The Medicaid Management Information System (MMIS) is a critical component of the healthcare infrastructure in the United States, playing a vital role in the administration of Medicaid programs across the country. As a complex system, MMIS is designed to manage the vast amounts of data and transactions involved in Medicaid, ensuring that benefits are delivered efficiently and effectively to eligible recipients. With a history dating back to the 1960s, MMIS has evolved significantly over the years, adapting to changes in healthcare policy, technology, and the growing needs of the Medicaid population.
At its core, MMIS is a comprehensive system that integrates various functional components, including eligibility determination, claims processing, provider management, and reporting. By leveraging advanced technology and data analytics, MMIS enables state Medicaid agencies to streamline their operations, reduce administrative costs, and improve the overall quality of care. Moreover, MMIS has become increasingly important in recent years, as the Affordable Care Act (ACA) has led to a significant expansion of Medicaid coverage, resulting in a substantial increase in enrollment and claims volume.
Key Points
- The Medicaid Management Information System (MMIS) is a critical component of the US healthcare infrastructure, managing Medicaid programs across the country.
- MMIS integrates various functional components, including eligibility determination, claims processing, provider management, and reporting.
- The system has evolved significantly over the years, adapting to changes in healthcare policy, technology, and the growing needs of the Medicaid population.
- MMIS enables state Medicaid agencies to streamline their operations, reduce administrative costs, and improve the overall quality of care.
- The system has become increasingly important in recent years, as the Affordable Care Act (ACA) has led to a significant expansion of Medicaid coverage.
History and Evolution of MMIS

The concept of MMIS dates back to the 1960s, when the US government first introduced Medicaid as a joint federal-state program to provide health insurance coverage to low-income individuals and families. Initially, MMIS was designed as a basic claims processing system, with limited functionality and manual data entry. Over the years, however, MMIS has undergone significant transformations, driven by advances in technology, changes in healthcare policy, and the growing needs of the Medicaid population.
In the 1980s, MMIS began to adopt more advanced technologies, including mainframe computers and automated data processing systems. This enabled state Medicaid agencies to process claims more efficiently and effectively, reducing errors and improving payment accuracy. The 1990s saw further advancements, with the introduction of client-server architecture and the development of more sophisticated software applications. These improvements enabled MMIS to support more complex business processes, including eligibility determination and provider management.
Modern MMIS Architecture
Today, MMIS is a highly sophisticated system, leveraging advanced technologies such as cloud computing, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI). Modern MMIS architecture is designed to be modular, flexible, and scalable, enabling state Medicaid agencies to respond quickly to changing healthcare needs and policy requirements. The system typically consists of several key components, including:
- Eligibility determination: This module is responsible for verifying the eligibility of individuals and families for Medicaid benefits, using data from various sources, including income verification and identity authentication.
- Claims processing: This module processes claims submitted by healthcare providers, using advanced algorithms and business rules to determine payment accuracy and detect potential fraud.
- Provider management: This module manages the registration and certification of healthcare providers, ensuring that they meet the necessary qualifications and standards to participate in the Medicaid program.
- Reporting and analytics: This module provides real-time reporting and analytics capabilities, enabling state Medicaid agencies to track key performance indicators, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
| MMIS Component | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Eligibility Determination | Verifies individual and family eligibility for Medicaid benefits |
| Claims Processing | Processes claims submitted by healthcare providers, determining payment accuracy and detecting potential fraud |
| Provider Management | Manages the registration and certification of healthcare providers, ensuring compliance with Medicaid standards |
| Reporting and Analytics | Provides real-time reporting and analytics capabilities, enabling data-driven decision-making |
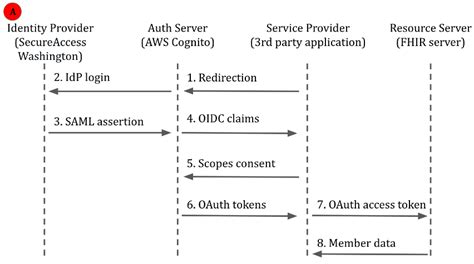
Benefits and Challenges of MMIS

The implementation of MMIS has numerous benefits, including improved efficiency, reduced administrative costs, and enhanced quality of care. By automating many of the manual processes involved in Medicaid administration, MMIS enables state Medicaid agencies to process claims more quickly and accurately, reducing errors and improving payment accuracy. Additionally, MMIS provides real-time reporting and analytics capabilities, enabling agencies to track key performance indicators and make data-driven decisions.
However, the implementation of MMIS also presents several challenges, including the need for significant upfront investment in technology and infrastructure, as well as the requirement for ongoing maintenance and support. Moreover, MMIS requires highly skilled personnel to design, implement, and operate the system, which can be a challenge for state Medicaid agencies with limited resources. Furthermore, the complexity of MMIS can make it difficult to integrate with other healthcare systems and technologies, requiring careful planning and coordination to ensure seamless interoperability.
Future Directions for MMIS
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, MMIS is likely to play an increasingly important role in the administration of Medicaid programs. In the future, MMIS is expected to leverage advanced technologies such as AI, machine learning, and blockchain to support more efficient and effective administration of Medicaid benefits. Additionally, MMIS is likely to be integrated with other healthcare systems and technologies, such as electronic health records (EHRs) and health information exchanges (HIEs), to support more coordinated and patient-centered care.
Moreover, MMIS is expected to play a critical role in supporting the growing needs of the Medicaid population, including the increasing demand for behavioral health services, long-term care, and community-based care. By providing real-time reporting and analytics capabilities, MMIS can help state Medicaid agencies to identify trends and patterns in healthcare utilization, enabling them to make data-driven decisions and optimize resource allocation.
What is the primary purpose of MMIS?
+The primary purpose of MMIS is to manage the administration of Medicaid programs, including eligibility determination, claims processing, provider management, and reporting.
How has MMIS evolved over the years?
+MMIS has undergone significant transformations over the years, driven by advances in technology, changes in healthcare policy, and the growing needs of the Medicaid population. From basic claims processing to sophisticated software applications, MMIS has become a highly advanced system, leveraging cloud computing, big data analytics, and AI to support more efficient and effective administration of Medicaid benefits.
What are the benefits of MMIS?
+The benefits of MMIS include improved efficiency, reduced administrative costs, and enhanced quality of care. By automating many of the manual processes involved in Medicaid administration, MMIS enables state Medicaid agencies to process claims more quickly and accurately, reducing errors and improving payment accuracy.



