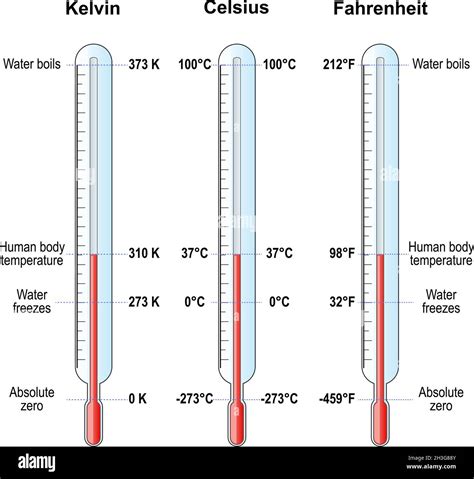
The concept of Kelvin room temperature is often misunderstood, yet it is a fundamental aspect of understanding temperature scales. To delve into this topic, it's essential to first establish a foundational understanding of the Kelvin scale and its relationship to other temperature scales. The Kelvin scale, named after Lord Kelvin, is an absolute temperature scale that is used in scientific research and engineering applications. It is defined such that 0 Kelvin (K) is absolute zero, the theoretical temperature at which all matter would have zero entropy, meaning all molecular movement would cease.
In everyday applications, particularly in settings like homes and offices, the term "room temperature" is commonly used to refer to a comfortable temperature range for human habitation, typically around 20 to 25 degrees Celsius (68 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit). However, when discussing Kelvin room temperature, we're referring to the same range but expressed in the Kelvin scale. Since the Kelvin scale is an absolute scale, to convert Celsius to Kelvin, you simply add 273.15 to the Celsius temperature. Thus, 20 degrees Celsius is equivalent to 293.15 Kelvin, and 25 degrees Celsius is equivalent to 298.15 Kelvin.
Key Points
- The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale with 0 K as absolute zero.
- Room temperature, when discussed in the context of Kelvin, refers to the range of about 293.15 K to 298.15 K.
- Conversion from Celsius to Kelvin is done by adding 273.15 to the Celsius temperature.
- Kelvin is used in scientific and engineering contexts due to its absolute nature.
- The concept of Kelvin room temperature is essential for understanding precise temperature control in various applications.
Understanding the Kelvin Scale

The Kelvin scale is significant because it provides a consistent and absolute reference point for temperature measurement. Unlike the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales, which are relative and have arbitrary zero points, the Kelvin scale is based on a fundamental physical principle—the concept of absolute zero. This makes the Kelvin scale particularly useful in scientific research, where precise temperature control is crucial. For instance, in cryogenics, the study of materials at very low temperatures, the Kelvin scale is indispensable for achieving and measuring temperatures close to absolute zero.
Practical Applications of Kelvin Room Temperature
While the term “Kelvin room temperature” might seem esoteric, its practical applications are widespread. In laboratory settings, maintaining equipment and experiments at a stable room temperature is critical. This stability is often ensured by temperature control systems that operate based on the Kelvin scale, providing precise temperature management. Furthermore, in industries such as pharmaceuticals and biotechnology, where chemical reactions and biological processes are highly temperature-sensitive, understanding and controlling temperature in Kelvin is vital for product quality and safety.
| Temperature Scale | Room Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| Celsius | 20°C to 25°C |
| Fahrenheit | 68°F to 77°F |
| Kelvin | 293.15 K to 298.15 K |
Implications and Future Directions
The importance of Kelvin room temperature extends beyond current applications, as advancements in technology continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in terms of temperature control and manipulation. For instance, in the field of quantum computing, operating temperatures are often near absolute zero, requiring extremely precise temperature control systems. As research and development in such areas continue, the role of the Kelvin scale and the concept of Kelvin room temperature will remain fundamental to achieving the desired outcomes.
In conclusion, the concept of Kelvin room temperature, while seemingly niche, is a critical aspect of understanding and applying temperature scales in scientific and industrial contexts. Its significance lies not only in providing a precise language for discussing temperature but also in enabling the precise control and measurement necessary for advancing various fields of science and technology.
What is the Kelvin scale, and how does it differ from other temperature scales?
+The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale with 0 K as absolute zero. It differs from the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales by having a non-arbitrary zero point and being based on the concept of absolute zero.
How is room temperature expressed in Kelvin?
+Room temperature, typically around 20 to 25 degrees Celsius, is equivalent to approximately 293.15 K to 298.15 K when expressed in Kelvin.
What are the practical applications of understanding Kelvin room temperature?
+Understanding Kelvin room temperature is crucial for precise temperature control in scientific research, industrial applications, and technological advancements, particularly in fields requiring stability and accuracy such as cryogenics, pharmaceuticals, and quantum computing.