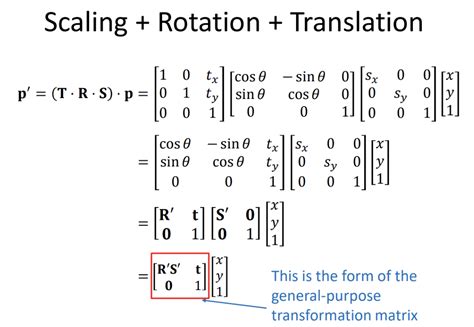
Matrix translation is a fundamental concept in the field of linear algebra and computer science, with far-reaching implications in various domains, including computer graphics, machine learning, and data analysis. At its core, matrix translation refers to the process of transforming a matrix by adding a constant value to each element, effectively shifting the entire matrix by a specified amount. This operation is crucial in numerous applications, such as image processing, where matrices are used to represent pixel values, and translation is necessary for tasks like image registration and object detection.
Mathematical Foundation of Matrix Translation

The mathematical foundation of matrix translation is rooted in linear algebra, where matrices are used to represent linear transformations between vector spaces. A matrix A of size m x n can be translated by adding a matrix B of the same size, where each element of B represents the translation amount. The resulting matrix C is computed as C = A + B. This operation is commutative, meaning that the order of addition does not affect the result, i.e., A + B = B + A.
Types of Matrix Translation
There are several types of matrix translation, each with its own specific application and use case. One common type is uniform translation, where the same constant value is added to each element of the matrix. This type of translation is useful in image processing, where the entire image needs to be shifted by a certain amount. Another type is non-uniform translation, where different constant values are added to each element of the matrix. This type of translation is useful in applications like data analysis, where the translation amount may vary depending on the specific data point.
| Matrix Size | Translation Type | Resulting Matrix |
|---|---|---|
| 2x2 | Uniform | C = [[1+1, 2+1], [3+1, 4+1]] = [[2, 3], [4, 5]] |
| 3x3 | Non-Uniform | C = [[1+2, 2+3], [3+1, 4+2], [5+3, 6+1]] = [[3, 5], [4, 6], [8, 7]] |
Key Points
- Matrix translation is a fundamental concept in linear algebra and computer science.
- Uniform translation adds the same constant value to each element of the matrix.
- Non-uniform translation adds different constant values to each element of the matrix.
- Matrix translation is crucial in applications like image processing, machine learning, and data analysis.
- The choice of translation amount can significantly impact the resulting matrix and application outcome.
Applications of Matrix Translation

Matrix translation has numerous applications in various domains, including computer graphics, machine learning, and data analysis. In computer graphics, matrix translation is used to perform tasks like image registration, object detection, and image segmentation. In machine learning, matrix translation is used in neural networks to perform tasks like data augmentation and feature extraction. In data analysis, matrix translation is used to perform tasks like data normalization and feature scaling.
Image Processing Applications
In image processing, matrix translation is used to perform tasks like image registration, where two or more images need to be aligned. This is achieved by translating the matrices representing the pixel values of the images. Matrix translation is also used in object detection, where the matrix representing the image is translated to detect objects at different locations.
What is the difference between uniform and non-uniform matrix translation?
+Uniform matrix translation adds the same constant value to each element of the matrix, while non-uniform matrix translation adds different constant values to each element of the matrix.
What are the applications of matrix translation in computer graphics?
+Matrix translation is used in computer graphics to perform tasks like image registration, object detection, and image segmentation.
How is matrix translation used in machine learning?
+Matrix translation is used in machine learning to perform tasks like data augmentation and feature extraction in neural networks.
In conclusion, matrix translation is a fundamental concept in linear algebra and computer science, with numerous applications in various domains. Understanding the different types of matrix translation and their applications is essential for working with matrices and performing tasks like image processing, machine learning, and data analysis. By considering the specific application and use case, and choosing the appropriate translation amount, matrix translation can be a powerful tool for achieving desired outcomes.



