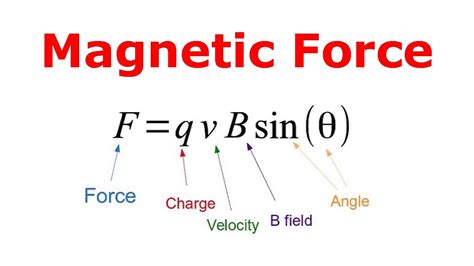
The study of magnetic forces is a fundamental aspect of physics, particularly in the realm of electromagnetism. Magnetic forces are responsible for the interaction between magnetic fields and charged particles or other magnetic fields. Understanding these forces is crucial for the development of various technologies, including electric motors, generators, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines. In this article, we will delve into the concept of magnetic forces, exploring the key formulas that describe their behavior.
Key Points
- The Lorentz force equation describes the force experienced by a charged particle in the presence of electric and magnetic fields.
- The magnetic field around a current-carrying wire can be calculated using the Biot-Savart law.
- The force between two magnetic poles can be determined using the magnetic pole strength formula.
- The torque experienced by a current loop in a magnetic field can be calculated using the torque equation.
- The magnetic force between two current-carrying wires can be determined using Ampere's law.
Introduction to Magnetic Forces

Magnetic forces are a result of the interaction between magnetic fields and moving charges or other magnetic fields. These forces can be attractive or repulsive, depending on the orientation of the magnetic fields and the direction of the moving charges. The study of magnetic forces is essential for understanding various phenomena, including the behavior of charged particles in magnetic fields, the operation of electric motors and generators, and the Earth’s magnetic field.
The Lorentz Force Equation
The Lorentz force equation is a fundamental formula that describes the force experienced by a charged particle in the presence of electric and magnetic fields. The equation is given by:
F = q(E + v × B)
where F is the force experienced by the charged particle, q is the charge of the particle, E is the electric field strength, v is the velocity of the particle, and B is the magnetic field strength.
Magnetic Field Formulas

The magnetic field around a current-carrying wire can be calculated using the Biot-Savart law, which states that the magnetic field B at a point P due to a small element of a current-carrying wire is given by:
B = (μ₀ \* I \* dl × r) / (4π \* r³)
where μ₀ is the magnetic constant, I is the current flowing through the wire, dl is the length of the small element, r is the distance from the element to the point P, and × denotes the cross product.
Magnetic Pole Strength Formula
The force between two magnetic poles can be determined using the magnetic pole strength formula, which states that the force F between two poles is given by:
F = (μ₀ \* m₁ \* m₂) / (4π \* r²)
where μ₀ is the magnetic constant, m₁ and m₂ are the pole strengths of the two poles, and r is the distance between the poles.
Torque and Magnetic Force
The torque experienced by a current loop in a magnetic field can be calculated using the torque equation, which states that the torque τ is given by:
τ = m × B
where m is the magnetic moment of the loop and B is the magnetic field strength.
Ampere’s Law
The magnetic force between two current-carrying wires can be determined using Ampere’s law, which states that the force F per unit length between two wires is given by:
F / L = (μ₀ \* I₁ \* I₂) / (2π \* r)
where μ₀ is the magnetic constant, I₁ and I₂ are the currents flowing through the two wires, and r is the distance between the wires.
| Magnetic Force Formula | Description |
|---|---|
| Lorentz Force Equation | Describes the force experienced by a charged particle in electric and magnetic fields |
| Biot-Savart Law | Calculates the magnetic field around a current-carrying wire |
| Magnetic Pole Strength Formula | Determines the force between two magnetic poles |
| Torque Equation | Calculates the torque experienced by a current loop in a magnetic field |
| Ampere's Law | Determines the magnetic force between two current-carrying wires |
What is the Lorentz force equation, and how is it used?
+The Lorentz force equation describes the force experienced by a charged particle in the presence of electric and magnetic fields. It is used to calculate the force on a charged particle in various situations, including in electric motors and generators.
How is the magnetic field around a current-carrying wire calculated?
+The magnetic field around a current-carrying wire can be calculated using the Biot-Savart law, which takes into account the current flowing through the wire, the length of the wire, and the distance from the wire to the point where the magnetic field is being measured.
What is the magnetic pole strength formula, and how is it used?
+The magnetic pole strength formula is used to determine the force between two magnetic poles. It takes into account the pole strengths of the two poles and the distance between them.
In conclusion, magnetic forces play a vital role in various aspects of physics and engineering. By understanding the formulas that describe these forces, including the Lorentz force equation, the Biot-Savart law, the magnetic pole strength formula, the torque equation, and Ampere’s law, we can design and optimize devices that harness the power of magnetic forces. Whether it’s in the development of electric motors, generators, or MRI machines, the application of these formulas is crucial for advancing our understanding of the physical world and improving our daily lives.