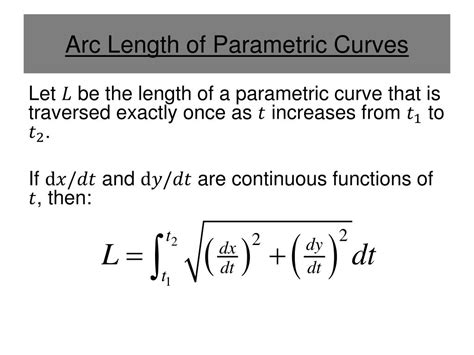
Calculating the length of various objects or distances is a fundamental aspect of numerous fields, including physics, engineering, and geography. The method used to calculate length can vary significantly depending on the context, the precision required, and the tools available. Here, we explore five distinct ways to calculate length, each applicable to different scenarios and offering varying degrees of accuracy and complexity.
Naturally worded primary topic section with semantic relevance
The calculation of length is essential in many real-world applications, from determining the distance between two points on the Earth’s surface to measuring the dimensions of objects in a workshop. Each method of calculating length has its own set of advantages and limitations. For instance, using a ruler or tape measure is straightforward and sufficient for many everyday tasks, but it lacks the precision needed for scientific or engineering applications. In contrast, more advanced techniques, such as using lasers or GPS technology, offer high precision but may be more complex and expensive to implement.
Specific subtopic with natural language phrasing
Method 1: Direct Measurement involves using a physical measuring tool like a ruler, tape measure, or caliper to directly measure the length of an object. This method is the most straightforward and is suitable for most everyday applications. However, its accuracy is limited by the precision of the measuring tool and the skill of the person taking the measurement. For example, a ruler might be accurate to the nearest millimeter, while a caliper can offer precision down to a fraction of a millimeter.
| Method | Description | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Measurement | Using rulers, tape measures, or calipers | Varies by tool, typically mm to fractions of a mm |
| Geometric Calculation | Applying geometric principles to known dimensions | High, dependent on known dimensions' accuracy |
| Laser Measurement | Utilizing laser technology for distance measurement | Very high, often to within a few millimeters |
| GPS Technology | Employing Global Positioning System for location and distance | High, typically within a few meters |
| Trigonometric Calculation | Using angles and side lengths to calculate distances | High, dependent on accuracy of angle and side length measurements |
Advanced Methods for Length Calculation

Beyond direct measurement, there are several advanced methods for calculating length, each with its unique applications and advantages. Geometric calculation involves using known dimensions and geometric principles to determine unknown lengths. This method is highly accurate when the known dimensions are precise but requires a good understanding of geometry. Laser measurement offers very high accuracy and is commonly used in construction and engineering for measuring distances and heights. GPS technology is useful for calculating distances between two points on the Earth’s surface and has become indispensable for navigation and mapping. Lastly, trigonometric calculation uses the principles of trigonometry to calculate lengths based on known angles and side lengths, which is particularly useful in surveying and physics.
Key Points
- The choice of method for calculating length depends on the required precision, the context of the measurement, and the available resources.
- Direct measurement is straightforward but limited in precision, while advanced methods like laser measurement and GPS technology offer higher accuracy but may be more complex.
- Geometric and trigonometric calculations provide high accuracy when the known dimensions or measurements are precise.
- Understanding the principles and limitations of each method is crucial for selecting the appropriate technique for a given task.
- The development and application of these methods reflect the evolving needs of various fields for accurate length calculation.
In conclusion, calculating length is a fundamental task that can be approached in various ways, each suited to different applications and precision requirements. By understanding the principles, advantages, and limitations of these methods, individuals can select the most appropriate technique for their specific needs, whether in everyday tasks, scientific research, or engineering projects.
What is the most accurate method for calculating length?
+The most accurate method can vary depending on the context and available tools. However, laser measurement and trigonometric calculation, when applied correctly, can offer very high accuracy.
How does GPS technology calculate distances?
+GPS technology calculates distances by determining the precise location of two points on the Earth’s surface using signals from a network of satellites. The distance between these two points can then be calculated using geometric principles.
What are the limitations of direct measurement methods?
+The limitations of direct measurement methods include the potential for human error, the precision of the measuring tool, and the difficulty in measuring very large or very small distances accurately.