The Law of Total Expectation, also known as the Law of Iterated Expectations, is a fundamental concept in probability theory and statistics. It states that the expected value of a random variable can be calculated by conditioning on another random variable, and then taking the expected value of the resulting conditional expectations. This law is crucial in understanding complex stochastic processes and has numerous applications in fields such as economics, finance, and engineering. In this article, we will delve into the details of the Law of Total Expectation, its mathematical formulation, and its practical implications.
Mathematical Formulation
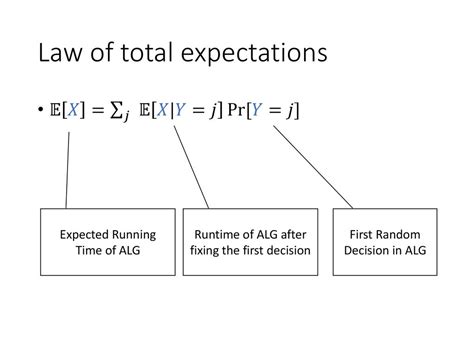
The Law of Total Expectation can be mathematically stated as follows: Let X and Y be two random variables defined on the same probability space. Then, the expected value of X can be expressed as:
E(X) = E(E(X|Y))
where E(X|Y) represents the conditional expectation of X given Y. This equation implies that the expected value of X can be obtained by first conditioning on Y, and then taking the expected value of the resulting conditional expectations.
Conditional Expectation
Conditional expectation is a concept that plays a crucial role in the Law of Total Expectation. It represents the expected value of a random variable given that another random variable has taken on a specific value. The conditional expectation of X given Y is denoted by E(X|Y) and is defined as:
E(X|Y) = ∑xP(X=x|Y=y)x
where P(X=x|Y=y) represents the conditional probability of X taking on the value x given that Y has taken on the value y.
| Random Variable | Conditional Expectation |
|---|---|
| X | E(X|Y) |
| Y | E(Y|X) |

Practical Implications

The Law of Total Expectation has numerous practical implications in various fields. In economics, it is used to model the behavior of economic agents under uncertainty. In finance, it is used to calculate the expected returns of investment portfolios. In engineering, it is used to model and analyze complex systems subject to random disturbances.
Applications in Economics
In economics, the Law of Total Expectation is used to model the behavior of economic agents under uncertainty. For example, it can be used to calculate the expected utility of a consumer given their income and preferences. It can also be used to model the behavior of firms under uncertainty, such as calculating the expected profit of a firm given its production costs and demand.
Key Points
- The Law of Total Expectation states that the expected value of a random variable can be calculated by conditioning on another random variable.
- Conditional expectation is a concept that represents the expected value of a random variable given that another random variable has taken on a specific value.
- The Law of Total Expectation has numerous practical implications in fields such as economics, finance, and engineering.
- It allows researchers to decompose complex stochastic processes into simpler components, making it easier to analyze and understand the behavior of random variables.
- The Law of Total Expectation is used to model the behavior of economic agents under uncertainty, calculate the expected returns of investment portfolios, and model complex systems subject to random disturbances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Law of Total Expectation is a fundamental concept in probability theory and statistics that has numerous practical implications in various fields. It allows researchers to decompose complex stochastic processes into simpler components, making it easier to analyze and understand the behavior of random variables. By understanding the Law of Total Expectation, researchers and practitioners can gain valuable insights into the behavior of complex systems and make more informed decisions under uncertainty.
What is the Law of Total Expectation?
+The Law of Total Expectation states that the expected value of a random variable can be calculated by conditioning on another random variable, and then taking the expected value of the resulting conditional expectations.
What is conditional expectation?
+Conditional expectation represents the expected value of a random variable given that another random variable has taken on a specific value.
What are the practical implications of the Law of Total Expectation?
+The Law of Total Expectation has numerous practical implications in fields such as economics, finance, and engineering. It allows researchers to decompose complex stochastic processes into simpler components, making it easier to analyze and understand the behavior of random variables.
Meta Description: Learn about the Law of Total Expectation, a fundamental concept in probability theory and statistics, and its practical implications in economics, finance, and engineering.