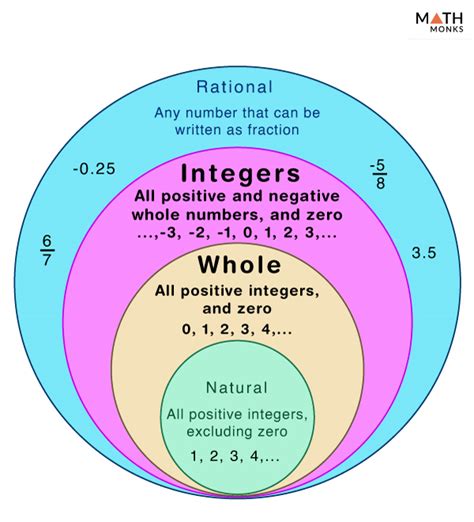
The question of whether zero is a whole number has been a topic of debate among mathematicians and educators for a long time. The answer to this question depends on the context and the definition of whole numbers being used. In general, whole numbers are defined as non-negative integers, which include 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on. However, some definitions of whole numbers exclude zero, and instead, define whole numbers as positive integers only.
Historical Perspective on Zero as a Whole Number
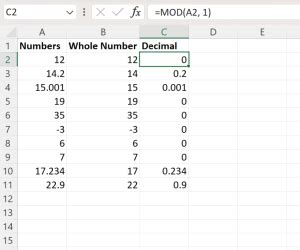
Historically, the concept of zero as a number developed over time, and its inclusion as a whole number was not always clear-cut. In ancient civilizations, such as the Babylonians and Egyptians, zero was not considered a number in its own right, but rather a placeholder or a symbol to indicate the absence of a digit. It wasn’t until the development of the Hindu-Arabic numeral system in the Middle Ages that zero began to be recognized as a distinct numerical value.
Mathematical Definition of Whole Numbers
From a mathematical perspective, whole numbers are often defined as non-negative integers, which include zero. This definition is based on the Peano axioms, which are a set of fundamental principles that define the properties of arithmetic. According to the Peano axioms, zero is a whole number, and it satisfies the usual properties of arithmetic, such as commutativity, associativity, and distributivity.
| Definition | Description |
|---|---|
| Non-negative integers | 0, 1, 2, 3,... |
| Positive integers | 1, 2, 3,... |
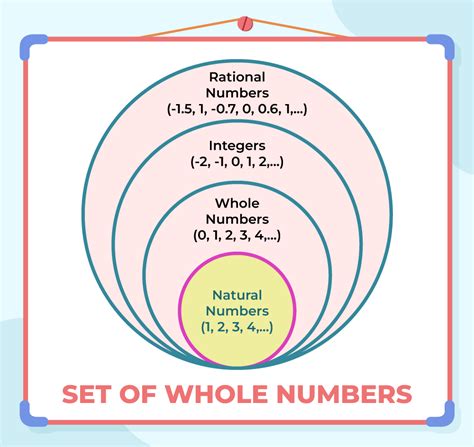
Practical Applications of Zero as a Whole Number
In practical applications, such as counting, measurement, and calculation, zero is often treated as a whole number. For example, when counting objects, we start with zero and increment by one for each object. Similarly, in measurement, zero is used as a reference point to indicate the absence of a quantity. In calculation, zero is used as a placeholder to indicate the position of a digit in a numerical value.
Pedagogical Considerations
From a pedagogical perspective, the question of whether zero is a whole number can be a source of confusion for students. Some educators argue that excluding zero from the set of whole numbers can help students develop a clearer understanding of the concept of whole numbers. However, others argue that including zero as a whole number helps students develop a more nuanced understanding of mathematical operations and properties.
Key Points
- Zero is a whole number according to the mathematical definition of non-negative integers.
- The inclusion of zero as a whole number has significant implications for mathematical operations.
- Practical applications, such as counting, measurement, and calculation, often treat zero as a whole number.
- Pedagogical considerations suggest that the question of whether zero is a whole number can be a source of confusion for students.
- The definition of whole numbers can vary depending on the context and the definition being used.
In conclusion, the question of whether zero is a whole number depends on the context and the definition being used. From a mathematical perspective, zero is a whole number, and it satisfies the usual properties of arithmetic. However, pedagogical considerations and practical applications may suggest that the definition of whole numbers can vary depending on the situation. Ultimately, a nuanced understanding of the concept of whole numbers and the role of zero in mathematical operations is essential for developing a deep understanding of mathematics.
What is the mathematical definition of whole numbers?
+Whole numbers are defined as non-negative integers, which include 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on.
Is zero a whole number in practical applications?
+Yes, in practical applications, such as counting, measurement, and calculation, zero is often treated as a whole number.
Why is the definition of whole numbers important in mathematics?
+The definition of whole numbers is important because it affects how we perform mathematical operations, such as addition and multiplication, and how we understand mathematical properties, such as commutativity and associativity.
Meta Description: Is zero a whole number? Explore the mathematical definition, practical applications, and pedagogical considerations surrounding this question. Discover the nuances of whole numbers and the role of zero in mathematical operations.