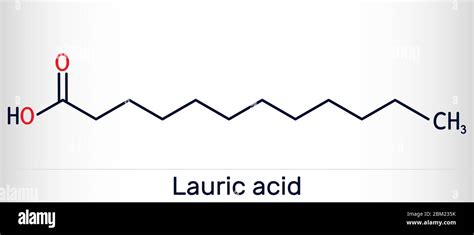
Lauric acid, a medium-chain fatty acid, is a key component of various natural products, including coconut oil and palm kernel oil. Its unique properties, such as antimicrobial activity and stability, can be attributed to its molecular structure and interactions. One crucial aspect of lauric acid's behavior is its ability to form hydrogen bonds, which play a significant role in determining its physical and chemical characteristics. In this article, we will delve into the world of lauric acid hydrogen bonding, exploring the types of hydrogen bonds it can form and their implications for its applications.
Key Points
- Lauric acid can form weak hydrogen bonds due to its molecular structure, which consists of a hydrophobic tail and a hydrophilic head.
- The type of hydrogen bonding in lauric acid is primarily determined by its carboxylic acid group, which can act as both a hydrogen bond donor and acceptor.
- Hydrogen bonding in lauric acid affects its physical properties, such as melting point and solubility, as well as its chemical reactivity and biological activity.
- The strength and nature of hydrogen bonds in lauric acid can be influenced by factors like temperature, concentration, and the presence of other molecules.
- Understanding the hydrogen bonding behavior of lauric acid is essential for optimizing its applications in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food science.
Hydrogen Bonding in Lauric Acid: An Overview
Lauric acid’s molecular structure, comprising a 12-carbon chain with a carboxylic acid group at one end, enables it to engage in hydrogen bonding interactions. The carboxylic acid group, in particular, is responsible for the formation of hydrogen bonds, as it can donate a hydrogen atom to another molecule or accept a hydrogen bond from a neighboring molecule. This dual capability allows lauric acid to participate in a variety of hydrogen bonding arrangements, influencing its behavior in different environments.
Types of Hydrogen Bonds in Lauric Acid
There are several types of hydrogen bonds that lauric acid can form, including:
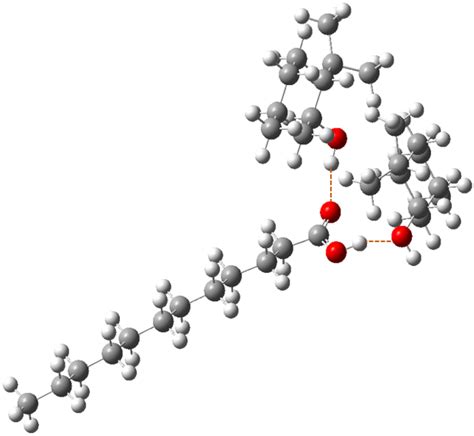
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonds: These occur between two separate lauric acid molecules, where the carboxylic acid group of one molecule interacts with the carboxylic acid group of another molecule.
- Intramolecular hydrogen bonds: These take place within a single lauric acid molecule, where the carboxylic acid group forms a hydrogen bond with another part of the molecule, such as the hydrophobic tail.
- Hydrogen bonds with other molecules: Lauric acid can also form hydrogen bonds with other molecules, like water or other solvents, which affects its solubility and reactivity.
| Type of Hydrogen Bond | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Intermolecular hydrogen bond | Between two separate lauric acid molecules | Lauric acid dimer formation |
| Intramolecular hydrogen bond | Within a single lauric acid molecule | Hydrogen bond between carboxylic acid group and hydrophobic tail |
| Hydrogen bond with other molecules | Between lauric acid and another molecule | Lauric acid-water interaction |
Factors Influencing Hydrogen Bonding in Lauric Acid
Several factors can influence the hydrogen bonding behavior of lauric acid, including:
- Temperature: Changes in temperature can affect the strength and nature of hydrogen bonds, influencing lauric acid’s melting point, solubility, and reactivity.
- Concentration: The concentration of lauric acid can impact the formation of hydrogen bonds, with higher concentrations leading to increased intermolecular interactions.
- Presence of other molecules: The presence of other molecules, such as solvents or additives, can alter the hydrogen bonding behavior of lauric acid, affecting its properties and applications.
Implications of Hydrogen Bonding in Lauric Acid
The hydrogen bonding behavior of lauric acid has significant implications for its applications in various fields, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: Understanding the hydrogen bonding properties of lauric acid can help optimize its use as an excipient or active ingredient in pharmaceutical formulations.
- Cosmetics: The hydrogen bonding behavior of lauric acid can influence its performance in cosmetic products, such as soaps, lotions, and creams.
- Food science: The hydrogen bonding properties of lauric acid can affect its functionality in food products, such as its texture, stability, and bioavailability.
What is the primary factor determining the hydrogen bonding behavior of lauric acid?
+The primary factor determining the hydrogen bonding behavior of lauric acid is its carboxylic acid group, which can act as both a hydrogen bond donor and acceptor.
How does temperature affect the hydrogen bonding behavior of lauric acid?
+Temperature can affect the strength and nature of hydrogen bonds in lauric acid, influencing its physical and chemical properties, such as melting point, solubility, and reactivity.
What are the implications of hydrogen bonding in lauric acid for its applications?
+The hydrogen bonding behavior of lauric acid has significant implications for its applications in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food science, where understanding its hydrogen bonding properties can help optimize its performance and functionality.
In conclusion, the hydrogen bonding behavior of lauric acid is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon, influenced by various factors, including its molecular structure, temperature, concentration, and the presence of other molecules. Understanding the types and implications of hydrogen bonds in lauric acid is essential for optimizing its applications and harnessing its unique properties. By recognizing the significance of hydrogen bonding in lauric acid, researchers and practitioners can unlock its full potential and explore new avenues for innovation and development.