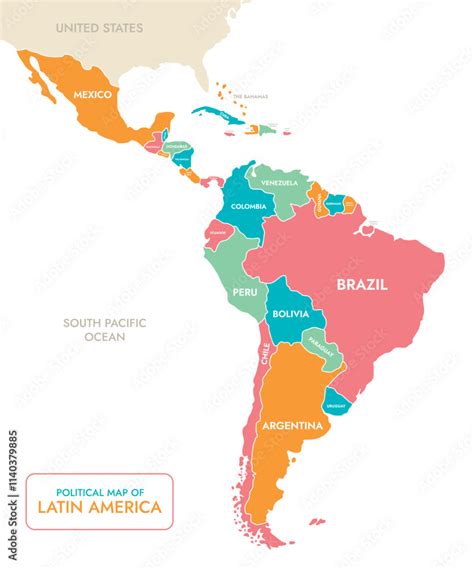
Latin America, a region of immense cultural, geographical, and historical diversity, stretches from the southern border of the United States to the tip of South America, encompassing a vast array of landscapes, climates, and ecosystems. The region's complex history, shaped by indigenous civilizations, European colonization, and African influences, has resulted in a rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and traditions. For travelers, researchers, and enthusiasts alike, navigating this vast and varied territory requires a comprehensive understanding of its geography, political boundaries, and cultural nuances.
Geographical Overview of Latin America
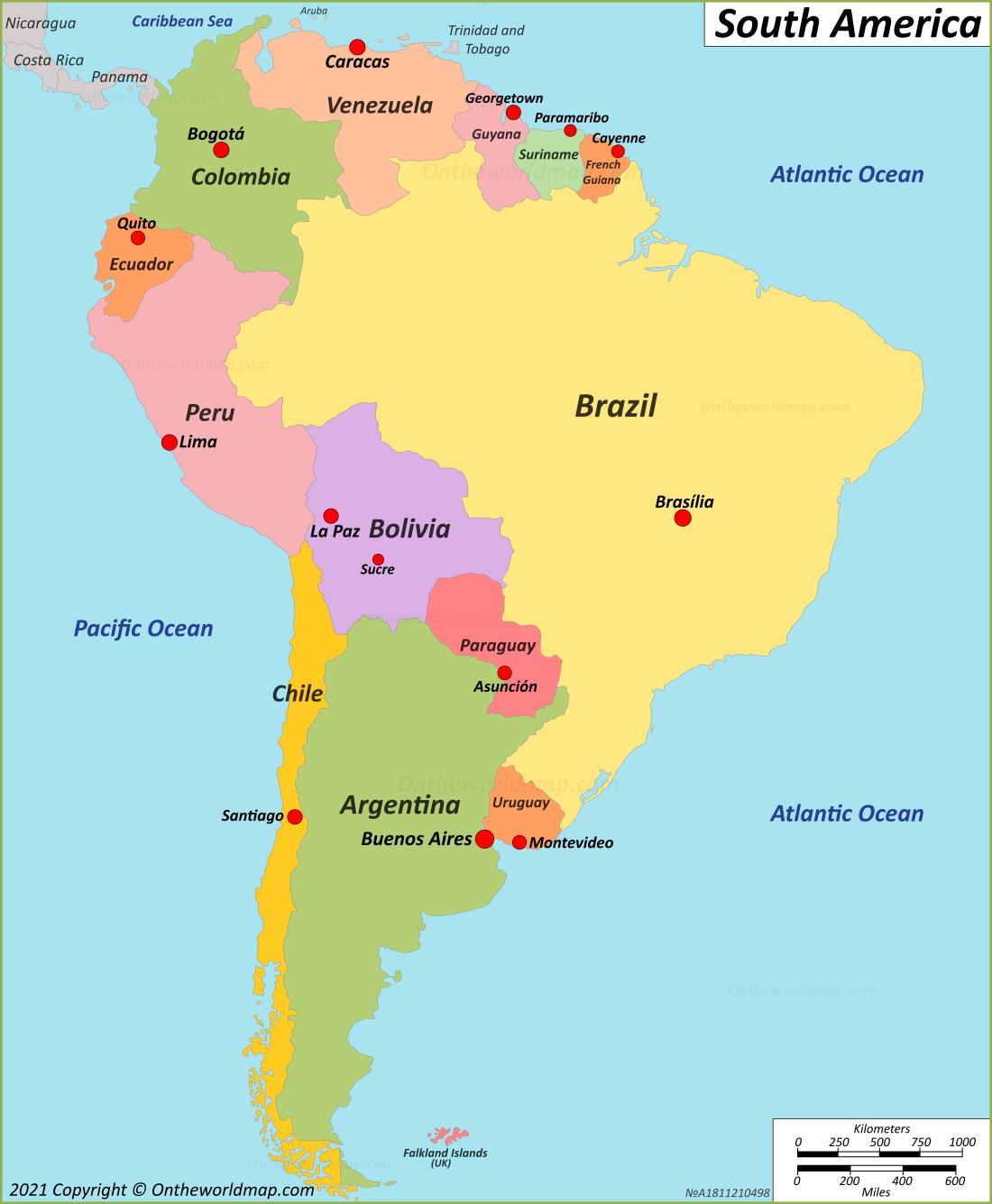
Latin America’s geography is characterized by its extreme diversity, featuring the Amazon rainforest, the world’s largest tropical rainforest; the Andes mountain range, the longest mountain range in the world; and the Caribbean and Pacific coastlines, which offer a plethora of beaches, islands, and marine ecosystems. The region’s geography has played a significant role in shaping the climate, biodiversity, and human settlement patterns. Understanding the geographical layout is essential for anyone seeking to explore or study Latin America, as it influences everything from language and culture to economy and politics.
