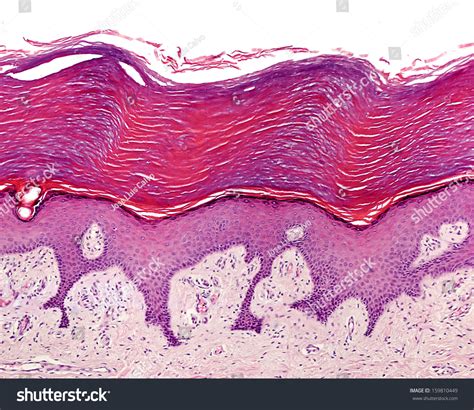
Keratinized epithelium is a type of epithelial tissue that plays a crucial role in protecting the body from external factors such as water loss, temperature extremes, and mechanical damage. This type of epithelium is characterized by the presence of keratin, a protein that provides strength and rigidity to the tissue. In this article, we will delve into five key facts about keratinized epithelium, exploring its structure, function, and importance in maintaining the body's homeostasis.
Key Points
- Keratinized epithelium is found in the skin, where it forms the outermost layer, known as the stratum corneum.
- The keratinization process involves the production of keratin filaments, which are embedded in a matrix of lipids and other proteins.
- Keratinized epithelium provides a barrier against water loss, helping to maintain the body's hydration levels.
- This type of epithelium also offers protection against mechanical damage, such as abrasion and pressure.
- Dysregulation of keratinization can lead to various skin disorders, including psoriasis and ichthyosis.
Structure and Function of Keratinized Epithelium
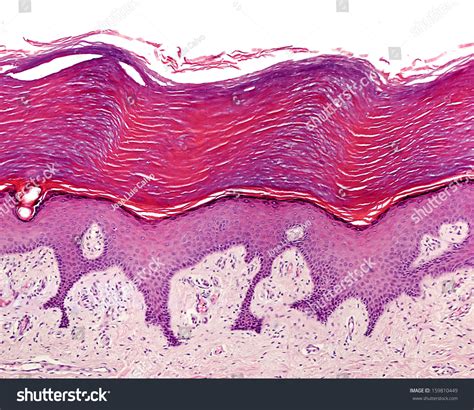
Keratinized epithelium is composed of multiple layers of epithelial cells, with the outermost layer being the most keratinized. The process of keratinization involves the production of keratin filaments, which are embedded in a matrix of lipids and other proteins. This matrix provides a hydrophobic barrier that prevents water loss and protects the underlying tissues from damage. The keratin filaments, on the other hand, provide mechanical strength and rigidity to the tissue.
Keratinization Process
The keratinization process involves a series of complex biochemical reactions, including the expression of specific genes, the synthesis of keratin proteins, and the assembly of keratin filaments. This process is tightly regulated by a variety of factors, including hormones, growth factors, and environmental stimuli. Dysregulation of keratinization can lead to various skin disorders, including psoriasis and ichthyosis, which are characterized by abnormal keratinization and barrier dysfunction.
| Layer | Description |
|---|---|
| Stratum corneum | Outermost layer, composed of fully keratinized cells |
| Stratum granulosum | Layer of cells undergoing keratinization |
| Stratum spinosum | Layer of cells with desmosomes, providing mechanical strength |
| Stratum basale | Innermost layer, composed of stem cells and progenitor cells |
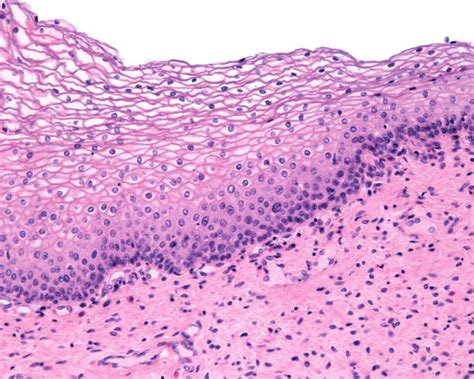
Importance of Keratinized Epithelium
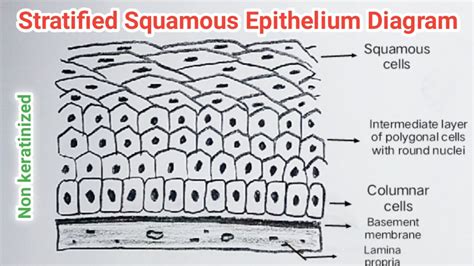
Keratinized epithelium plays a vital role in maintaining the body’s homeostasis, providing a barrier against water loss, mechanical damage, and other external factors. The skin’s ability to regulate water loss is essential for maintaining proper hydration levels, and keratinized epithelium is critical in this process. Additionally, the mechanical strength and rigidity provided by keratin filaments help to protect the underlying tissues from damage and injury.
Protective Functions
Keratinized epithelium also offers protection against a variety of external factors, including temperature extremes, humidity, and mechanical stress. The hydrophobic barrier provided by the keratinized epithelium helps to prevent water loss and protect the underlying tissues from damage. Furthermore, the mechanical strength and rigidity of keratin filaments help to resist mechanical stress and prevent injury.
In conclusion, keratinized epithelium is a critical component of the skin, providing a barrier against water loss, mechanical damage, and other external factors. The keratinization process involves the production of keratin filaments, which are embedded in a matrix of lipids and other proteins. Dysregulation of keratinization can lead to various skin disorders, including psoriasis and ichthyosis. Understanding the structure, function, and importance of keratinized epithelium is essential for appreciating the complex biology of the skin and developing effective treatments for skin disorders.
What is the main function of keratinized epithelium?
+The main function of keratinized epithelium is to provide a barrier against water loss, mechanical damage, and other external factors, helping to maintain the body’s homeostasis.
Where is keratinized epithelium found in the body?
+Keratinized epithelium is found in the skin, where it forms the outermost layer, known as the stratum corneum.
What happens when keratinization is dysregulated?
+Dysregulation of keratinization can lead to various skin disorders, including psoriasis and ichthyosis, which are characterized by abnormal keratinization and barrier dysfunction.