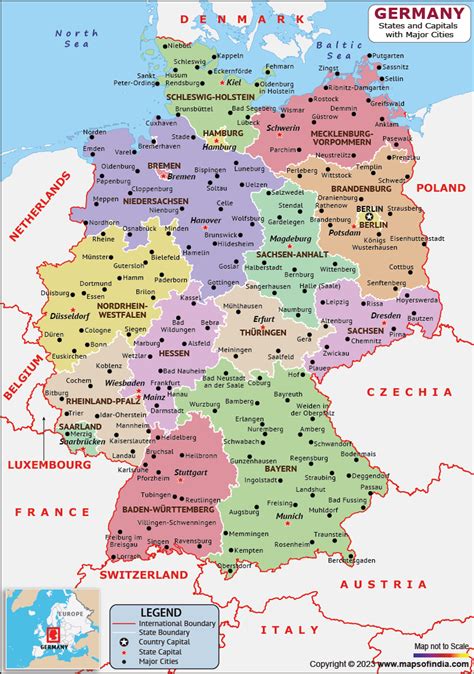
Germany, a country located in the heart of Europe, boasts a rich history, vibrant culture, and breathtaking landscapes. From the majestic Alps in the south to the scenic coastlines of the North Sea and Baltic Sea, Germany's geography is as diverse as it is fascinating. For travelers and map enthusiasts alike, understanding the layout of Germany is essential for exploring its many wonders. Here are five ways to explore and understand the Germany map, each offering a unique perspective on this incredible country.
Geographical Overview
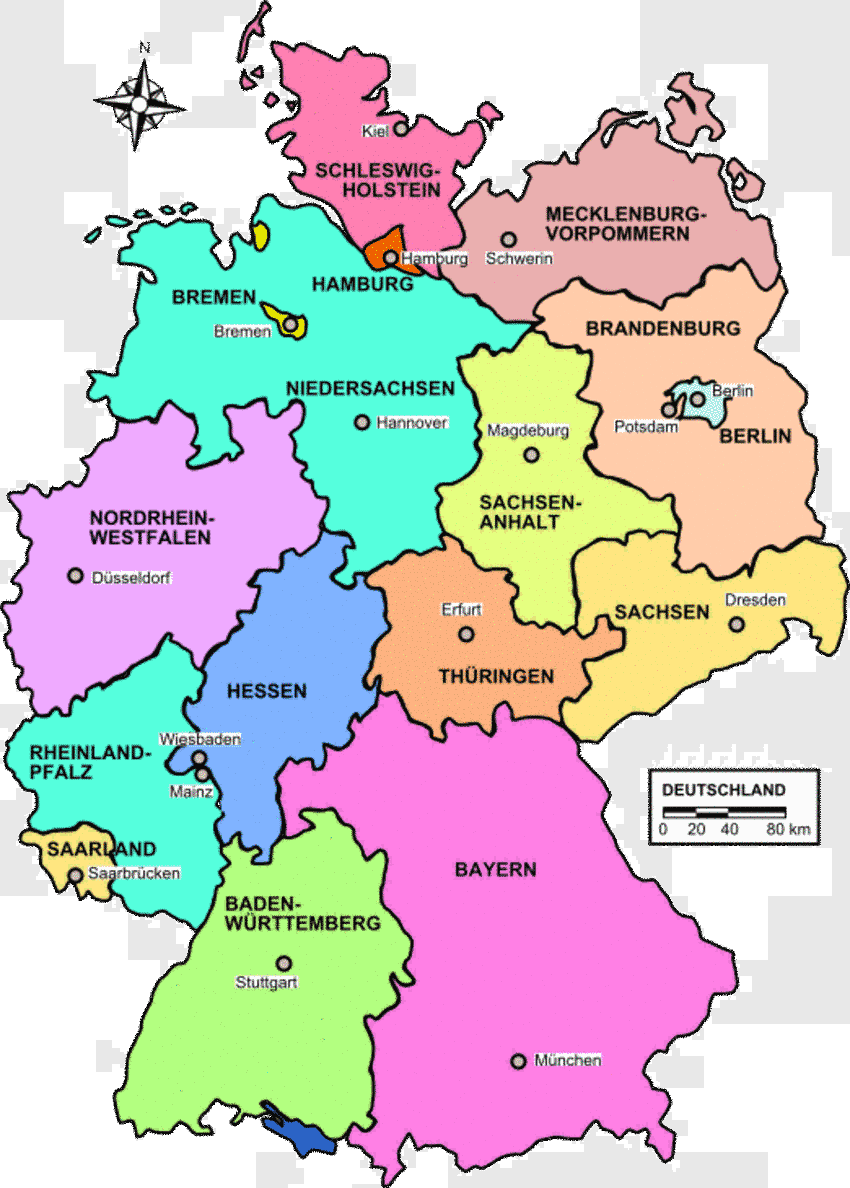
Germany is bordered by Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, France and Luxembourg to the southwest, and Belgium and the Netherlands to the northwest. This strategic location makes Germany a central hub in European geography and trade. The country can be broadly divided into four main geographical regions: the North German Plain, the Central Uplands, the Alpine Foreland, and the Alps. Each region has its own distinct features, from the low-lying plains of the north to the mountainous peaks of the south.