Regional Divisions and Countries
Latin America can be broadly divided into several subregions, each with its unique characteristics and countries. These include Central America, which connects North America to South America; the Caribbean, comprising island nations with a distinct cultural and historical identity; South America, the continent’s southern part, which includes countries like Brazil, Argentina, and Chile; and Mexico, often culturally and geographically associated with both North and Latin America. Each country within these subregions boasts its own set of languages, customs, and natural wonders, contributing to the region’s overall diversity.
| Country | Capital | Population (2020 Estimate) |
|---|---|---|
| Argentina | Buenos Aires | 45.6 million |
| Brazil | Brasília | 212.2 million |
| Chile | Santiago | 18.4 million |
| Mexico | Mexico City | 127.5 million |
Cultural and Historical Significance
Latin America’s cultural landscape is a vibrant mosaic of indigenous, European, African, and Asian influences. The region is home to numerous UNESCO World Heritage sites, including the ancient Inca city of Machu Picchu in Peru, the Mayan ruins of Tulum in Mexico, and the historic city of Cartagena in Colombia. These sites, along with the region’s resilient indigenous communities and the African diaspora, highlight the complex and often tumultuous history of Latin America, marked by colonization, slavery, and resistance.
Language and Cuisine
Language plays a significant role in Latin America, with Spanish and Portuguese being the predominant languages, alongside a myriad of indigenous languages and French in some Caribbean islands. The region’s cuisine is equally diverse, reflecting its cultural melting pot. From the spicy dishes of Mexico and the seafood stews of Brazil to the grilled meats of Argentina and the empanadas of Colombia, each country offers a unique gastronomic experience that blends native, European, and African culinary traditions.
Key Points
- Latin America's geographical diversity includes rainforests, mountain ranges, and coastlines along the Caribbean and Pacific.
- The region is divided into subregions like Central America, the Caribbean, South America, and Mexico, each with distinct cultural and geographical characteristics.
- Countries in Latin America have diverse languages, customs, and natural wonders, contributing to the region's overall diversity.
- Understanding the region's cultural and historical context is essential for exploring its UNESCO World Heritage sites, indigenous communities, and historical cities.
- Language and cuisine in Latin America reflect the region's complex cultural melting pot, with influences from indigenous, European, African, and Asian sources.
Economic and Political Landscape
The economic and political landscape of Latin America is complex and dynamic, with countries at various stages of development and facing unique challenges. The region is rich in natural resources, including oil, minerals, and agricultural products, which has both benefited and hindered economic development. Political systems range from democracies to authoritarian regimes, with ongoing issues related to corruption, inequality, and social unrest. Despite these challenges, many Latin American countries have made significant strides in economic growth, social reform, and regional integration.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the challenges, Latin America also presents numerous opportunities for investment, trade, and cultural exchange. The region’s growing middle class, technological advancements, and strategic geopolitical position make it an attractive market for international businesses. Additionally, initiatives for regional integration, such as the Union of South American Nations (UNASUR) and the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC), aim to foster cooperation and solidarity among Latin American countries, promoting a stronger, more unified presence on the global stage.
What are the main geographical features of Latin America?
+Latin America is characterized by its diverse geography, including the Amazon rainforest, the Andes mountain range, and extensive coastlines along the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean.
Which languages are predominantly spoken in Latin America?
+Spanish and Portuguese are the predominant languages in Latin America, with Spanish being the official language in most countries and Portuguese spoken in Brazil.
What are some of the cultural influences in Latin American cuisine?
+Latin American cuisine reflects a blend of indigenous, European, African, and Asian influences, resulting in a diverse range of dishes and flavors across different countries.
In conclusion, Latin America is a region of profound beauty, complexity, and resilience. Its geographical, cultural, and historical diversity offers a unique experience for travelers, researchers, and business investors. As the region continues to evolve, facing challenges and seizing opportunities, understanding its multifaceted nature is essential for fostering deeper connections and collaborations within and beyond its borders.