The concept of molar mass is fundamental in chemistry, serving as a bridge between the atomic scale and the macroscopic world. Molar mass, also known as molecular weight, is the mass of one mole of a substance, which is defined as 6.022 x 10^23 particles (atoms or molecules). For chemical compounds, calculating molar mass involves summing the atomic masses of all atoms in the molecule. Potassium chloride (KCl), a compound used in various applications including as a fertilizer, in photography, and as a salt substitute, provides a straightforward example for understanding molar mass calculations.
Understanding Atomic Mass
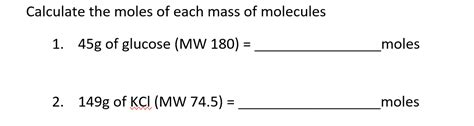
Before diving into the calculation of KCl’s molar mass, it’s essential to understand atomic mass. Atomic mass is the mass of an atom, typically expressed in unified atomic mass units (u), where 1 u is approximately equal to 1.66 x 10^-27 kilograms. The atomic masses of elements are usually averages of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of those elements. For potassium (K), the atomic mass is approximately 39.1 u, and for chlorine (Cl), it is about 35.5 u.
Calculating Molar Mass of KCl
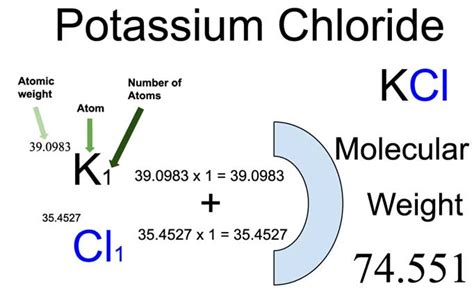
To calculate the molar mass of KCl, one simply adds the atomic mass of potassium to the atomic mass of chlorine. The calculation is as follows: Molar mass of KCl = Atomic mass of K + Atomic mass of Cl = 39.1 u + 35.5 u = 74.6 u. This result means that one mole of KCl has a mass of approximately 74.6 grams.
| Element | Atomic Mass (u) |
|---|---|
| Potassium (K) | 39.1 |
| Chlorine (Cl) | 35.5 |
| KCl Molar Mass | 74.6 |

5 Key Points in Calculating and Understanding Molar Mass of KCl
Key Points
- The molar mass of a compound is the sum of the atomic masses of its constituent atoms, providing a link between the microscopic and macroscopic properties of substances.
- For KCl, the calculation involves adding the atomic mass of potassium (approximately 39.1 u) to the atomic mass of chlorine (approximately 35.5 u), resulting in a molar mass of about 74.6 u.
- Understanding molar mass is essential for stoichiometry, the part of chemistry that studies amounts of substances that are involved in reactions.
- The concept of molar mass applies to all types of chemical compounds, from simple molecules like KCl to complex biomolecules, highlighting its universality and importance in chemistry.
- Calculations of molar mass must consider the atomic masses of the elements involved, which are averages reflecting the natural abundance of isotopes, ensuring accuracy in chemical analyses and reactions.
Implications and Applications
The ability to calculate and understand the molar mass of compounds like KCl has significant implications for various fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science. In chemistry, accurate molar mass calculations are crucial for synthesizing compounds, predicting reaction outcomes, and analyzing the composition of substances. In biology, understanding the molar masses of biomolecules is essential for studying their interactions, functions, and metabolic pathways. In environmental science, knowing the molar masses of pollutants and other substances helps in assessing their impact on ecosystems and in developing strategies for their removal or mitigation.
What is the significance of molar mass in chemistry?
+Molar mass is significant because it allows chemists to calculate the amounts of substances needed for reactions and to determine the yield of products, facilitating quantitative chemical analysis and synthesis.
How does the molar mass of KCl relate to its chemical properties?
+The molar mass of KCl influences its physical and chemical properties, such as its melting and boiling points, solubility, and reactivity. Understanding these properties is crucial for its applications in various industries.
Can molar mass be used to identify substances?
+While molar mass can provide clues about the composition of a substance, it cannot uniquely identify a substance because different compounds can have the same molar mass. Other analytical techniques are often required for definitive identification.
In conclusion, the calculation and understanding of the molar mass of KCl, and indeed any chemical compound, are foundational aspects of chemistry. They underpin the quantitative aspects of chemical reactions, synthesis, and analysis, highlighting the importance of precise calculations and a deep understanding of chemical principles for advancements in science and technology.