When analyzing blood test results, it's not uncommon to come across terms like low lymphocytes and high neutrophils. These terms refer to specific types of white blood cells that play crucial roles in our immune system. Lymphocytes and neutrophils are two of the five main types of white blood cells, each with distinct functions in protecting the body against infections and diseases. Understanding the significance of abnormal levels of these cells can provide valuable insights into one's health status.
Understanding Lymphocytes and Neutrophils

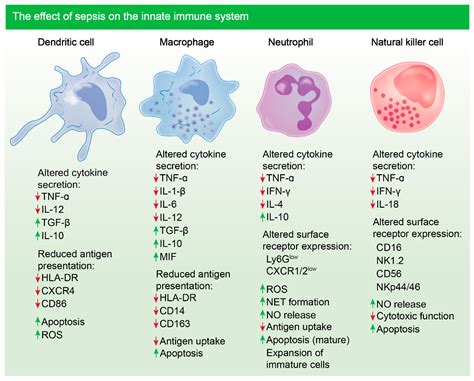
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that is critical for the immune system’s adaptive response. They are responsible for recognizing and remembering specific pathogens, allowing for a targeted and effective immune response. Lymphocytes are further divided into B cells, T cells, and natural killer cells, each with unique functions. B cells produce antibodies to fight infections, while T cells directly attack infected cells or produce chemical signals that activate the immune response. Natural killer cells, on the other hand, recognize and destroy tumor cells and virus-infected cells.
Neutrophils, another type of white blood cell, are the body's first line of defense against infections. They are the most abundant type of white blood cell and are crucial for the innate immune response. Neutrophils primarily target bacterial infections and fungi by engulfing and destroying these pathogens through a process called phagocytosis. They also release granules that contain enzymes and antimicrobial peptides to kill microorganisms.
Implications of Low Lymphocytes and High Neutrophils
A condition characterized by low lymphocytes (lymphocytopenia) and high neutrophils (neutrophilia) can indicate a specific set of health issues. Lymphocytopenia may result from a variety of factors, including viral infections (like HIV), autoimmune disorders (such as rheumatoid arthritis), severe burns, or treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy. On the other hand, neutrophilia can be caused by acute bacterial infections, severe inflammatory conditions (like appendicitis), or other stressors that trigger the release of neutrophils from the bone marrow.
| White Blood Cell Type | Normal Range | Implications of Abnormal Levels |
|---|---|---|
| Lymphocytes | 500-4,500 cells per microliter | Low levels may indicate immune system suppression or certain infections, while high levels can be seen in viral infections or lymphoproliferative disorders. |
| Neutrophils | 1,500-8,000 cells per microliter | High levels often suggest bacterial infection or inflammation, while low levels can indicate a weakened immune response or specific conditions like neutropenia. |
Clinical Significance and Diagnosis

The diagnosis of conditions associated with abnormal white blood cell counts involves a comprehensive approach. This includes physical examination, detailed medical history, and a range of diagnostic tests. In addition to complete blood counts (CBC) that measure the levels of different types of blood cells, other tests might be ordered to identify the underlying cause of the abnormality. For example, blood cultures can help identify bacterial infections, while imaging studies like X-rays or CT scans can reveal signs of inflammation or infection in specific parts of the body.
Treatment strategies depend on the underlying cause of the low lymphocytes and high neutrophils. For instance, if the abnormal counts are due to a bacterial infection, antibiotics would be the primary treatment. In cases where the condition is caused by an autoimmune disorder or another underlying health issue, the treatment would focus on managing that specific condition. Supportive care, including rest, hydration, and nutritional support, is also crucial in helping the body recover from the underlying illness.
Key Points
- Lymphocytes and neutrophils are crucial components of the immune system, with distinct roles in fighting infections and diseases.
- Low lymphocytes (lymphocytopenia) can result from immune system suppression, viral infections, or other health issues, while high neutrophils (neutrophilia) often indicate bacterial infections or inflammatory conditions.
- A comprehensive diagnostic approach, including medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests, is necessary to determine the cause of abnormal white blood cell counts.
- Treatment strategies vary based on the underlying cause and may include antibiotics for bacterial infections, management of autoimmune disorders, or supportive care for recovery.
- Healthcare professionals must interpret white blood cell counts in the context of the patient's overall clinical picture to provide accurate diagnoses and effective treatments.
Management and Prevention
Preventing conditions that lead to abnormal white blood cell counts involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, can help prevent the spread of infections. Additionally, staying up to date with recommended vaccinations can protect against certain viral and bacterial infections.
For individuals with conditions that affect their immune system, such as HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, preventive measures might include taking prophylactic antibiotics, practicing safe sex, and avoiding close contact with individuals who have infectious diseases. Regular monitoring of white blood cell counts and other health parameters by a healthcare provider is also essential for early detection and management of any emerging issues.
What are the common causes of low lymphocytes and high neutrophils?
+Low lymphocytes can be caused by viral infections, autoimmune disorders, severe burns, or treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy. High neutrophils are often seen in acute bacterial infections, severe inflammatory conditions, or other stressors.
How are conditions with abnormal white blood cell counts diagnosed?
+Diagnosis involves a comprehensive approach including physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests like complete blood counts, blood cultures, and imaging studies.
What are the treatment options for conditions associated with low lymphocytes and high neutrophils?
+Treatment strategies depend on the underlying cause and may include antibiotics for bacterial infections, management of autoimmune disorders, or supportive care for recovery. The goal is to address the underlying condition causing the abnormal white blood cell counts.
In conclusion, understanding the implications of low lymphocytes and high neutrophils requires a deep dive into the roles these cells play in our immune system and the various factors that can influence their counts. By recognizing the signs of abnormal white blood cell counts and seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining their health and addressing any underlying conditions that may arise.