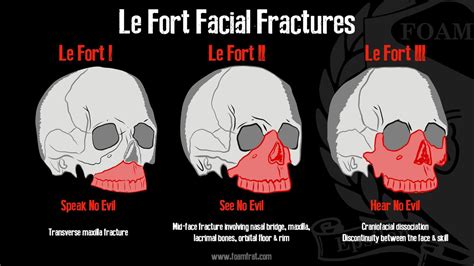
Le Fort fractures are a type of facial fracture that involves the maxillary bone and surrounding structures. These fractures are typically caused by high-impact trauma, such as car accidents or falls, and can result in significant facial deformity and functional impairment. The treatment of Le Fort fractures requires a comprehensive approach, taking into account the severity of the injury, the patient's overall health, and the potential for long-term complications. In this article, we will discuss the various treatment options available for Le Fort fractures, including surgical and non-surgical approaches, and highlight the importance of individualized care and multidisciplinary management.
Key Points
- Le Fort fractures are classified into three types, each with distinct characteristics and treatment requirements
- Surgical treatment options include open reduction and internal fixation, and may involve the use of plates, screws, and bone grafts
- Non-surgical treatment options, such as observation and medical management, may be suitable for less severe fractures or patients with significant comorbidities
- Individualized care and multidisciplinary management are crucial for optimal outcomes in Le Fort fracture treatment
- Long-term follow-up and rehabilitation are essential for maximizing functional and aesthetic recovery
Classification and Diagnosis of Le Fort Fractures
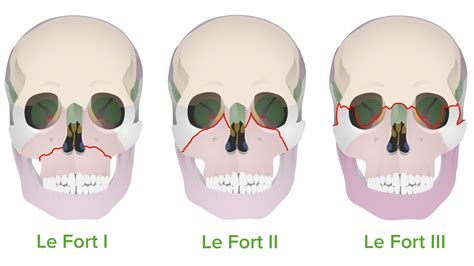
Le Fort fractures are classified into three types, based on the level of the fracture and the extent of facial involvement. Type I Le Fort fractures involve the lower part of the maxillary bone, while Type II and Type III fractures involve progressively higher levels of the face, including the nasal bones, orbits, and zygomatic arches. Accurate diagnosis is critical for determining the most effective treatment approach, and typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies (such as CT scans), and clinical evaluation.
Treatment Options for Le Fort Fractures
The treatment of Le Fort fractures depends on the severity of the injury, the patient’s overall health, and the potential for long-term complications. Surgical treatment options, such as open reduction and internal fixation, may be necessary for more severe fractures, while non-surgical treatment options, such as observation and medical management, may be suitable for less severe fractures or patients with significant comorbidities. The use of plates, screws, and bone grafts may be necessary to stabilize the fracture and promote healing.
| Fracture Type | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
| Type I Le Fort fracture | Open reduction and internal fixation, observation and medical management |
| Type II Le Fort fracture | Open reduction and internal fixation, use of plates and screws, bone grafting |
| Type III Le Fort fracture | Complex surgical reconstruction, use of bone grafts and fixation devices, multidisciplinary management |
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
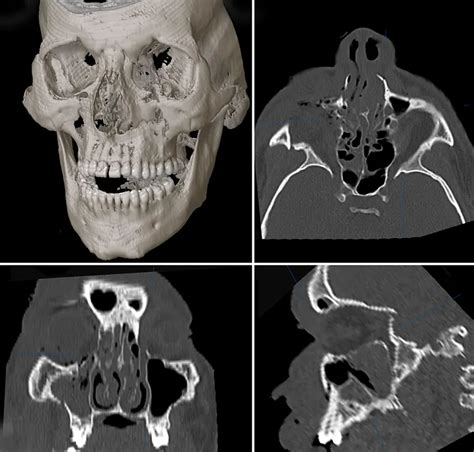
Postoperative care and rehabilitation are critical for maximizing functional and aesthetic recovery after Le Fort fracture treatment. Patients typically require close monitoring and follow-up, with ongoing evaluation of facial function, occlusion, and overall health. Rehabilitation may involve physical therapy, speech therapy, and other interventions, aimed at restoring facial function and promoting optimal healing.
Potential Complications and Long-Term Outcomes
Le Fort fractures can be associated with significant long-term complications, including facial deformity, malocclusion, and functional impairment. The risk of complications can be minimized with prompt and effective treatment, as well as ongoing follow-up and rehabilitation. Patients with Le Fort fractures require long-term monitoring and care, to ensure optimal outcomes and to address any potential complications or concerns.
What are the most common causes of Le Fort fractures?
+Le Fort fractures are typically caused by high-impact trauma, such as car accidents or falls. Other potential causes include sports injuries, assaults, and industrial accidents.
How are Le Fort fractures diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of Le Fort fractures typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies (such as CT scans), and clinical evaluation. Accurate diagnosis is critical for determining the most effective treatment approach.
What are the potential complications of Le Fort fractures?
+Le Fort fractures can be associated with significant long-term complications, including facial deformity, malocclusion, and functional impairment. Prompt and effective treatment, as well as ongoing follow-up and rehabilitation, can help minimize the risk of complications.
In conclusion, the treatment of Le Fort fractures requires a comprehensive approach, taking into account the severity of the injury, the patient’s overall health, and the potential for long-term complications. A multidisciplinary team, including surgeons, anesthesiologists, and other specialists, may be necessary to ensure optimal outcomes. With prompt and effective treatment, as well as ongoing follow-up and rehabilitation, patients with Le Fort fractures can achieve optimal functional and aesthetic recovery.