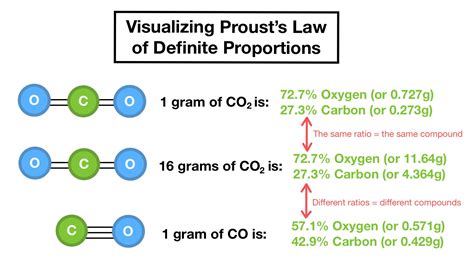
The Law of Definite Proportions, also known as the Law of Definite Composition, is a fundamental principle in chemistry that states that a chemical compound always contains its component elements in fixed ratio by mass, regardless of its source and method of preparation. This law was first discovered by the French chemist Joseph Proust in 1797 and is considered one of the most important laws in chemistry. The Law of Definite Proportions is a cornerstone of modern chemistry and has far-reaching implications for our understanding of the composition and properties of matter.
According to the Law of Definite Proportions, the percentage composition of a compound is always the same, regardless of how it is prepared or where it is found. For example, water (H2O) is always composed of 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom, and the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is always 2:1 by mass. This means that if you have a sample of water from a river, a lake, or a laboratory, the percentage of hydrogen and oxygen will always be the same. The Law of Definite Proportions applies to all chemical compounds, including simple compounds like water and carbon dioxide, as well as complex compounds like proteins and DNA.
Key Points
- The Law of Definite Proportions states that a chemical compound always contains its component elements in fixed ratio by mass.
- The percentage composition of a compound is always the same, regardless of how it is prepared or where it is found.
- The Law of Definite Proportions applies to all chemical compounds, including simple and complex compounds.
- The law has far-reaching implications for our understanding of the composition and properties of matter.
- The Law of Definite Proportions is a fundamental principle in chemistry that has been extensively experimentally verified.
Historical Background and Development

The Law of Definite Proportions was first discovered by Joseph Proust in 1797, while he was working at the Royal Laboratory in Madrid, Spain. At the time, Proust was studying the composition of tin oxides and noticed that the ratio of tin to oxygen was always the same, regardless of how the oxides were prepared. He realized that this was a general principle that applied to all chemical compounds and published his findings in a series of papers. The Law of Definite Proportions was a major breakthrough in chemistry and helped to establish the field as a scientific discipline. Over the years, the law has been extensively experimentally verified and has become a cornerstone of modern chemistry.
Implications and Applications
The Law of Definite Proportions has far-reaching implications for our understanding of the composition and properties of matter. It suggests that the properties of a compound are determined by the fixed ratio of its component elements, rather than by the method of preparation or the source of the compound. This has important implications for fields like materials science, where the properties of materials are critical for their performance and application. The Law of Definite Proportions also has practical applications in fields like chemistry, biology, and pharmacology, where the composition and properties of compounds are critical for their use and effectiveness.
| Compound | Elemental Composition | Percentage Composition |
|---|---|---|
| Water (H2O) | 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 oxygen atom | Hydrogen: 11.1%, Oxygen: 88.9% |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | 1 carbon atom, 2 oxygen atoms | Carbon: 27.3%, Oxygen: 72.7% |
| Sodium Chloride (NaCl) | 1 sodium atom, 1 chlorine atom | Sodium: 39.3%, Chlorine: 60.7% |
Criticisms and Limitations

While the Law of Definite Proportions is a fundamental principle in chemistry, it has some limitations and criticisms. One of the main limitations is that the law only applies to pure compounds, and not to mixtures or solutions. Additionally, the law does not take into account the possibility of isotopic variation, where the same element can have different numbers of neutrons in its atomic nucleus. This can affect the percentage composition of a compound, although the difference is usually small. Despite these limitations, the Law of Definite Proportions remains a cornerstone of modern chemistry and has been extensively experimentally verified.
Modern Developments and Extensions
In recent years, there have been several modern developments and extensions to the Law of Definite Proportions. One of the main developments is the discovery of isotopic variation, where the same element can have different numbers of neutrons in its atomic nucleus. This has led to a greater understanding of the composition and properties of matter, and has important implications for fields like materials science and pharmacology. Additionally, there have been several extensions to the Law of Definite Proportions, including the development of new analytical techniques like mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. These techniques have allowed for the precise determination of the composition and properties of compounds, and have helped to further establish the Law of Definite Proportions as a fundamental principle in chemistry.
What is the Law of Definite Proportions?
+The Law of Definite Proportions is a fundamental principle in chemistry that states that a chemical compound always contains its component elements in fixed ratio by mass, regardless of its source and method of preparation.
What are the implications of the Law of Definite Proportions?
+The Law of Definite Proportions has far-reaching implications for our understanding of the composition and properties of matter. It suggests that the properties of a compound are determined by the fixed ratio of its component elements, rather than by the method of preparation or the source of the compound.
What are some limitations of the Law of Definite Proportions?
+One of the main limitations of the Law of Definite Proportions is that it only applies to pure compounds, and not to mixtures or solutions. Additionally, the law does not take into account the possibility of isotopic variation, where the same element can have different numbers of neutrons in its atomic nucleus.