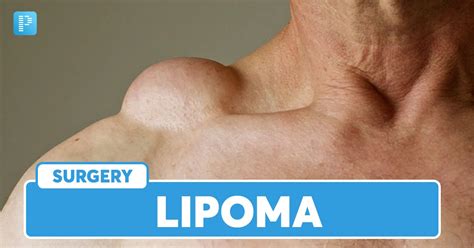
Lipoma disease, also known as lipomatosis, is a condition characterized by the growth of non-cancerous tumors composed of fat tissue. These tumors, called lipomas, can occur anywhere in the body where fat cells are present. Lipomas are typically soft, movable, and painless, but they can cause discomfort or cosmetic concerns depending on their size and location. Understanding lipoma disease and its manifestations through visual aids like photos can help in diagnosing and managing the condition.
Types of Lipomas and Their Characteristics
Lipomas can be classified into several types based on their location, characteristics, and the type of tissue involved. The most common types include:
- Subcutaneous lipomas: These occur just under the skin and are the most common type. They feel like soft, movable lumps under the skin.
- Deep lipomas: Located deeper in the body, these lipomas can be found within muscles or near internal organs.
- Intramuscular lipomas: These grow within the muscle and can cause pain or discomfort.
- Intercostal lipomas: Occurring between the ribs, these lipomas can cause discomfort or affect breathing.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing lipoma disease typically involves a physical examination and imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans to confirm the presence and characteristics of the lipoma. Treatment options vary depending on the size, location, and symptoms of the lipoma. Small, asymptomatic lipomas may not require treatment, while larger or symptomatic ones might be surgically removed.
| Type of Lipoma | Treatment Approach |
|---|---|
| Subcutaneous | Surgical excision or liposuction |
| Deep or Intramuscular | Surgical removal, possibly requiring more complex procedures |
| Intercostal | Surgical removal, considering the risk to surrounding structures |
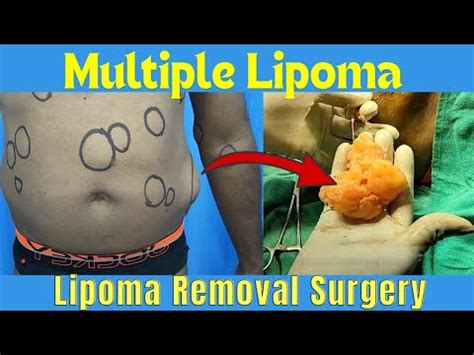
Key Points
- Lipoma disease is characterized by the growth of benign fat tumors in the body.
- The condition can manifest in various forms, including subcutaneous, deep, intramuscular, and intercostal lipomas.
- Diagnosis involves physical examination and imaging tests, with treatment options ranging from observation to surgical removal.
- The choice of treatment depends on the size, location, and symptoms of the lipoma, as well as the patient's overall health.
- Understanding the different types of lipomas and their characteristics is crucial for effective management and patient care.
While lipoma disease is generally benign, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional if you notice any unusual growths or experience discomfort. Early evaluation can help determine the best course of action and alleviate concerns about the nature of the growth.
What are the common symptoms of lipoma disease?
+Common symptoms include the presence of soft, movable lumps under the skin, and in some cases, discomfort or pain, especially if the lipoma is large or located near nerves or internal organs.
How are lipomas diagnosed?
+Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional and may include imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans to confirm the presence and characteristics of the lipoma.
Can lipomas be prevented?
+While the exact cause of lipomas is not fully understood, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and avoiding obesity may reduce the risk of developing lipomas. However, there is no proven method to prevent lipomas entirely.
In conclusion, lipoma disease, though generally benign, requires attention to its various manifestations and the appropriate treatment options. By understanding the condition and its characteristics, individuals can better navigate the diagnosis and treatment process, ensuring they receive the care needed to manage their condition effectively.