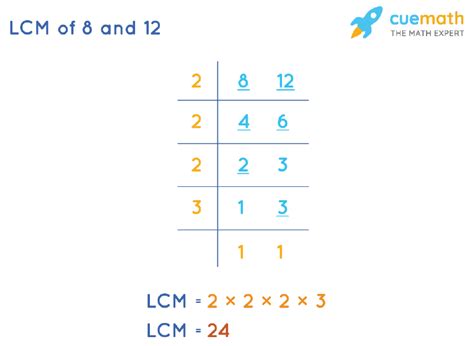
The Least Common Multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory. It represents the smallest multiple that is exactly divisible by each of the two numbers. For the numbers 8 and 12, finding the LCM is essential in various mathematical operations and real-world applications. To calculate the LCM of 8 and 12, we first need to factorize these numbers into their prime factors. The prime factorization of 8 is 2^3, and the prime factorization of 12 is 2^2 * 3. Then, we take the highest power of each prime number from these factorizations. So, for 2, we take 2^3 (from 8), and for 3, we take 3^1 (from 12), resulting in the LCM as 2^3 * 3^1 = 24.
Understanding the Concept of LCM

The concept of LCM is crucial for understanding how to add, subtract, and compare fractions with different denominators. It’s also vital in solving problems involving time, music, and other cyclic patterns. For instance, if two events occur at intervals of 8 and 12 minutes, respectively, the LCM (24 minutes) would be the first time they occur together after starting from the same reference point.
Real-World Applications of LCM
LCM has numerous practical applications. For example, in construction, if you are laying tiles that come in packs of 8 and 12, knowing the LCM helps in determining the minimum number of tiles you need to buy to ensure you can evenly distribute them without any leftover pieces. Similarly, in manufacturing, if production lines operate on cycles of 8 and 12 minutes, the LCM would help in synchronizing these cycles for efficient production planning.
| Number | Prime Factorization | LCM Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | 2^3 | 2^3 |
| 12 | 2^2 * 3 | 3 |
| LCM of 8 and 12 | 2^3 * 3 | 24 |
Key Points
- The LCM of 8 and 12 is calculated by taking the highest powers of prime numbers from their factorizations, resulting in 2^3 * 3 = 24.
- LCM is essential for operations involving fractions with different denominators and for solving problems related to cyclic patterns.
- Real-world applications of LCM include construction, manufacturing, and any scenario requiring synchronization of cycles or patterns.
- Understanding LCM enhances problem-solving skills and is crucial for efficiency in planning and execution across various industries.
- The calculation and application of LCM demonstrate how fundamental mathematical concepts underpin practical solutions in everyday life.
Calculating LCM for Other Numbers

Beyond the example of 8 and 12, calculating the LCM for any two numbers involves the same process: factorize each number into its prime factors and then take the highest power of each prime factor found in either factorization. This method ensures that the resulting LCM is divisible by both original numbers without a remainder, making it a versatile tool for mathematical and practical applications.
Advanced Applications of LCM
In more advanced mathematical contexts, LCM plays a role in number theory, particularly in the study of divisibility and the properties of integers. It’s also a key concept in algebra, where it’s used in the study of polynomials and their roots. Moreover, in computer science, understanding LCM is crucial for algorithms dealing with cyclic data structures and scheduling tasks that require synchronization.
To further illustrate the utility of LCM, consider a scenario where two machines produce parts at different rates, one every 8 minutes and the other every 12 minutes. The LCM of 8 and 12, which is 24 minutes, would be the time interval at which both machines would have produced an integer number of parts, facilitating efficient production planning and inventory management.
What is the purpose of calculating the LCM of two numbers?
+The primary purpose of calculating the LCM of two numbers is to find the smallest number that is a multiple of both, which is essential for various mathematical operations and real-world applications, such as adding fractions with different denominators, finding the smallest time interval at which two cyclic events occur together, and planning production in manufacturing.
How do you calculate the LCM of two numbers?
+To calculate the LCM of two numbers, first, factorize each number into its prime factors. Then, take the highest power of each prime factor found in either factorization. Multiply these highest powers together to get the LCM.
What are some real-world applications of LCM?
+LCM has numerous real-world applications, including construction (for laying tiles or bricks), manufacturing (for synchronizing production cycles), and any scenario requiring the synchronization of cyclic events or patterns, such as scheduling tasks or managing inventories.
In conclusion, the LCM of 8 and 12, which is 24, is a fundamental concept that not only aids in mathematical calculations but also has significant implications for problem-solving in various fields. Understanding how to calculate and apply LCM is crucial for efficiency in planning and execution across different industries, showcasing the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and real-world applications.