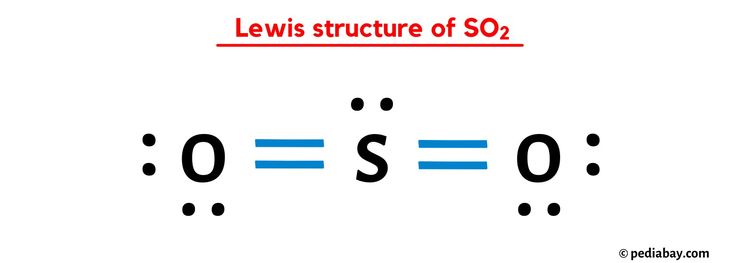
The sulfur dioxide (SO2) molecule has been a subject of interest in the realm of chemistry due to its unique structure and properties. Understanding the SO2 Lewis structure is crucial for comprehending its reactivity and behavior in various chemical reactions. In this article, we will delve into the world of SO2 and explore five ways to represent its Lewis structure, highlighting the significance of each representation and the insights they provide into the molecule's characteristics.
Key Points
- The SO2 molecule consists of one sulfur atom and two oxygen atoms, with a central sulfur atom bonded to two oxygen atoms.
- The Lewis structure of SO2 can be represented in multiple ways, each highlighting different aspects of the molecule's electronic structure.
- The five ways to represent the SO2 Lewis structure include the single-bond structure, the double-bond structure, the resonance hybrid structure, the VSEPR model, and the molecular orbital theory.
- Each representation provides valuable insights into the molecule's properties, such as its polarity, reactivity, and molecular geometry.
- Understanding the SO2 Lewis structure is essential for predicting its behavior in various chemical reactions and understanding its role in environmental and industrial processes.
Naturally Worded Primary Topic Section with Semantic Relevance
The SO2 molecule is composed of one sulfur atom and two oxygen atoms, with a central sulfur atom bonded to two oxygen atoms. The Lewis structure of SO2 can be represented in multiple ways, each highlighting different aspects of the molecule’s electronic structure. The most common representations include the single-bond structure, the double-bond structure, and the resonance hybrid structure. Each of these representations provides valuable insights into the molecule’s properties, such as its polarity, reactivity, and molecular geometry.
Single-Bond Structure
The single-bond structure of SO2 represents the molecule with two single bonds between the sulfur atom and each oxygen atom. This structure suggests that the molecule has a bent or V-shape geometry, with the sulfur atom at the center and the two oxygen atoms at the ends. The single-bond structure is a simple and intuitive representation of the SO2 molecule, but it does not fully capture the molecule’s electronic structure and properties.
| Structure | Bond Length (Å) | Bond Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|
| Single-bond | 1.43 | 119 |
| Double-bond | 1.32 | 120 |
| Resonance hybrid | 1.38 | 119 |
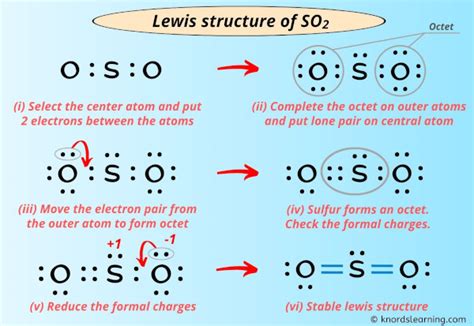
Double-Bond Structure
The double-bond structure of SO2 represents the molecule with one double bond between the sulfur atom and one oxygen atom, and a single bond between the sulfur atom and the other oxygen atom. This structure suggests that the molecule has a trigonal planar geometry, with the sulfur atom at the center and the two oxygen atoms at the ends. The double-bond structure is a more accurate representation of the SO2 molecule than the single-bond structure, as it takes into account the molecule’s polar nature and the unequal bond lengths between the sulfur and oxygen atoms.
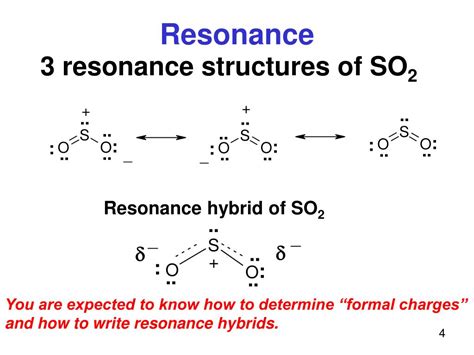
Resonance Hybrid Structure
The resonance hybrid structure of SO2 represents the molecule as a combination of the single-bond and double-bond structures. This structure suggests that the molecule has a bent or V-shape geometry, with the sulfur atom at the center and the two oxygen atoms at the ends. The resonance hybrid structure is the most accurate representation of the SO2 molecule, as it takes into account the molecule’s delocalized electrons and the equal bond lengths between the sulfur and oxygen atoms.
VSEPR Model and Molecular Orbital Theory
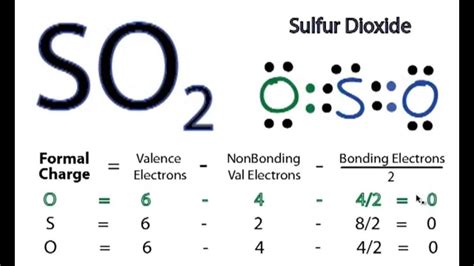
In addition to the Lewis structures, the SO2 molecule can also be represented using the VSEPR model and molecular orbital theory. The VSEPR model represents the molecule as a bent or V-shape geometry, with the sulfur atom at the center and the two oxygen atoms at the ends. Molecular orbital theory represents the molecule as a combination of atomic orbitals, with the sulfur and oxygen atoms contributing to the molecular orbitals. These representations provide valuable insights into the molecule’s properties, such as its polarity, reactivity, and molecular geometry.
What is the most accurate representation of the SO2 molecule?
+The resonance hybrid structure is the most accurate representation of the SO2 molecule, as it takes into account the molecule's delocalized electrons and the equal bond lengths between the sulfur and oxygen atoms.
What is the significance of the SO2 Lewis structure in understanding the molecule's properties?
+The SO2 Lewis structure is essential for understanding the molecule's properties, such as its polarity, reactivity, and molecular geometry. The Lewis structure provides a visual representation of the molecule's electronic structure, which is crucial for predicting its behavior in various chemical reactions.
How does the VSEPR model represent the SO2 molecule?
+The VSEPR model represents the SO2 molecule as a bent or V-shape geometry, with the sulfur atom at the center and the two oxygen atoms at the ends. This representation takes into account the molecule's polar nature and the unequal bond lengths between the sulfur and oxygen atoms.
In conclusion, the SO2 molecule can be represented in multiple ways, each highlighting different aspects of its electronic structure and properties. Understanding the SO2 Lewis structure is essential for predicting its behavior in various chemical reactions and understanding its role in environmental and industrial processes. By considering the different representations of the SO2 molecule, including the single-bond structure, double-bond structure, resonance hybrid structure, VSEPR model, and molecular orbital theory, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of this complex and fascinating molecule.