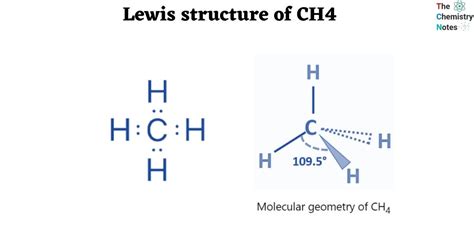
The CH4 Lewis dot structure, also known as the methane molecule, is a fundamental concept in chemistry that represents the arrangement of electrons in a molecule. To understand this structure, it's essential to have a basic knowledge of chemistry and the rules that govern the formation of molecules. In this article, we will delve into the world of Lewis dot structures, focusing on the CH4 molecule, and explore its significance in the field of chemistry.
Introduction to Lewis Dot Structures
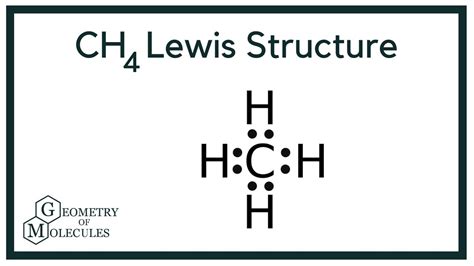
Lewis dot structures, also known as electron dot diagrams, are a way of representing the valence electrons in a molecule. They were developed by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1916 and have since become a crucial tool for chemists to visualize and understand the bonding between atoms in a molecule. The Lewis dot structure is a simple and effective way to represent the arrangement of electrons in a molecule, allowing chemists to predict the properties and behavior of the molecule.
Rules for Drawing Lewis Dot Structures
To draw a Lewis dot structure, there are several rules that need to be followed. These rules include:
- Determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule by adding up the valence electrons of each atom.
- Draw the skeleton of the molecule, connecting the atoms with single bonds.
- Distribute the remaining valence electrons around the atoms, making sure that each atom has a full outer energy level (i.e., 8 electrons in the outermost energy level, except for hydrogen, which can have 2 electrons).
- Form multiple bonds between atoms if necessary, to satisfy the octet rule.
By following these rules, chemists can draw the Lewis dot structure of a molecule, which provides valuable information about the molecule's properties and behavior.
CH4 Lewis Dot Structure
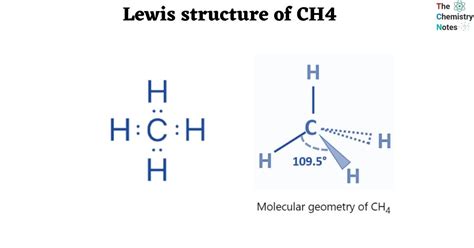
The CH4 molecule, also known as methane, consists of one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms. To draw the Lewis dot structure of CH4, we need to follow the rules outlined above.
First, we determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. Carbon has 4 valence electrons, and each hydrogen atom has 1 valence electron, so the total number of valence electrons in CH4 is:
4 (carbon) + 4 x 1 (hydrogen) = 8 valence electrons
Next, we draw the skeleton of the molecule, connecting the carbon atom to the four hydrogen atoms with single bonds. This uses up 4 of the valence electrons, leaving 4 remaining valence electrons to be distributed around the atoms.
The carbon atom has 4 remaining valence electrons, which are distributed around the atom to form 4 bonds with the hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen atom has 2 electrons, which are shared with the carbon atom to form a covalent bond.
The resulting Lewis dot structure of CH4 is:
C (carbon) - H (hydrogen) - H (hydrogen) - H (hydrogen) - H (hydrogen)
With 4 bonds between the carbon atom and the hydrogen atoms, and no lone pairs on the carbon atom.
| Atom | Valence Electrons | Bonds | Lone Pairs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
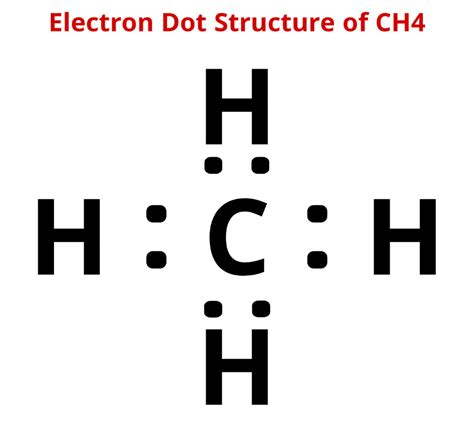
Key Points
- The CH4 molecule consists of one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms.
- The Lewis dot structure of CH4 shows that the carbon atom is bonded to four hydrogen atoms, with no lone pairs on the carbon atom.
- The molecule has a tetrahedral geometry, with the carbon atom at the center and the hydrogen atoms at the corners of the tetrahedron.
- The CH4 molecule is a stable molecule, with a low reactivity due to the lack of lone pairs on the carbon atom.
- Understanding the Lewis dot structure of CH4 is crucial for predicting the properties and behavior of the molecule.
Properties and Behavior of CH4
The CH4 molecule has several properties and behaviors that can be predicted from its Lewis dot structure. These include:
- Tetrahedral geometry: The molecule has a tetrahedral geometry, with the carbon atom at the center and the hydrogen atoms at the corners of the tetrahedron.
- Stability: The molecule is stable, with a low reactivity due to the lack of lone pairs on the carbon atom.
- Polarity: The molecule is non-polar, due to the symmetrical arrangement of the hydrogen atoms around the carbon atom.
- Boiling point: The molecule has a low boiling point, due to the weak intermolecular forces between the molecules.
These properties and behaviors are consistent with the Lewis dot structure of CH4, and demonstrate the importance of understanding the molecular structure in predicting the properties and behavior of a molecule.
What is the Lewis dot structure of CH4?
+The Lewis dot structure of CH4 shows that the carbon atom is bonded to four hydrogen atoms, with no lone pairs on the carbon atom.
What is the geometry of the CH4 molecule?
+The CH4 molecule has a tetrahedral geometry, with the carbon atom at the center and the hydrogen atoms at the corners of the tetrahedron.
Is the CH4 molecule polar or non-polar?
+The CH4 molecule is non-polar, due to the symmetrical arrangement of the hydrogen atoms around the carbon atom.
In conclusion, the CH4 Lewis dot structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry that provides valuable information about the properties and behavior of the methane molecule. By understanding the Lewis dot structure, chemists can predict the geometry, stability, polarity, and boiling point of the molecule, and gain insight into its chemical behavior. The CH4 molecule is a stable, non-polar molecule with a tetrahedral geometry, and its properties and behaviors are consistent with its Lewis dot structure.