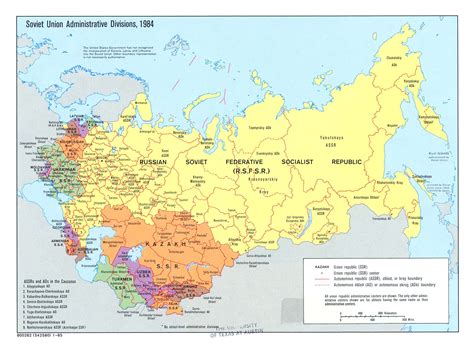
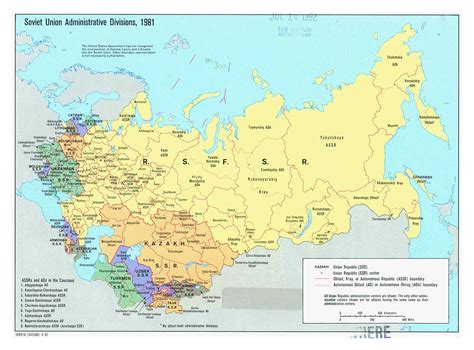
The USSR, or the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, was a vast and complex country that existed from 1922 to 1991. At its peak, it was the largest country in the world, covering over 22 million square kilometers and comprising 15 Soviet Socialist Republics. The USSR’s geography was incredibly diverse, ranging from the frozen tundras of Siberia to the subtropical beaches of the Black Sea. In this article, we will explore the USSR map, highlighting its key features, regions, and cities.
Geography and Climate
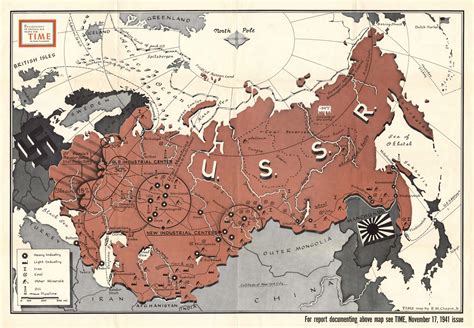
The USSR spanned across much of northern Eurasia, bordering several countries including Norway, Finland, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, Turkey, Iran, Afghanistan, China, and Mongolia. The country’s terrain was characterized by vast plains, mountains, and forests, with the Ural Mountains marking the dividing line between Europe and Asia. The USSR’s climate varied greatly, from the Arctic tundra in the north to the desert climates of Central Asia.
The USSR's geography played a significant role in shaping its history, economy, and culture. The country's vast natural resources, including oil, gas, coal, and minerals, were a major factor in its industrialization and economic growth. The USSR's diverse climate and geography also supported a wide range of agricultural activities, from wheat and grain production in the Ukraine and Russia to cotton and rice production in Central Asia.
Regions and Republics
The USSR was divided into 15 Soviet Socialist Republics, each with its own distinct culture, history, and geography. The largest republic was the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR), which covered over 17 million square kilometers and accounted for over 50% of the USSR’s population. Other major republics included Ukraine, Belarus, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia.| Republic | Capital | Population (1989) |
|---|---|---|
| Russia | Moscow | 147 million |
| Ukraine | Kiev | 51 million |
| Belarus | Minsk | 10 million |
| Georgia | Tbilisi | 5 million |
| Azerbaijan | Baku | 7 million |
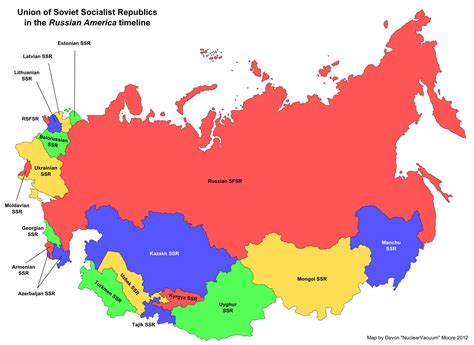
Key Points
- The USSR was the largest country in the world, covering over 22 million square kilometers.
- The country was divided into 15 Soviet Socialist Republics, each with its own distinct culture and history.
- The USSR's geography was incredibly diverse, ranging from the frozen tundras of Siberia to the subtropical beaches of the Black Sea.
- The country's natural resources, including oil, gas, coal, and minerals, played a major role in its industrialization and economic growth.
- The USSR's diverse climate and geography supported a wide range of agricultural activities, from wheat and grain production to cotton and rice production.
Cities and Urbanization
The USSR had a number of major cities, including Moscow, Leningrad (now St. Petersburg), Kiev, Minsk, and Tashkent. These cities were centers of industry, culture, and education, and played a significant role in the country’s economic and social development. The USSR’s urbanization rate was relatively high, with over 60% of the population living in urban areas.
Moscow, the capital city, was the largest city in the USSR, with a population of over 8 million people. The city was a major center of industry, culture, and education, and was home to many of the country's most prestigious universities and research institutions. Other major cities, such as Leningrad and Kiev, were also important centers of industry and culture, and played a significant role in the country's economic and social development.
Transportation and Infrastructure
The USSR had a well-developed transportation system, including a comprehensive network of roads, railways, and waterways. The country’s railway system was one of the largest in the world, with over 140,000 kilometers of track. The USSR also had a number of major ports, including the Port of Leningrad, the Port of Odessa, and the Port of Vladivostok.The USSR's transportation system played a significant role in the country's economic development, facilitating the movement of goods and people across the vast territory. The country's infrastructure, including its roads, bridges, and canals, was also well-developed, and supported a wide range of economic activities, from industry and agriculture to trade and tourism.
Conclusion
The USSR map is a fascinating topic, offering insights into the country’s geography, climate, regions, and cities. The USSR’s diverse natural resources, including oil, gas, coal, and minerals, played a major role in its industrialization and economic growth. The country’s transportation system, including its roads, railways, and waterways, facilitated the movement of goods and people across the vast territory. As we explore the USSR map, we gain a deeper understanding of the country’s complex history, economy, and culture, and appreciate the significance of its geography and climate in shaping its development.What was the USSR’s largest republic?
+The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR) was the largest republic in the USSR, covering over 17 million square kilometers and accounting for over 50% of the country’s population.
What was the USSR’s population in 1989?
+The USSR’s population in 1989 was approximately 287 million people.
What was the USSR’s main industry?
+The USSR’s main industry was heavy industry, including steel production, coal mining, and oil extraction. The country was also a major producer of agricultural products, including wheat, grain, and cotton.