The Limit Comparison Test is a powerful tool in calculus, used to determine the convergence or divergence of a series by comparing it to another series whose behavior is known. This test is particularly useful when dealing with series that involve complicated expressions, as it allows for a simpler comparison to be made. In this article, we will explore five ways the Limit Comparison Test can be applied, highlighting its versatility and importance in the study of series convergence.
Key Points
- The Limit Comparison Test is used to determine the convergence or divergence of a series by comparing it to another series.
- This test is particularly useful for series involving complicated expressions.
- It can be applied to various types of series, including geometric series, harmonic series, and series with logarithmic terms.
- The test relies on the limit of the ratio of the terms of the two series as n approaches infinity.
- Understanding the Limit Comparison Test is crucial for advanced calculus and mathematical analysis.
Understanding the Limit Comparison Test
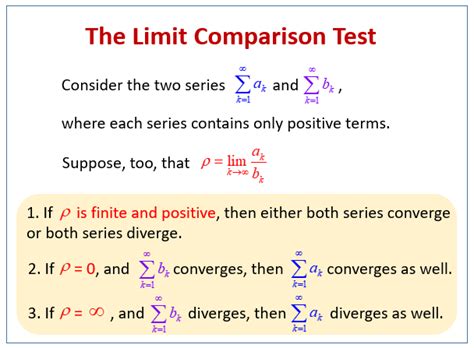
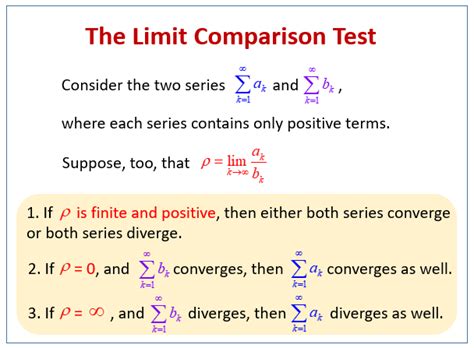
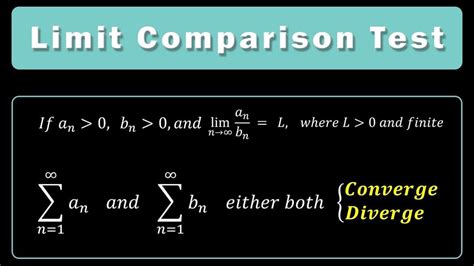
The Limit Comparison Test states that if we have two series, \sum a_n and \sum b_n, with positive terms, and the limit of the ratio \frac{a_n}{b_n} as n approaches infinity is a finite, positive number, then either both series converge or both diverge. This is often denoted as \lim_{n\to\infty} \frac{a_n}{b_n} = c, where c is a finite, positive number. The test provides a straightforward method to assess the convergence of a series by comparing it to a series whose convergence properties are well understood.
Application to Geometric Series
A geometric series is a series of the form \sum ar^n, where a is the first term and r is the common ratio. The convergence of a geometric series depends on the value of r: if |r| < 1, the series converges; if |r| \geq 1, the series diverges. The Limit Comparison Test can be used to compare a given series to a geometric series, helping to determine its convergence. For example, if we have a series \sum \frac{1}{2^n}, comparing it to the geometric series \sum \frac{1}{3^n} using the Limit Comparison Test can help establish its convergence.
| Series Type | Convergence Condition |
|---|---|
| Geometric Series | $|r| < 1$ |
| Harmonic Series | Diverges |
| p-Series | Converges if $p > 1$, diverges if $p \leq 1$ |
Comparison with Harmonic Series

The harmonic series, \sum \frac{1}{n}, is a classic example of a divergent series. By comparing a given series to the harmonic series using the Limit Comparison Test, we can determine if the series in question also diverges. For instance, considering the series \sum \frac{1}{n^2}, applying the Limit Comparison Test with the harmonic series helps conclude that \sum \frac{1}{n^2} converges because its terms decrease faster than those of the harmonic series.
Application to Series with Logarithmic Terms
Series involving logarithmic terms, such as \sum \frac{1}{n\log n}, can be challenging to analyze directly. However, by applying the Limit Comparison Test and comparing such a series to a known series, like the harmonic series, we can deduce its convergence properties. This approach simplifies the analysis and provides a clear understanding of how the presence of logarithmic terms affects the series’ behavior.
Strategic Considerations for Applying the Limit Comparison Test
When deciding which series to compare to, it’s essential to choose a series whose convergence properties are well understood and whose terms have a similar growth rate to the terms of the series in question. This strategic selection is crucial for the effective application of the Limit Comparison Test. Moreover, understanding the limit of the ratio of the terms as n approaches infinity requires careful analysis, especially when dealing with series involving complex expressions or functions.
What is the primary condition for applying the Limit Comparison Test?
+The primary condition is that the series must have positive terms, and the limit of the ratio of the terms of the two series as n approaches infinity must be a finite, positive number.
How does the Limit Comparison Test help in determining the convergence of a series?
+It helps by allowing the comparison of the series to another series with known convergence properties. If the limit of the ratio of their terms is a positive finite number, then either both series converge or both diverge.
What types of series are commonly compared using the Limit Comparison Test?
+Commonly compared series include geometric series, harmonic series, p-series, and series with logarithmic terms. The choice of series for comparison depends on the nature of the terms of the series in question.
In conclusion, the Limit Comparison Test is a versatile and powerful tool for determining the convergence or divergence of series. Its application can be seen in various contexts, from simple geometric series to more complex series involving logarithmic terms. By strategically selecting a series for comparison and carefully analyzing the limit of the ratio of the terms, one can leverage the Limit Comparison Test to understand the convergence behavior of a wide range of series, making it an indispensable technique in the study of calculus and mathematical analysis.