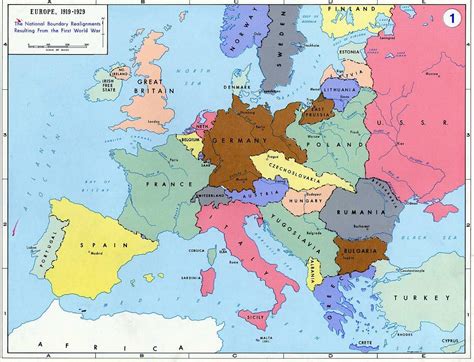
The Europe map before World War 2 was a complex and dynamic entity, with various alliances, treaties, and territorial disputes that ultimately contributed to the outbreak of the war. In the aftermath of World War 1, the Treaty of Versailles imposed significant territorial and economic penalties on Germany, which led to widespread resentment and a desire for revenge among the German people. The treaty also established the League of Nations, an international organization dedicated to promoting peace and preventing future wars. However, the League proved ineffective in preventing the aggressive expansion of fascist powers such as Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, and Imperial Japan.
Key Points
- The Treaty of Versailles imposed significant penalties on Germany, contributing to widespread resentment and a desire for revenge.
- The League of Nations was established to promote peace and prevent future wars, but proved ineffective in preventing the aggressive expansion of fascist powers.
- Nazi Germany, led by Adolf Hitler, began to challenge the Treaty of Versailles and expand its territory through a series of aggressive actions.
- The policy of appeasement, pursued by Britain and France, aimed to avoid war by giving in to Germany's demands, but ultimately emboldened Hitler's aggression.
- The Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, a non-aggression treaty between Germany and the Soviet Union, paved the way for the invasion of Poland and the start of World War 2.
Pre-War European Politics

In the years leading up to World War 2, European politics were marked by a complex web of alliances, treaties, and territorial disputes. The Treaty of Versailles had imposed significant penalties on Germany, including the loss of territory, military restrictions, and reparations. This led to widespread resentment and a desire for revenge among the German people, which was exploited by the Nazi Party, led by Adolf Hitler. The Nazis promised to restore German greatness, challenge the Treaty of Versailles, and provide jobs and economic stability to the German people.
Rise of Fascist Powers
The rise of fascist powers in Europe, including Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, and Imperial Japan, posed a significant threat to peace and stability. These powers were characterized by their aggressive militarism, authoritarianism, and racist ideologies. Nazi Germany, in particular, began to challenge the Treaty of Versailles and expand its territory through a series of aggressive actions, including the remilitarization of the Rhineland, the annexation of Austria, and the occupation of Czechoslovakia.
| Country | Territorial Changes |
|---|---|
| Germany | Lost territory, including Saar, Alsace-Lorraine, and Eupen-Malmedy |
| Poland | Gained territory, including the Polish Corridor and Danzig |
| Czechoslovakia | Lost territory, including the Sudetenland |
| Austria | Annexed by Nazi Germany |
