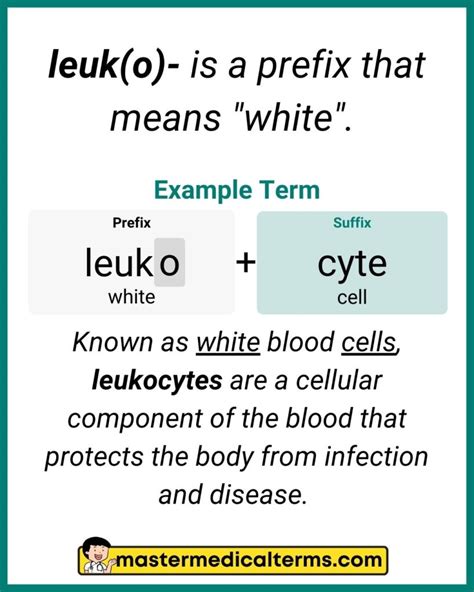
The medical term "Leuk" or "Leuco" refers to a prefix that originates from the Greek word "leukos," meaning white. This prefix is commonly used in medical terminology to describe conditions, procedures, or terms related to white blood cells, which are a crucial part of the immune system. White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, play a vital role in protecting the body against infections and diseases. The term "Leuk" is often combined with other roots and suffixes to form various medical terms, such as leukemia, leukocyte, and leukopenia.
Key Points
- The prefix "Leuk" originates from the Greek word "leukos," meaning white.
- It is commonly used in medical terminology to describe conditions related to white blood cells.
- White blood cells, or leukocytes, are a crucial part of the immune system.
- The term "Leuk" is often combined with other roots and suffixes to form various medical terms.
- Examples of medical terms using the "Leuk" prefix include leukemia, leukocyte, and leukopenia.
Understanding Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, characterized by an abnormal increase in white blood cells. The disease is classified into several types, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Each type of leukemia has distinct characteristics and requires different treatment approaches. The symptoms of leukemia may include fatigue, weight loss, frequent infections, and easy bruising or bleeding.
Leukocyte and Its Functions
A leukocyte, or white blood cell, is a type of cell that plays a vital role in the immune system. There are several types of leukocytes, including neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Each type of leukocyte has distinct functions, such as fighting infections, producing antibodies, and removing foreign substances from the body. The normal range for white blood cell count is typically between 4,000 and 11,000 cells per microliter of blood.
| Type of Leukocyte | Normal Range | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Neutrophils | 1,500-8,000 cells/μL | Fighting bacterial infections |
| Lymphocytes | 500-4,500 cells/μL | Producing antibodies and fighting viral infections |
| Monocytes | 200-1,000 cells/μL | Removing foreign substances and fighting infections |
| Eosinophils | 50-500 cells/μL | Fighting parasitic infections and playing a role in allergic reactions |
| Basophils | 20-100 cells/μL | Playing a role in allergic reactions and inflammation |

Leukopenia and Its Causes

Leukopenia is a condition characterized by a low white blood cell count, which can increase the risk of infections. There are several causes of leukopenia, including bone marrow disorders, autoimmune diseases, severe infections, and certain medications. The symptoms of leukopenia may include fatigue, weakness, and frequent infections. Treatment for leukopenia depends on the underlying cause and may involve medications, blood transfusions, or other therapies.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Leukemia and Leukopenia
The diagnosis of leukemia and leukopenia typically involves a physical examination, medical history, blood tests, and bone marrow biopsy. Treatment for leukemia may include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, and stem cell transplantation. Treatment for leukopenia depends on the underlying cause and may involve medications, blood transfusions, or other therapies. It’s essential to work with a healthcare professional to develop an individualized treatment plan.
What is the normal range for white blood cell count?
+The normal range for white blood cell count is typically between 4,000 and 11,000 cells per microliter of blood.
What are the symptoms of leukemia?
+The symptoms of leukemia may include fatigue, weight loss, frequent infections, and easy bruising or bleeding.
What is the treatment for leukopenia?
+Treatment for leukopenia depends on the underlying cause and may involve medications, blood transfusions, or other therapies.
Meta Description: Learn about the medical term “Leuk” and its relation to white blood cells, leukemia, and leukopenia. Understand the functions of leukocytes, diagnosis, and treatment options for these conditions.