The MACE medical abbreviation is a term commonly used in the field of cardiology and medical research. MACE stands for Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events. It is a composite endpoint that encompasses a range of serious cardiovascular events, including death, myocardial infarction (heart attack), stroke, and the need for repeat revascularization procedures. The use of MACE as an outcome measure allows clinicians and researchers to assess the overall risk of cardiovascular events in patients with heart disease or those undergoing cardiovascular procedures.
The MACE acronym is often used in clinical trials and observational studies to evaluate the efficacy and safety of various treatments, medications, and interventions aimed at reducing the risk of cardiovascular events. By combining these individual endpoints into a single composite measure, MACE provides a more comprehensive understanding of the cardiovascular risk profile of patients and the impact of different therapeutic strategies on patient outcomes. For instance, a study might report the MACE rate at one year as a way to summarize the incidence of major cardiovascular events in a patient population.
Key Points
- MACE is an acronym for Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events.
- It includes death, myocardial infarction, stroke, and the need for repeat revascularization procedures.
- MACE is used as a composite endpoint in clinical trials and observational studies to assess cardiovascular risk.
- It provides a comprehensive understanding of the cardiovascular risk profile of patients and the efficacy of treatments.
- MACE rates are often reported at specific time points, such as one year, to summarize patient outcomes.
Components of MACE

The components of MACE are critical in understanding its significance in cardiovascular medicine. Each component represents a significant adverse event that can impact patient outcomes and quality of life. Myocardial infarction, or heart attack, occurs when the blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. Stroke, another component of MACE, happens when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. Repeat revascularization procedures, such as angioplasty or bypass surgery, may be necessary for patients who have previously undergone these procedures and require further intervention due to recurrent symptoms or disease progression.
Importance of MACE in Clinical Trials
The importance of MACE in clinical trials cannot be overstated. By using MACE as an endpoint, researchers can more accurately assess the effectiveness of new treatments or interventions in reducing the risk of major cardiovascular events. This is particularly relevant in the development of new drugs, devices, or surgical techniques aimed at preventing or managing cardiovascular disease. For example, a clinical trial might compare the MACE rates between patients treated with a novel anticoagulant versus those receiving standard care, providing valuable insights into the safety and efficacy of the new treatment.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Myocardial Infarction | Death of heart muscle due to lack of blood flow |
| Stroke | Interrupted blood supply to the brain |
| Repeat Revascularization | Necessity for further procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery |
Limitations and Future Directions
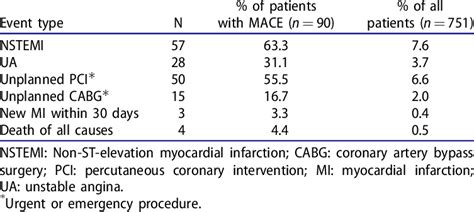
While MACE is a valuable tool in cardiovascular research, it is not without limitations. One of the main limitations is the potential for heterogeneity in the definition and reporting of MACE components across different studies. This can make it challenging to compare results and draw conclusions about the efficacy of treatments. Furthermore, MACE does not account for other important outcomes, such as hospitalization for heart failure or arrhythmias, which can also significantly impact patient quality of life and healthcare resource utilization.
Future research should aim to standardize the definition and reporting of MACE, potentially incorporating additional endpoints to provide a more complete picture of cardiovascular risk. The development of personalized medicine approaches, where treatments are tailored to individual patient profiles, may also require a reevaluation of how MACE is defined and used in clinical trials. As our understanding of cardiovascular disease and its management evolves, so too must our approach to assessing and reporting patient outcomes.
What does MACE stand for in medical terms?
+MACE stands for Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events, which includes death, myocardial infarction, stroke, and the need for repeat revascularization procedures.
Why is MACE used in clinical trials?
+MACE is used as a composite endpoint to assess the overall risk of cardiovascular events in patients and to evaluate the efficacy and safety of treatments aimed at reducing this risk.
What are the limitations of using MACE as an endpoint?
+The limitations include potential heterogeneity in the definition and reporting of MACE components across studies and the lack of inclusion of other important cardiovascular outcomes.
Meta Description: Learn about MACE, or Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events, a critical composite endpoint used in cardiology to assess the risk of serious heart-related events, including death, heart attack, stroke, and repeat revascularization procedures.