Regional Breakdown
A closer look at Germany’s map reveals 16 federal states (Bundesländer), each with its own capital and unique characteristics. The states are further divided into districts (Kreise) and municipalities (Gemeinden), offering a detailed insight into the country’s administrative and geographical structure. For instance, the state of Bavaria in the southeast is known for its picturesque Alps, traditional folk culture, and vibrant cities like Munich, while the state of Berlin, the capital, is an enclave of modernity and history, nestled within the state of Brandenburg.
| Region | Notable Features |
|---|---|
| North German Plain | Low-lying, coastal regions, major cities like Hamburg |
| Central Uplands | Rhine River, dense forests, historical sites |
| Alpine Foreland | Picturesque countryside, traditional villages, access to the Alps |
| Alps | Mountain peaks, ski resorts, traditional Bavarian culture |
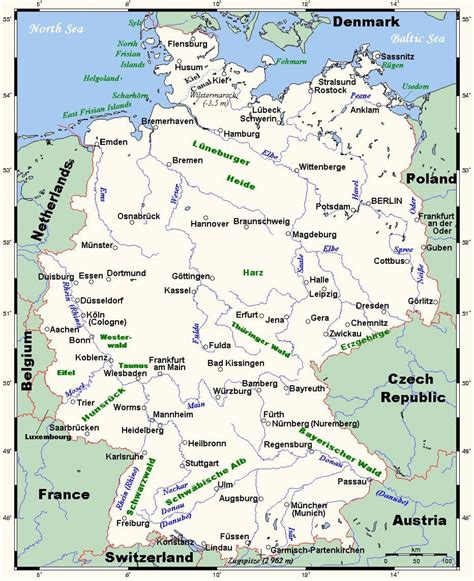
Transportation and Infrastructure

Germany’s transportation network is one of the most developed in Europe, with an extensive system of autobahns (highways), railways, and waterways. The country is easily accessible by air, with several international airports, including Frankfurt Airport, one of the busiest in Europe. For travelers, navigating Germany’s map is made easier by its comprehensive public transportation system, which includes buses, trams, and trains, connecting even the smallest towns to major cities.
Sustainable Travel
For those interested in sustainable travel, Germany offers a variety of eco-friendly options. The country has invested heavily in renewable energy and green technologies, and visitors can explore many of its attractions using environmentally friendly modes of transport. Cycling, in particular, is a popular way to see Germany, with dedicated bike paths and scenic routes that allow travelers to enjoy the countryside at a leisurely pace.
Key Points for Exploring Germany
- Understand the geographical regions of Germany for a deeper appreciation of its diversity.
- Use public transportation for an efficient and environmentally friendly way to travel.
- Explore Germany's 16 federal states to discover unique cultural and historical experiences.
- Consider sustainable travel options, such as cycling, to enjoy the countryside.
- Investigate local festivals and traditions, which vary significantly across different regions.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Germany’s map is not just a geographical outline but also a canvas of history and culture. From the remnants of the Berlin Wall to the fairytale castles of Bavaria, each region tells a story of the past. The country is home to numerous UNESCO World Heritage sites, including the Cologne Cathedral, the Rhine Valley, and the Museum Island in Berlin, showcasing its rich cultural heritage.
Historical Landmarks
For history enthusiasts, Germany’s map is dotted with landmarks that played significant roles in European history. The Neuschwanstein Castle, built in the 19th century, is a prime example of Romanesque Revival architecture and one of Germany’s most recognizable symbols. Other historical sites, such as the concentration camp memorial sites, serve as poignant reminders of the country’s complex past and its path towards reconciliation and peace.
As one delves into the intricacies of Germany's map, it becomes clear that the country is a treasure trove of experiences waiting to be discovered. Whether you're drawn to its natural beauty, its vibrant cities, or its historical significance, understanding the layout and diversity of Germany is the first step in planning an unforgettable journey through this incredible country.
What are the main geographical regions of Germany?
+Germany is broadly divided into four main geographical regions: the North German Plain, the Central Uplands, the Alpine Foreland, and the Alps.
How can I travel sustainably in Germany?
+Germany offers a variety of sustainable travel options, including cycling, using public transportation, and exploring the countryside on foot. These modes not only reduce your carbon footprint but also provide a more immersive experience of the local culture and landscapes.
What are some must-visit cultural and historical sites in Germany?
+Germany is home to numerous UNESCO World Heritage sites, including the Cologne Cathedral, the Rhine Valley, and the Museum Island in Berlin. Additionally, historical landmarks like Neuschwanstein Castle and the Berlin Wall Memorial are must-visits for anyone interested in history and culture.