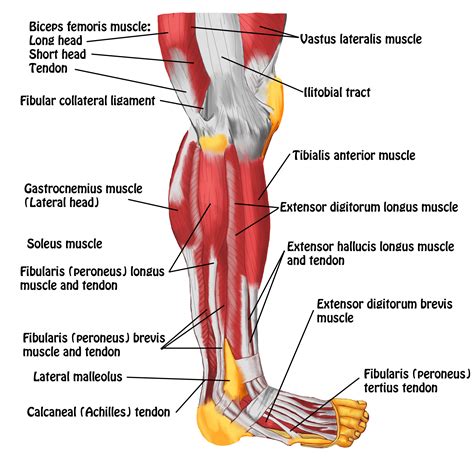
The human leg is a complex and fascinating anatomical structure, comprising multiple muscles that work in tandem to facilitate movement, support posture, and maintain balance. Among these, six key leg muscles play a crucial role in our daily activities, ranging from simple actions like walking and standing to more complex movements such as running and jumping. The six leg muscles in question are the quadriceps, hamstrings, gluteus maximus, adductor magnus, gastrocnemius, and soleus. Each of these muscles has a unique function and contributes significantly to our overall mobility and stability.
Understanding the Primary Functions of Each Leg Muscle
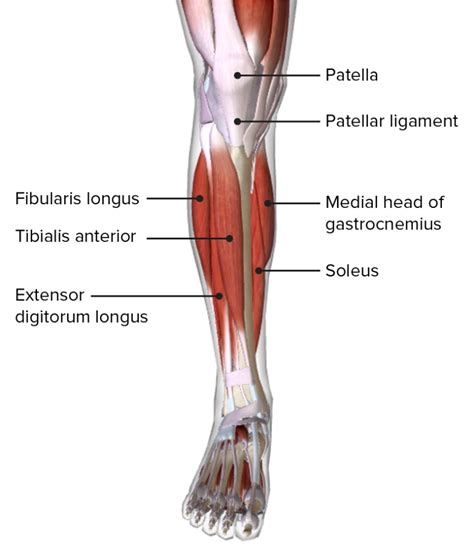
To appreciate the importance of these six leg muscles, it’s essential to understand their primary functions. The quadriceps, located at the front of the thigh, are responsible for knee extension, straightening the knee from a bent position. The hamstrings, situated at the back of the thigh, facilitate knee flexion, bending the knee. The gluteus maximus, one of the strongest muscles in the human body, plays a pivotal role in hip extension, aiding in movements such as climbing stairs or standing up from a seated position. The adductor magnus, while primarily involved in thigh adduction (bringing the thighs together), also assists in hip extension. The gastrocnemius and soleus, both located in the lower leg, are crucial for ankle flexion, enabling actions like pointing the foot downward.
Detailed Examination of the Quadriceps and Hamstrings
The quadriceps and hamstrings are often highlighted for their significant roles in athletic performance and everyday mobility. The quadriceps muscle group consists of four distinct muscles: the rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius. These muscles work synergistically to extend the knee, with the rectus femoris also contributing to hip flexion due to its unique origin on the anterior inferior iliac spine. The hamstrings, comprising the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus, are not only vital for knee flexion but also contribute to hip extension, making them essential for the propulsion phase of gait and sprinting.
| Muscle Group | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Quadriceps | Knee Extension |
| Hamstrings | Knee Flexion and Hip Extension |
| Gluteus Maximus | Hip Extension |
| Adductor Magnus | Thigh Adduction and Hip Extension |
| Gastrocnemius and Soleus | Ankle Flexion |
Key Points
- The quadriceps, hamstrings, gluteus maximus, adductor magnus, gastrocnemius, and soleus are the six primary leg muscles, each with distinct functions in mobility and stability.
- Understanding the primary functions of these muscles is essential for developing effective training programs and rehabilitation strategies.
- The quadriceps and hamstrings are critical for knee movement, with the quadriceps facilitating extension and the hamstrings facilitating flexion.
- The gluteus maximus and adductor magnus play significant roles in hip movement, with the gluteus maximus being one of the body's strongest muscles.
- The gastrocnemius and soleus are vital for ankle movement, enabling actions like walking and running.
Training and Injury Prevention Strategies
Given the importance of these six leg muscles, incorporating exercises that target each muscle group into a training regimen is advisable. For the quadriceps, squats, lunges, and leg press are effective. Hamstring exercises include deadlifts, leg curls, and glute-ham raises. The gluteus maximus can be targeted with squats, deadlifts, and hip thrusts. The adductor magnus is engaged through adduction exercises and certain variations of squats and lunges. Calf raises are ideal for strengthening the gastrocnemius and soleus. It’s also crucial to focus on injury prevention by ensuring proper warm-up routines, using appropriate training volumes, and incorporating stretching and recovery techniques to mitigate the risk of overuse injuries.
Nutrition and Recovery for Optimal Muscle Function
Beyond training, nutrition and recovery play pivotal roles in maintaining and enhancing the function of these leg muscles. A diet rich in protein is essential for muscle repair and growth, while carbohydrates provide the necessary energy for workouts. Adequate hydration is also vital for maintaining muscle function and overall health. Recovery techniques such as foam rolling, massage, and sufficient sleep are crucial for reducing muscle soreness and facilitating muscle adaptation to training stimuli.
What are the most effective exercises for strengthening the quadriceps and hamstrings?
+Exercises like squats, lunges, and leg press are highly effective for the quadriceps, while deadlifts, leg curls, and glute-ham raises target the hamstrings. It's essential to incorporate a variety of exercises to ensure comprehensive strengthening.
How can nutrition support the health and function of the six leg muscles?
+A balanced diet that includes sufficient protein for muscle repair, carbohydrates for energy, and adequate hydration is essential. Additionally, ensuring sufficient intake of vitamins and minerals, particularly those involved in muscle function like calcium and magnesium, can support overall muscle health.
What recovery techniques are most beneficial for reducing muscle soreness and enhancing muscle function?
+Techniques such as foam rolling, massage, and stretching can help reduce muscle soreness. Additionally, prioritizing sleep and ensuring adequate hydration are critical for recovery and muscle function. Active recovery methods, like light cardio or yoga, can also aid in the removal of metabolic byproducts that contribute to soreness.
In conclusion, the six primary leg muscles – quadriceps, hamstrings, gluteus maximus, adductor magnus, gastrocnemius, and soleus – are fundamental to human mobility and stability. Understanding their functions, incorporating targeted exercises into training regimens, and focusing on nutrition and recovery can significantly enhance muscle function and overall athletic performance. By adopting a comprehensive approach to leg muscle health, individuals can improve their mobility, reduce the risk of injury, and achieve their fitness goals.