The concept of matrices has been a cornerstone of linear algebra for centuries, with its roots tracing back to ancient civilizations. The term "matrix" was first introduced by the renowned English mathematician James Joseph Sylvester in 1848, derived from the Latin word for "womb," signifying a container or a supporter of a developing entity. Over time, matrices have evolved to become a fundamental tool in various fields, including mathematics, physics, engineering, computer science, and statistics. In this article, we will delve into the world of matrices, exploring their definition, types, operations, and applications, as well as providing insights into their importance and future prospects.
Introduction to Matrices

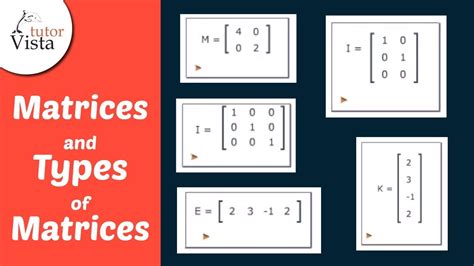
A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns. The individual entries in a matrix are called elements or entries, and they can be real or complex numbers, variables, or even functions. Matrices are commonly represented using uppercase letters, such as A, B, or C, and their elements are denoted by lowercase letters, such as a, b, or c. The size of a matrix is determined by the number of rows and columns it contains, with an m × n matrix having m rows and n columns.
Types of Matrices
There are several types of matrices, each with its own unique properties and applications. Some of the most common types of matrices include:
- Square matrix: A matrix with the same number of rows and columns, i.e., an m × m matrix.
- Rectangular matrix: A matrix with a different number of rows and columns, i.e., an m × n matrix where m ≠ n.
- Identity matrix: A square matrix with ones on the main diagonal and zeros elsewhere, denoted by I.
- Zero matrix: A matrix with all elements equal to zero, denoted by 0.
- Diagonal matrix: A square matrix with non-zero elements only on the main diagonal.
| Matrix Type | Properties |
|---|---|
| Square matrix | m × m, same number of rows and columns |
| Rectangular matrix | m × n, different number of rows and columns |
| Identity matrix | ones on main diagonal, zeros elsewhere |
| Zero matrix | |
| Diagonal matrix | non-zero elements only on main diagonal |

Matrix Operations

Matrix operations are used to manipulate and transform matrices, and they are essential in various mathematical and computational contexts. Some of the most common matrix operations include:
- Matrix addition: The sum of two matrices with the same size, element-wise.
- Matrix multiplication: The product of two matrices, where the number of columns in the first matrix must be equal to the number of rows in the second matrix.
- Matrix transpose: The operation of swapping the rows and columns of a matrix, denoted by AT.
- Matrix inverse: The inverse of a square matrix, denoted by A-1, which satisfies the property AA-1 = I.
Applications of Matrices
Matrices have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Linear algebra: Matrices are used to represent linear transformations, solve systems of linear equations, and find eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
- Physics and engineering: Matrices are used to describe the motion of objects, model complex systems, and analyze data.
- Computer science: Matrices are used in computer graphics, machine learning, and data analysis.
- Statistics: Matrices are used in statistical analysis, data visualization, and hypothesis testing.
Key Points
- Matrices are rectangular arrays of numbers, symbols, or expressions, with various types and operations.
- Matrix operations, such as addition, multiplication, and transpose, are essential in mathematical and computational contexts.
- Matrices have a wide range of applications in linear algebra, physics, engineering, computer science, and statistics.
- The choice of matrix type and operation depends on the specific problem or application.
- Understanding the properties of matrices is crucial for effective matrix operations and analysis.
In conclusion, matrices are a fundamental concept in mathematics and computer science, with a wide range of applications in various fields. Understanding the properties and operations of matrices is essential for effective problem-solving and analysis. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of matrices will only continue to grow, and their applications will expand into new and exciting areas.
What is a matrix in mathematics?
+A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns.
What are the different types of matrices?
+There are several types of matrices, including square matrices, rectangular matrices, identity matrices, zero matrices, and diagonal matrices.
What are some common matrix operations?
+Common matrix operations include matrix addition, matrix multiplication, matrix transpose, and matrix inverse.
What are some applications of matrices?
+Matrices have a wide range of applications in linear algebra, physics, engineering, computer science, and statistics.
Why are matrices important in computer science?
+Matrices are important in computer science because they are used in computer graphics, machine learning, and data analysis.