The concept of lordship has been a cornerstone of societal hierarchy throughout history, particularly in medieval Europe. The term "lord" refers to a person who has authority and control over others, often holding significant power and influence. Here are five key facts about lords that highlight their significance and the evolution of their role over time.
Key Points
- The feudal system, which emerged in the 9th century, was based on the relationship between lords and their vassals, with lords providing protection and land in exchange for loyalty and military service.
- Lords played a crucial role in the medieval economy, controlling the means of production and dictating the terms of trade and commerce within their domains.
- The concept of lordship was not limited to the nobility; ecclesiastical lords, such as bishops and abbots, also wielded significant power and influence in medieval society.
- The rise of absolutism in the 16th and 17th centuries led to a decline in the power of lords, as monarchs sought to consolidate their authority and reduce the influence of the nobility.
- Today, the term "lord" is still used in various contexts, including as a title of nobility in the United Kingdom and as a term of respect in certain social and cultural settings.
The Evolution of Lordship

The institution of lordship has undergone significant changes over the centuries, reflecting shifts in societal values, economic systems, and political structures. In medieval Europe, lords were the primary holders of power and authority, with their domains often serving as the basic units of governance. The relationship between lords and their vassals was based on a system of mutual obligations, with lords providing protection and land in exchange for loyalty and military service.
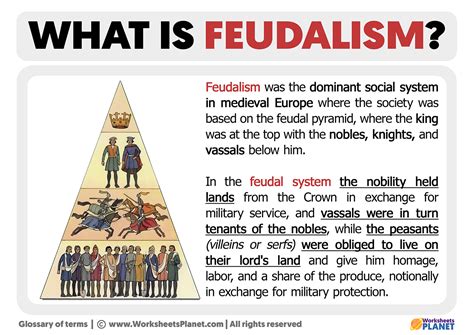
The Feudal System
The feudal system, which emerged in the 9th century, was characterized by a hierarchical structure, with the king at the top and the lords and vassals below him. Lords played a crucial role in the feudal system, serving as the intermediaries between the king and the common people. They were responsible for collecting taxes, maintaining law and order, and providing military service to the king. In return, lords were granted land and authority over their domains, which they could pass down to their heirs.
| Feudal Hierarchy | Description |
|---|---|
| King | The supreme ruler of the kingdom, responsible for defending the realm and maintaining order. |
| Lords | The nobles who held land and authority from the king, responsible for governing their domains and providing military service. |
| Vassals | The individuals who held land and authority from the lords, responsible for providing loyalty and military service to their lords. |
| Serfs | The common people who worked the land, responsible for providing labor and taxes to their lords. |

The Decline of Lordship
The rise of absolutism in the 16th and 17th centuries led to a decline in the power of lords, as monarchs sought to consolidate their authority and reduce the influence of the nobility. The emergence of modern nation-states and the development of centralized governments further eroded the power of lords, as they were increasingly replaced by bureaucratic officials and administrative systems. Today, the term “lord” is still used in various contexts, but its meaning and significance have evolved significantly over time.
The Legacy of Lordship
Despite the decline of lordship as a dominant institution, its legacy continues to shape modern society. The concept of lordship has influenced the development of social hierarchies, economic systems, and political structures, and its impact can still be seen in the modern-day use of titles and honorifics. Furthermore, the study of lordship and the feudal system provides valuable insights into the evolution of human societies and the complex relationships between power, authority, and social organization.
What was the primary role of lords in medieval society?
+Lords played a crucial role in medieval society, serving as the primary holders of power and authority. They were responsible for governing their domains, collecting taxes, maintaining law and order, and providing military service to the king.
How did the rise of absolutism affect the power of lords?
+The rise of absolutism led to a decline in the power of lords, as monarchs sought to consolidate their authority and reduce the influence of the nobility. The emergence of modern nation-states and the development of centralized governments further eroded the power of lords, as they were increasingly replaced by bureaucratic officials and administrative systems.
What is the legacy of lordship in modern society?
+The legacy of lordship continues to shape modern society, influencing the development of social hierarchies, economic systems, and political structures. The concept of lordship has also influenced the use of titles and honorifics, and its impact can still be seen in the modern-day use of terms such as “lord” and “noble”.