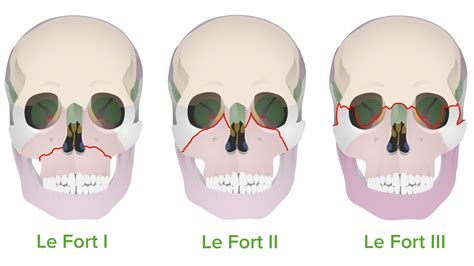
The LeFort fracture is a type of facial fracture that involves the maxillary bone and surrounding structures. It is classified into three main types, but there are also two additional subtypes that are sometimes recognized. Understanding the different types of LeFort fractures is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. In this article, we will delve into the five LeFort fracture types, their characteristics, and the implications for patient care.
Key Points
- The LeFort fracture is a complex facial fracture that involves the maxillary bone and surrounding structures.
- There are three main types of LeFort fractures: LeFort I, LeFort II, and LeFort III.
- Two additional subtypes, LeFort IV and LeFort V, are sometimes recognized, although their classification is not universally accepted.
- Accurate diagnosis and classification of LeFort fractures are critical for proper treatment and patient outcomes.
- Surgical intervention is often necessary to stabilize the fracture, restore facial symmetry, and ensure proper healing.
LeFort I Fracture

A LeFort I fracture, also known as a horizontal maxillary fracture, is the most common type of LeFort fracture. It occurs when the maxillary bone is fractured above the teeth and below the nose. This type of fracture typically results from a blow to the lower face and can be associated with other injuries, such as nasal fractures or orbital fractures. LeFort I fractures are often treated with surgical reduction and fixation to restore the normal anatomy of the face and ensure proper healing.
Characteristics of LeFort I Fracture
The characteristics of a LeFort I fracture include:
- A horizontal fracture line above the teeth and below the nose
- Separation of the maxillary bone from the surrounding bones
- Possible displacement of the maxillary bone
- Associated injuries, such as nasal fractures or orbital fractures
LeFort II Fracture
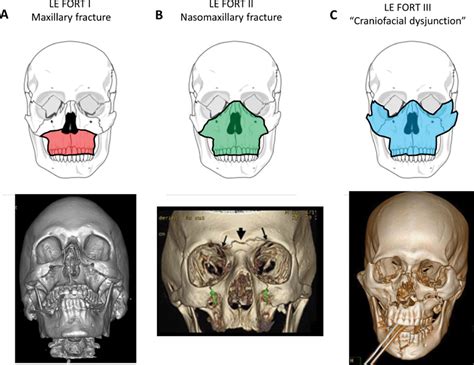
A LeFort II fracture, also known as a pyramidal maxillary fracture, is a more complex type of LeFort fracture. It occurs when the maxillary bone is fractured in a pyramidal shape, involving the nasal bones, orbital floors, and zygomatic bones. This type of fracture typically results from a more severe blow to the face and can be associated with other injuries, such as cranial fractures or cervical spine injuries. LeFort II fractures often require surgical intervention to stabilize the fracture and restore facial symmetry.
Characteristics of LeFort II Fracture
The characteristics of a LeFort II fracture include:
- A pyramidal fracture line involving the nasal bones, orbital floors, and zygomatic bones
- Separation of the maxillary bone from the surrounding bones
- Possible displacement of the maxillary bone
- Associated injuries, such as cranial fractures or cervical spine injuries
LeFort III Fracture
A LeFort III fracture, also known as a craniofacial separation, is the most severe type of LeFort fracture. It occurs when the maxillary bone is completely separated from the surrounding bones, resulting in a complete craniofacial separation. This type of fracture typically results from a severe blow to the face and can be associated with other life-threatening injuries, such as brain injuries or spinal cord injuries. LeFort III fractures often require emergency surgical intervention to stabilize the fracture and restore facial symmetry.
Characteristics of LeFort III Fracture
The characteristics of a LeFort III fracture include:
- A complete separation of the maxillary bone from the surrounding bones
- Craniofacial separation
- Possible displacement of the maxillary bone
- Associated injuries, such as brain injuries or spinal cord injuries
LeFort IV and LeFort V Fractures
Some sources recognize two additional subtypes of LeFort fractures, LeFort IV and LeFort V. However, the classification of these subtypes is not universally accepted, and their characteristics can vary depending on the source.
Characteristics of LeFort IV and LeFort V Fractures
The characteristics of LeFort IV and LeFort V fractures are not well established, but they may include:
- A combination of LeFort I, II, and III fractures
- A fracture line that involves the cranial base
- A fracture line that involves the facial bones and the cranial base
| LeFort Fracture Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| LeFort I | Horizontal maxillary fracture, separation of the maxillary bone from the surrounding bones |
| LeFort II | Pyramidal maxillary fracture, involvement of the nasal bones, orbital floors, and zygomatic bones |
| LeFort III | Craniofacial separation, complete separation of the maxillary bone from the surrounding bones |
| LeFort IV and LeFort V | Variable characteristics, may involve a combination of LeFort I, II, and III fractures or a fracture line that involves the cranial base |
Treatment and Management of LeFort Fractures

The treatment and management of LeFort fractures depend on the severity and type of fracture. Surgical intervention is often necessary to stabilize the fracture, restore facial symmetry, and ensure proper healing. The goal of treatment is to restore the normal anatomy of the face, ensure proper function, and minimize the risk of complications.
Surgical Intervention
Surgical intervention for LeFort fractures typically involves:
- Reduction and fixation of the fracture
- Restoration of facial symmetry
- Reconstruction of the orbital floors and zygomatic bones
- Stabilization of the craniofacial junction
Conclusion
In conclusion, LeFort fractures are complex facial fractures that require proper diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the different types of LeFort fractures, including LeFort I, II, III, IV, and V, is essential for providing effective care. Surgical intervention is often necessary to stabilize the fracture, restore facial symmetry, and ensure proper healing. By recognizing the characteristics of each type of LeFort fracture, healthcare professionals can provide optimal treatment and improve patient outcomes.
What is a LeFort fracture?
+A LeFort fracture is a type of facial fracture that involves the maxillary bone and surrounding structures. It is classified into three main types: LeFort I, LeFort II, and LeFort III.
What are the characteristics of a LeFort I fracture?
+A LeFort I fracture is characterized by a horizontal fracture line above the teeth and below the nose, separation of the maxillary bone from the surrounding bones, and possible displacement of the maxillary bone.
How are LeFort fractures treated?
+LeFort fractures are typically treated with surgical intervention to stabilize the fracture, restore facial symmetry, and ensure proper healing. The goal of treatment is to restore the normal anatomy of the face, ensure proper function, and minimize the risk of complications.
What is the difference between LeFort II and LeFort III fractures?
+A LeFort II fracture is characterized by a pyramidal fracture line involving the nasal bones, orbital floors, and zygomatic bones, while a LeFort III fracture is characterized by a complete separation of the maxillary bone from the surrounding bones, resulting in a craniofacial separation.
Are LeFort IV and LeFort V fractures recognized universally?
+No, the classification of LeFort IV and LeFort V fractures is not universally accepted, and their characteristics can vary depending on the source.