The distinction between linear and exponential functions is a fundamental concept in mathematics, with far-reaching implications in various fields, including economics, physics, and computer science. At its core, this distinction revolves around the rate at which these functions grow or decay. Understanding the differences between linear and exponential functions is crucial for modeling real-world phenomena, making predictions, and solving complex problems. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, characteristics, and applications of both linear and exponential functions, providing a comprehensive overview of their significance and utility.
Key Points
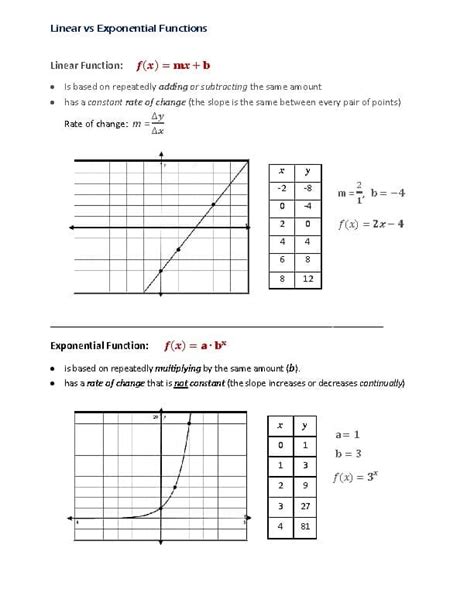
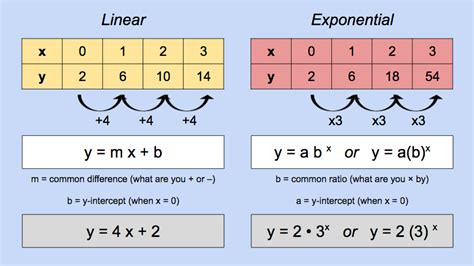
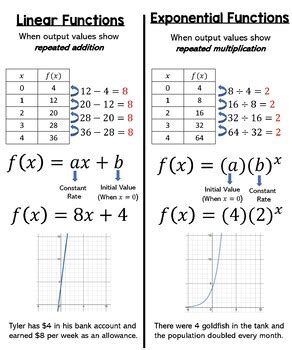
- Linear functions are characterized by a constant rate of change, often represented by the equation y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
- Exponential functions exhibit a variable rate of change, typically represented by the equation y = ab^x, where a is the initial value and b is the growth factor.
- Linear functions are often used to model situations where the rate of change is constant, such as the distance traveled by an object moving at a constant speed.
- Exponential functions are used to model situations where the rate of change is accelerating or decelerating, such as population growth, chemical reactions, or compound interest.
- The distinction between linear and exponential growth has significant implications for predicting outcomes, making decisions, and solving problems in various fields.
Linear Functions: Definition and Characteristics
A linear function is defined as a polynomial function of degree one, which can be represented by the equation y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. The slope (m) represents the rate of change of the function, indicating how much the output (y) changes when the input (x) changes by one unit. The y-intercept (b) is the point at which the function crosses the y-axis, providing a starting value for the function. Linear functions are characterized by a constant rate of change, meaning that the slope (m) remains the same throughout the entire domain of the function.
Examples of Linear Functions
Linear functions are commonly used to model real-world situations where the rate of change is constant. For instance, the distance traveled by an object moving at a constant speed can be represented by a linear function. If an object travels at a speed of 50 miles per hour, the distance traveled (y) can be represented by the equation y = 50x, where x is the time traveled in hours. Another example is the cost of producing a product, which can be represented by a linear function if the cost per unit remains constant.
| Linear Function | Equation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Distance traveled | y = 50x | Object moving at 50 miles per hour |
| Cost of production | y = 10x + 500 | Cost per unit: $10, fixed cost: $500 |
Exponential Functions: Definition and Characteristics
An exponential function is a type of function where the rate of change is not constant, but rather increases or decreases exponentially. Exponential functions can be represented by the equation y = ab^x, where a is the initial value and b is the growth factor. The growth factor (b) determines the rate at which the function grows or decays. If b is greater than 1, the function grows exponentially; if b is between 0 and 1, the function decays exponentially.
Examples of Exponential Functions
Exponential functions are used to model situations where the rate of change is accelerating or decelerating. Population growth, chemical reactions, and compound interest are all examples of exponential growth. For instance, the population of a city can be represented by an exponential function if the growth rate is constant. If the population grows at a rate of 5% per year, the population (y) can be represented by the equation y = 100(1.05)^x, where x is the number of years.
| Exponential Function | Equation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Population growth | y = 100(1.05)^x | Population grows at 5% per year |
| Chemical reaction | y = 200(0.8)^x | Concentration decreases by 20% per minute |
Comparison of Linear and Exponential Functions
Linear and exponential functions exhibit distinct differences in terms of their growth rates and applications. Linear functions are characterized by a constant rate of change, whereas exponential functions exhibit a variable rate of change. Linear functions are often used to model situations where the rate of change is constant, such as the distance traveled by an object moving at a constant speed. Exponential functions, on the other hand, are used to model situations where the rate of change is accelerating or decelerating, such as population growth, chemical reactions, or compound interest.
Implications of Linear and Exponential Growth
The distinction between linear and exponential growth has significant implications for predicting outcomes, making decisions, and solving problems in various fields. Exponential growth can lead to rapid increases or decreases in a short period, whereas linear growth is more predictable and stable. Understanding the characteristics of linear and exponential functions is essential for making accurate predictions and informed decisions.
What is the main difference between linear and exponential functions?
+The main difference between linear and exponential functions is the rate of change. Linear functions have a constant rate of change, whereas exponential functions have a variable rate of change that increases or decreases exponentially.
What are some examples of linear functions in real-world applications?
+Linear functions are commonly used to model situations where the rate of change is constant, such as the distance traveled by an object moving at a constant speed, the cost of producing a product, or the revenue generated by a business.
What are some examples of exponential functions in real-world applications?
+Exponential functions are used to model situations where the rate of change is accelerating or decelerating, such as population growth, chemical reactions, or compound interest. These functions are essential for predicting outcomes and making informed decisions in various fields.