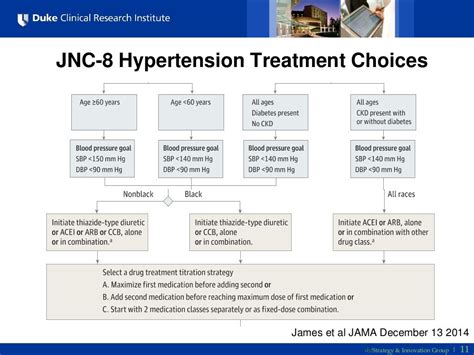
The management of hypertension has undergone significant transformations over the years, with various guidelines being published to help healthcare professionals make informed decisions. One of the most influential sets of guidelines in this area is the JNC 8 (Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure) guidelines, which were released in 2014. These guidelines have had a profound impact on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of hypertension, and it is essential to understand their key recommendations and implications.
Introduction to JNC 8 Guidelines

The JNC 8 guidelines were developed by a panel of experts in the field of hypertension, with the aim of providing evidence-based recommendations for the management of high blood pressure in adults. The guidelines are based on a comprehensive review of the literature, including randomized controlled trials, observational studies, and meta-analyses. The panel used a systematic approach to evaluate the evidence and develop recommendations that are tailored to specific patient populations.
Key Points
- The JNC 8 guidelines recommend a blood pressure target of less than 140/90 mmHg for most adults.
- The guidelines emphasize the importance of lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes, weight loss, and increased physical activity, as the first line of treatment for hypertension.
- The panel recommends the use of thiazide-type diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, or ARBs as initial therapy for hypertension, with the choice of agent depending on the patient's specific characteristics and comorbidities.
- The guidelines also provide recommendations for the management of hypertension in specific patient populations, including those with chronic kidney disease, diabetes, and heart failure.
- The panel emphasizes the importance of regular monitoring of blood pressure and adjustment of treatment as needed to achieve optimal blood pressure control.
Blood Pressure Targets and Lifestyle Modifications
The JNC 8 guidelines recommend a blood pressure target of less than 140⁄90 mmHg for most adults, with a target of less than 130⁄80 mmHg for those with chronic kidney disease or diabetes. The guidelines also emphasize the importance of lifestyle modifications as the first line of treatment for hypertension. These modifications include dietary changes, such as the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, weight loss, and increased physical activity. The panel recommends that adults engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity per week, with an additional 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity per week.
| Recommended Lifestyle Modifications | Description |
|---|---|
| Dietary changes | Adopt the DASH diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products. |
| Weight loss | Aim for a weight loss of 5-10% of initial body weight over 6-12 months. |
| Physical activity | Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity per week, with an additional 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity per week. |
| Sodium intake | Limit sodium intake to less than 2,400 mg per day. |
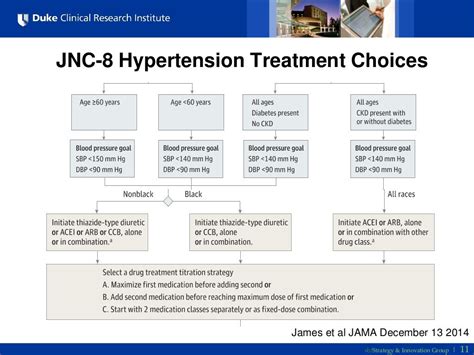
Pharmacological Treatment of Hypertension
The JNC 8 guidelines provide recommendations for the pharmacological treatment of hypertension, including the use of thiazide-type diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, or ARBs as initial therapy. The choice of agent depends on the patient’s specific characteristics and comorbidities, such as chronic kidney disease, diabetes, or heart failure. The panel also recommends the use of combination therapy, which involves the use of two or more antihypertensive agents, to achieve optimal blood pressure control.
Management of Hypertension in Specific Patient Populations
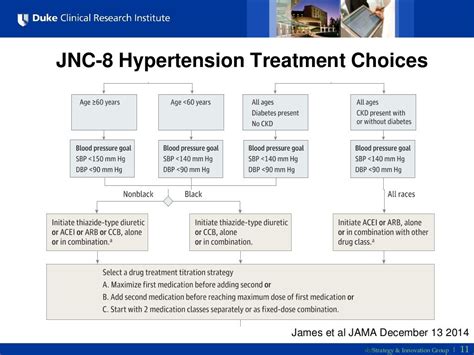
The JNC 8 guidelines provide recommendations for the management of hypertension in specific patient populations, including those with chronic kidney disease, diabetes, and heart failure. For example, the guidelines recommend the use of ACE inhibitors or ARBs as initial therapy in patients with chronic kidney disease or diabetes, due to their ability to slow the progression of kidney disease and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. The panel also recommends the use of beta blockers in patients with heart failure, due to their ability to improve survival and reduce the risk of hospitalization.
Regular Monitoring and Adjustment of Treatment
The JNC 8 guidelines emphasize the importance of regular monitoring of blood pressure and adjustment of treatment as needed to achieve optimal blood pressure control. The panel recommends that adults with hypertension have their blood pressure checked at least every 6 months, with more frequent monitoring in those with uncontrolled hypertension or those who are at high risk of cardiovascular events. The guidelines also recommend the use of home blood pressure monitoring, which can provide valuable information about blood pressure patterns and help identify potential issues with treatment adherence.
What are the key recommendations of the JNC 8 guidelines for the management of hypertension?
+The JNC 8 guidelines recommend a blood pressure target of less than 140/90 mmHg for most adults, with a target of less than 130/80 mmHg for those with chronic kidney disease or diabetes. The guidelines also emphasize the importance of lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes, weight loss, and increased physical activity, as the first line of treatment for hypertension.
What are the recommended pharmacological treatments for hypertension?
+The JNC 8 guidelines recommend the use of thiazide-type diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, or ARBs as initial therapy for hypertension, with the choice of agent depending on the patient's specific characteristics and comorbidities.
How often should blood pressure be monitored in adults with hypertension?
+The JNC 8 guidelines recommend that adults with hypertension have their blood pressure checked at least every 6 months, with more frequent monitoring in those with uncontrolled hypertension or those who are at high risk of cardiovascular events.
In conclusion, the JNC 8 guidelines provide a comprehensive framework for the management of hypertension in adults. The guidelines emphasize the importance of lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes, weight loss, and increased physical activity, as the first line of treatment for hypertension. The panel also provides recommendations for the pharmacological treatment of hypertension, including the use of thiazide-type diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, or ARBs as initial therapy. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and adjustment of treatment as needed are also essential components of the guidelines. By following these recommendations, healthcare professionals can help adults with hypertension achieve optimal blood pressure control and reduce their risk of cardiovascular events.