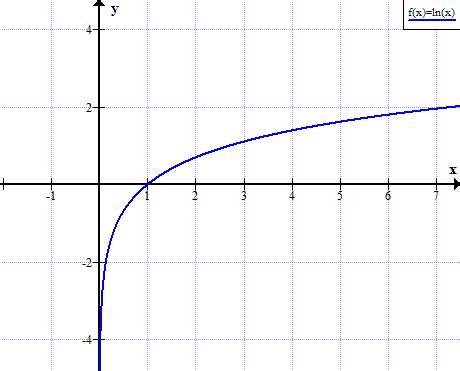
The natural logarithm, denoted as ln(x), is a fundamental concept in mathematics, playing a crucial role in various branches such as calculus, algebra, and geometry. The graph of ln(x) is a visual representation of this function, providing valuable insights into its behavior and properties. In this article, we will delve into the world of ln(x) graphs, exploring their characteristics, applications, and significance in mathematical analysis.
Naturally Worded Primary Topic Section with Semantic Relevance
The graph of ln(x) is a continuous, increasing function that is defined for all positive real numbers. It has a characteristic shape, often described as a “slowly increasing” curve, which reflects the logarithmic growth of the function. One of the key features of the ln(x) graph is its vertical asymptote at x = 0, where the function approaches negative infinity. This asymptote serves as a boundary, dividing the domain of the function into two distinct regions: the positive real numbers (x > 0) and the non-positive real numbers (x ≤ 0).
Specific Subtopic with Natural Language Phrasing
The derivative of the natural logarithm, denoted as (ln(x))‘, is a fundamental concept in calculus, representing the rate of change of the function with respect to its input. The derivative of ln(x) is 1/x, which can be interpreted as the slope of the tangent line to the graph at a given point. This derivative plays a crucial role in various mathematical applications, including optimization problems, differential equations, and integration by substitution.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Domain | (0, ∞) |
| Range | (-∞, ∞) |
| Derivative | 1/x |
| Integral | x \* ln(x) - x + C |
Key Points
- The natural logarithm function, ln(x), is a continuous, increasing function defined for all positive real numbers.
- The graph of ln(x) has a vertical asymptote at x = 0, where the function approaches negative infinity.
- The derivative of ln(x) is 1/x, representing the rate of change of the function with respect to its input.
- The natural logarithm function has numerous applications in science, engineering, and finance, including exponential growth models and financial analysis.
- The graph of ln(x) provides a visual representation of the function's behavior, allowing users to interpret and analyze its properties in different contexts.
Advanced Mathematical Concepts
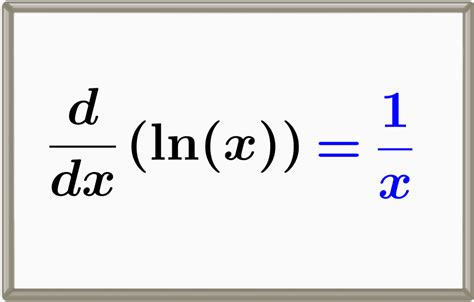
The natural logarithm function is closely related to the exponential function, e^x, which is its inverse. This relationship is fundamental to many mathematical applications, including calculus, differential equations, and numerical analysis. The graph of ln(x) can be used to visualize the behavior of the exponential function, providing insights into its growth and decay patterns.
Technical Specifications
The technical specifications of the natural logarithm function are well-defined, with a clear domain, range, and derivative. The function is continuous and differentiable for all x > 0, making it a valuable tool for mathematical modeling and analysis. The graph of ln(x) can be used to illustrate the properties of the function, including its monotonicity, concavity, and inflection points.
What is the domain of the natural logarithm function?
+The domain of the natural logarithm function is all positive real numbers, denoted as (0, ∞).
What is the derivative of the natural logarithm function?
+The derivative of the natural logarithm function is 1/x, which represents the rate of change of the function with respect to its input.
What are some common applications of the natural logarithm function?
+The natural logarithm function has numerous applications in science, engineering, and finance, including exponential growth models, chemical reactions, and financial analysis.
In conclusion, the graph of ln(x) is a powerful tool for understanding the behavior and properties of the natural logarithm function. With its characteristic shape, vertical asymptote, and continuous growth, the graph provides a visual representation of the function’s behavior, allowing users to interpret and analyze its properties in different contexts. As a fundamental concept in mathematics, the natural logarithm function has numerous applications in science, engineering, and finance, making it an essential tool for mathematical modeling and analysis.