The NH3 Lewis structure, also known as the ammonia molecule, is a fundamental concept in chemistry that represents the arrangement of atoms and electrons within the molecule. To understand the NH3 Lewis structure, it's essential to have a basic knowledge of chemistry and the rules that govern the formation of Lewis structures. In this article, we'll delve into the world of NH3 and explore five ways to represent its Lewis structure, highlighting the importance of each method and providing a comprehensive understanding of the molecule.
Key Points
- The NH3 Lewis structure consists of one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms.
- The nitrogen atom is the central atom, and the hydrogen atoms are bonded to it through single covalent bonds.
- The NH3 molecule has a trigonal pyramidal shape due to the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom.
- There are five ways to represent the NH3 Lewis structure, each with its own unique characteristics and importance.
- Understanding the NH3 Lewis structure is crucial in predicting the physical and chemical properties of the molecule.
Introduction to NH3 Lewis Structure
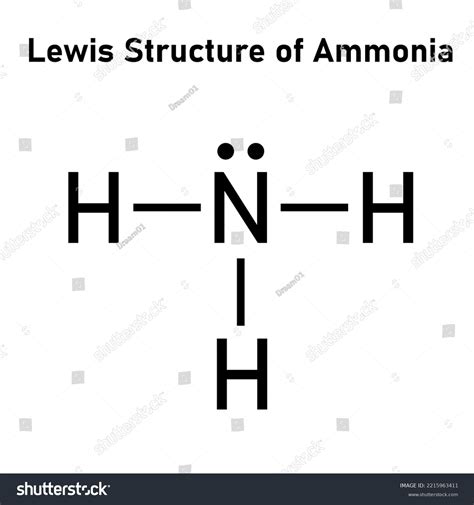
The NH3 Lewis structure is represented by a nitrogen atom (N) bonded to three hydrogen atoms (H) through single covalent bonds. The nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons, which plays a crucial role in determining the shape and properties of the molecule. To draw the NH3 Lewis structure, we need to follow the basic rules of Lewis structures, including the octet rule, which states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer energy level.
Method 1: Basic Lewis Structure
The basic Lewis structure of NH3 consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms through single covalent bonds. The nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons, which is represented by two dots. This structure is the simplest representation of the NH3 molecule and provides a foundation for understanding its properties.
| Atom | Electrons |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | 5 valence electrons |
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 valence electron |
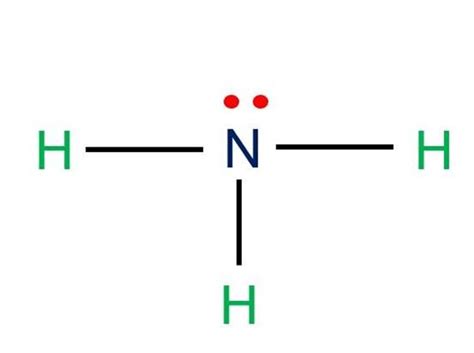
Method 2: Expanded Octet Lewis Structure
The expanded octet Lewis structure of NH3 takes into account the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. In this structure, the nitrogen atom is represented with an expanded octet, which means it has more than eight electrons in its valence shell. This structure is important in understanding the reactivity of the NH3 molecule and its ability to form bonds with other molecules.
Method 3: Resonance Structures
Resonance structures are a set of Lewis structures that contribute to the overall structure of a molecule. In the case of NH3, there are two resonance structures that represent the delocalization of electrons within the molecule. These structures are important in understanding the stability and reactivity of the NH3 molecule.
Method 4: 3D Representation
A 3D representation of the NH3 Lewis structure provides a more accurate visualization of the molecule’s shape and structure. The nitrogen atom is at the center, and the three hydrogen atoms are bonded to it through single covalent bonds. The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom occupies a position in space, giving the molecule a trigonal pyramidal shape.
Method 5: Molecular Orbital Theory
Molecular orbital theory provides a more advanced understanding of the NH3 Lewis structure. This theory describes the distribution of electrons within the molecule in terms of molecular orbitals. The molecular orbitals of NH3 are formed by the combination of atomic orbitals from the nitrogen and hydrogen atoms. This theory is essential in understanding the electronic properties of the molecule and its reactivity.
What is the shape of the NH3 molecule?
+The NH3 molecule has a trigonal pyramidal shape due to the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom.
Why is the NH3 Lewis structure important?
+The NH3 Lewis structure is important in understanding the physical and chemical properties of the molecule, including its reactivity and stability.
How many valence electrons does the nitrogen atom have?
+The nitrogen atom has 5 valence electrons.
In conclusion, the NH3 Lewis structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry that represents the arrangement of atoms and electrons within the molecule. Understanding the NH3 Lewis structure is crucial in predicting the physical and chemical properties of the molecule, including its reactivity and stability. The five methods of representing the NH3 Lewis structure provide a comprehensive understanding of the molecule and its properties, making it an essential topic in chemistry.