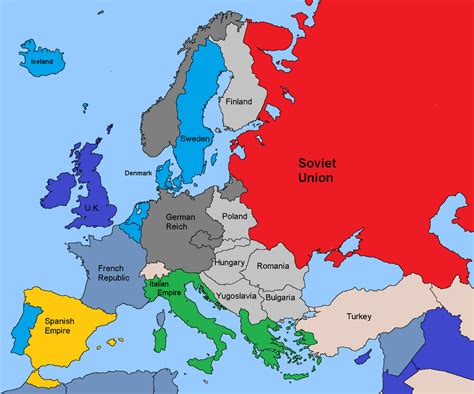
European Alliances and Treaties
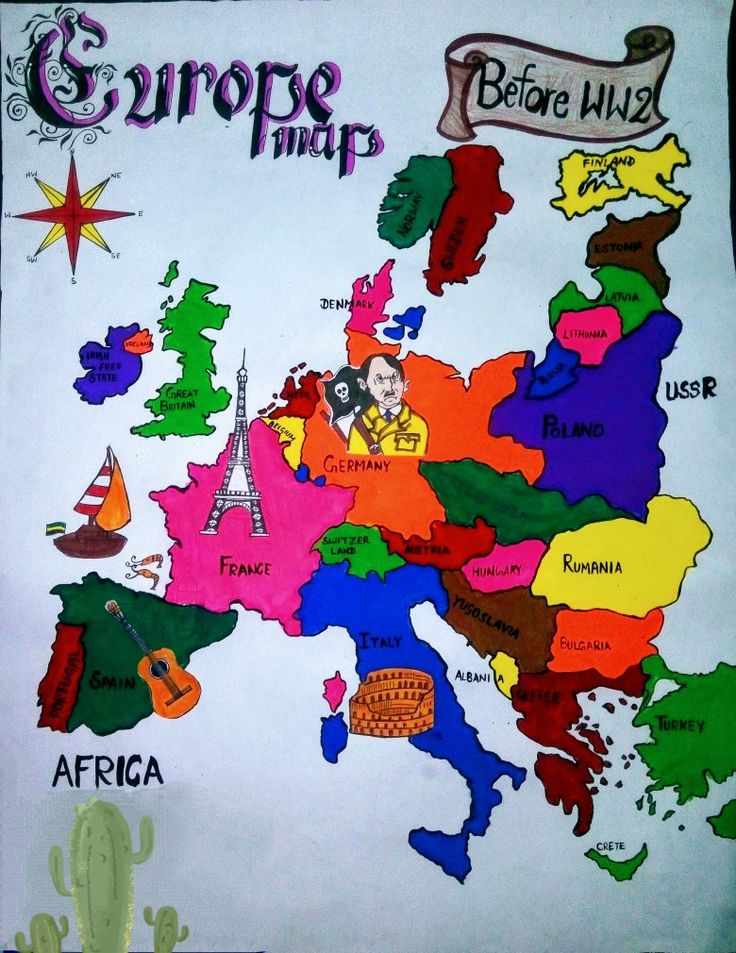
In the years leading up to World War 2, European alliances and treaties played a significant role in shaping the continent’s politics and paving the way for the war. The Treaty of Versailles, for example, imposed significant penalties on Germany and established the League of Nations, which proved ineffective in preventing the aggressive expansion of fascist powers. The Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, a non-aggression treaty between Germany and the Soviet Union, paved the way for the invasion of Poland and the start of World War 2.
Policy of Appeasement
The policy of appeasement, pursued by Britain and France, aimed to avoid war by giving in to Germany’s demands, but ultimately emboldened Hitler’s aggression. This policy was based on the belief that Germany had legitimate grievances and that giving in to its demands would satisfy its ambitions and prevent further conflict. However, the policy of appeasement only served to encourage Hitler’s aggression, and ultimately contributed to the outbreak of World War 2.
What were the main causes of World War 2?
+The main causes of World War 2 were the rise of fascist powers, including Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, and Imperial Japan, and the policy of appeasement pursued by Britain and France. The Treaty of Versailles also played a significant role in contributing to the outbreak of the war.
What was the significance of the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact?
+The Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact was a non-aggression treaty between Germany and the Soviet Union, which paved the way for the invasion of Poland and the start of World War 2. The pact also included a secret protocol, which divided Eastern Europe into Soviet and German spheres of influence.
What were the consequences of the policy of appeasement?
+The policy of appeasement ultimately emboldened Hitler's aggression and contributed to the outbreak of World War 2. The policy also damaged the credibility of Britain and France, and paved the way for the rise of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers.
In conclusion, the Europe map before World War 2 was a complex and dynamic entity, marked by a complex web of alliances, treaties, and territorial disputes. The rise of fascist powers, including Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, and Imperial Japan, posed a significant threat to peace and stability, and the policy of appeasement pursued by Britain and France ultimately emboldened Hitler’s aggression and contributed to the outbreak of the war. The consequences of the war were devastating, with millions of people killed, and entire cities and communities destroyed. The war also led to the rise of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers, and paved the way for the Cold War and the modern geopolitical landscape.