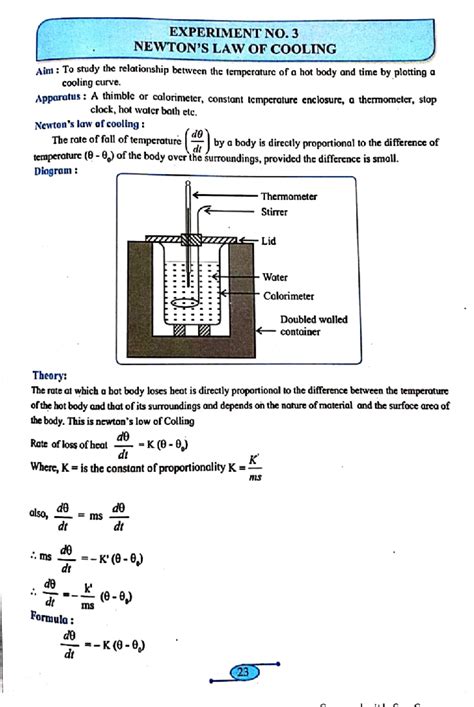
The concept of law cooling, also known as Newton's law of cooling, is a fundamental principle in thermodynamics that describes how the temperature of an object changes over time as it comes into contact with its surroundings. This natural process is crucial in understanding various phenomena, from the cooling of engines to the preservation of food. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of how law cooling works, exploring its underlying principles, applications, and the factors that influence its rate.
Key Points
- Law cooling is based on the principle that the rate of heat loss of an object is directly proportional to the difference in temperature between the object and its surroundings.
- The cooling process is influenced by several factors, including the surface area of the object, the temperature difference, and the thermal conductivity of the surrounding medium.
- Newton's law of cooling is expressed by the equation dT/dt = -k(T - T_s), where T is the temperature of the object, T_s is the temperature of the surroundings, and k is the cooling constant.
- Law cooling has numerous practical applications, including the design of cooling systems for electronic devices, the optimization of heat exchangers, and the understanding of environmental processes.
- The rate of cooling can be enhanced by increasing the surface area of the object, using materials with high thermal conductivity, or decreasing the temperature of the surroundings.
Principle of Law Cooling
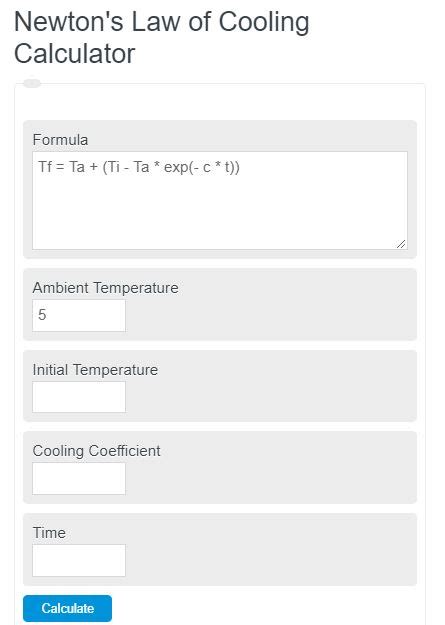
At the heart of law cooling is the principle that the rate of heat loss of an object is directly proportional to the difference in temperature between the object and its surroundings. This relationship is described by Newton’s law of cooling, which can be mathematically expressed as dT/dt = -k(T - T_s). Here, T represents the temperature of the object, T_s is the temperature of the surroundings, t is time, and k is the cooling constant, which depends on the properties of the object and the surrounding medium.
Influence of Surface Area
The surface area of the object plays a significant role in the cooling process. A larger surface area exposed to the surroundings allows for a greater rate of heat transfer, thus cooling the object more rapidly. This principle is applied in the design of heat sinks for electronic devices, where a larger surface area is often desired to efficiently dissipate heat and prevent overheating.
| Surface Area | Cooling Rate |
|---|---|
| Small | Slow |
| Medium | Moderate |
| Large | Fast |
Applications of Law Cooling
Law cooling has a wide range of applications across various fields. In engineering, it is essential for the design of cooling systems for engines, where the efficient dissipation of heat is critical for performance and longevity. In food preservation, understanding the cooling process helps in maintaining the quality and safety of perishable goods by slowing down bacterial growth. Furthermore, law cooling plays a vital role in environmental science, particularly in the study of climate and weather patterns, where the cooling of the Earth’s surface influences global temperature distributions.
Enhancing Cooling Rates
The rate of cooling can be enhanced by several means. Increasing the surface area of the object, as mentioned, is one method. Another approach is to use materials with high thermal conductivity, which facilitate the transfer of heat from the object to the surroundings. Additionally, decreasing the temperature of the surroundings can also accelerate the cooling process, as it increases the temperature gradient between the object and its environment.
Moreover, the use of fans or forced convection can significantly enhance the cooling rate by increasing the convective heat transfer coefficient. This method is commonly employed in electronic devices, such as computers and smartphones, where built-in fans help to cool the internal components.
What is the primary factor influencing the rate of cooling according to Newton's law of cooling?
+The primary factor is the difference in temperature between the object and its surroundings.
How can the cooling rate of an object be increased?
+The cooling rate can be increased by increasing the surface area of the object, using materials with high thermal conductivity, decreasing the temperature of the surroundings, or employing forced convection techniques.
What are some practical applications of law cooling?
+Practical applications include the design of cooling systems for electronic devices and engines, food preservation, and the study of environmental processes.
In conclusion, law cooling is a fundamental concept that underlies many natural and engineered processes. Understanding its principles and applications can lead to the development of more efficient cooling systems, better preservation methods, and a deeper insight into environmental phenomena. By recognizing the factors that influence cooling rates and applying this knowledge in practical contexts, we can harness the power of law cooling to achieve a wide range of technological and environmental goals.