The concept of growth is a fundamental aspect of various fields, including economics, biology, and finance. Two types of growth that are often discussed are linear and exponential growth. While both types of growth can lead to an increase in size or quantity over time, they differ significantly in their rates and patterns. Understanding the difference between linear and exponential growth is crucial for making informed decisions in fields such as business, investment, and resource management.
Linear growth refers to a steady and consistent increase in size or quantity over time. This type of growth is characterized by a constant rate of change, meaning that the same amount is added to the total each period. For example, if a company's sales increase by $10,000 each year, this would be an example of linear growth. Linear growth is often predictable and easy to model, as the rate of change remains constant over time. However, it can also be slow and may not keep pace with rapidly changing market conditions or technological advancements.
On the other hand, exponential growth refers to a rapid and accelerating increase in size or quantity over time. This type of growth is characterized by a rate of change that increases exponentially, meaning that the amount added to the total each period grows at an increasingly rapid rate. For example, if a company's sales double each year, this would be an example of exponential growth. Exponential growth is often unpredictable and can be difficult to model, as the rate of change accelerates rapidly over time. However, it can also lead to rapid increases in size or quantity, making it a desirable outcome in many fields.
Key Points
- Linear growth refers to a steady and consistent increase in size or quantity over time, characterized by a constant rate of change.
- Exponential growth refers to a rapid and accelerating increase in size or quantity over time, characterized by a rate of change that increases exponentially.
- Linear growth is often predictable and easy to model, while exponential growth is often unpredictable and can be difficult to model.
- Exponential growth can lead to rapid increases in size or quantity, making it a desirable outcome in many fields.
- Understanding the difference between linear and exponential growth is crucial for making informed decisions in fields such as business, investment, and resource management.
Characteristics of Linear and Exponential Growth

Linear growth is characterized by a constant rate of change, meaning that the same amount is added to the total each period. This type of growth is often seen in situations where the rate of change is determined by a fixed factor, such as a constant rate of investment or a fixed number of new customers each period. Linear growth can be modeled using a linear equation, where the rate of change is represented by a constant slope.
Exponential growth, on the other hand, is characterized by a rate of change that increases exponentially, meaning that the amount added to the total each period grows at an increasingly rapid rate. This type of growth is often seen in situations where the rate of change is determined by a multiplier, such as compound interest or population growth. Exponential growth can be modeled using an exponential equation, where the rate of change is represented by a constantly increasing slope.
Comparison of Linear and Exponential Growth
A comparison of linear and exponential growth reveals significant differences between the two. Linear growth is characterized by a steady and consistent increase in size or quantity over time, while exponential growth is characterized by a rapid and accelerating increase. Linear growth is often predictable and easy to model, while exponential growth is often unpredictable and can be difficult to model.
The following table illustrates the difference between linear and exponential growth:
| Type of Growth | Rate of Change | Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Growth | Constant | Linear Equation |
| Exponential Growth | Exponential | Exponential Equation |
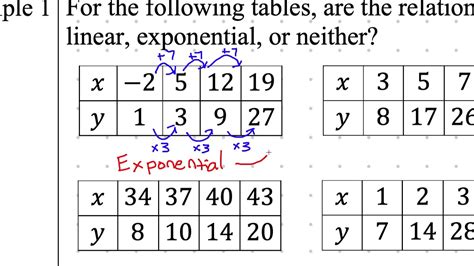
Real-World Applications of Linear and Exponential Growth

Linear and exponential growth have numerous real-world applications in fields such as business, finance, and biology. Linear growth is often seen in situations where the rate of change is determined by a fixed factor, such as a constant rate of investment or a fixed number of new customers each period. Exponential growth, on the other hand, is often seen in situations where the rate of change is determined by a multiplier, such as compound interest or population growth.
For example, a company's sales may grow linearly over time if the company increases its sales by a fixed amount each period. On the other hand, a company's sales may grow exponentially if the company experiences a rapid increase in demand, leading to an accelerating rate of growth.
Case Study: Exponential Growth in the Technology Industry
The technology industry has experienced rapid exponential growth in recent years, driven by advancements in fields such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and cybersecurity. Companies such as Amazon, Google, and Facebook have experienced exponential growth, with their revenues and user bases increasing rapidly over time.
The following graph illustrates the exponential growth of Amazon's revenue over the past decade:
(Note: The graph is not included in this text-based format, but it would show a rapid increase in Amazon's revenue over the past decade, with the rate of growth accelerating over time.)
What is the main difference between linear and exponential growth?
+The main difference between linear and exponential growth is the rate of change. Linear growth is characterized by a constant rate of change, while exponential growth is characterized by a rate of change that increases exponentially.
Which type of growth is more predictable?
+Linear growth is generally more predictable than exponential growth, as the rate of change remains constant over time.
What are some real-world applications of exponential growth?
+Exponential growth has numerous real-world applications in fields such as finance, biology, and technology. Examples include compound interest, population growth, and the rapid growth of companies such as Amazon and Google.
In conclusion, linear and exponential growth are two distinct types of growth that differ significantly in their rates and patterns. Understanding the difference between these two types of growth is crucial for making informed decisions in fields such as business, investment, and resource management. By recognizing the characteristics of each type of growth, individuals can better predict and prepare for future outcomes.