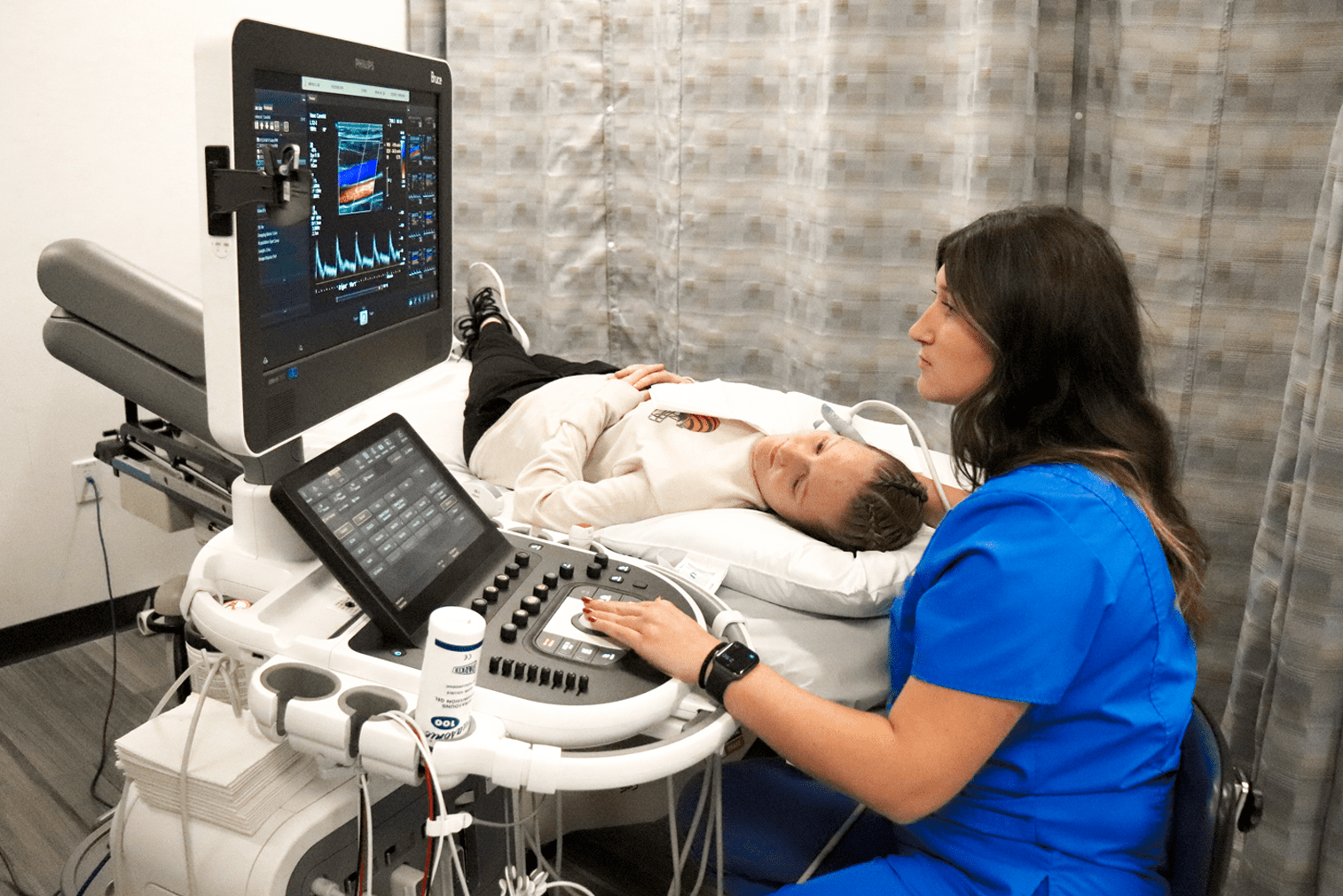
Medical diagnostic sonography, also known as ultrasound technology, is a non-invasive medical imaging modality that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of internal structures within the body. As a diagnostic tool, sonography plays a crucial role in various medical specialties, including obstetrics, cardiology, and radiology. The technology has evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in equipment, techniques, and applications. Today, sonography is an essential component of modern medical practice, enabling healthcare professionals to diagnose and monitor a wide range of medical conditions.
The history of sonography dates back to the 1940s, when the first ultrasound machines were developed. Initially, the technology was used primarily for diagnostic purposes in obstetrics and gynecology. However, with advancements in technology and the development of new techniques, sonography soon found applications in other medical specialties. The 1980s saw the introduction of Doppler ultrasound, which enabled the measurement of blood flow and detection of vascular disorders. Today, sonography is used in various medical specialties, including cardiology, neurology, and orthopedics.
Key Points
- Medical diagnostic sonography uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of internal structures within the body.
- The technology has evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in equipment, techniques, and applications.
- Sonography is an essential component of modern medical practice, enabling healthcare professionals to diagnose and monitor a wide range of medical conditions.
- The technology has applications in various medical specialties, including obstetrics, cardiology, and radiology.
- Advances in sonography have improved patient outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, and enhanced the quality of medical care.
Principles of Sonography
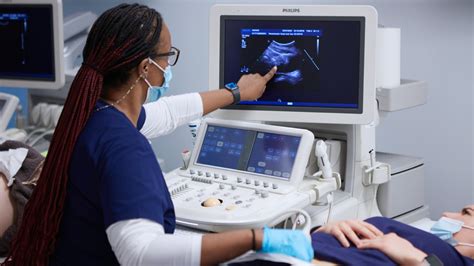
Sonography is based on the principle of sound wave reflection. When high-frequency sound waves are directed at internal structures within the body, they reflect off these structures and return to the ultrasound machine as echoes. The machine then uses these echoes to create images of the internal structures. The frequency of the sound waves used in sonography ranges from 2 to 15 megahertz, which is higher than the frequency range of human hearing. The choice of frequency depends on the depth of the structure being imaged and the level of detail required.
Types of Sonography
There are several types of sonography, including 2D, 3D, and 4D ultrasound. 2D ultrasound is the most commonly used type of sonography and provides a two-dimensional image of internal structures. 3D ultrasound provides a three-dimensional image, which can be useful in certain applications, such as fetal imaging. 4D ultrasound provides a real-time, three-dimensional image, which can be useful in applications such as cardiac imaging.
| Type of Sonography | Description |
|---|---|
| 2D Ultrasound | Provides a two-dimensional image of internal structures. |
| 3D Ultrasound | Provides a three-dimensional image of internal structures. |
| 4D Ultrasound | Provides a real-time, three-dimensional image of internal structures. |
Applications of Sonography

Sonography has a wide range of applications in various medical specialties. In obstetrics, sonography is used to monitor fetal development, detect congenital anomalies, and guide invasive procedures such as amniocentesis. In cardiology, sonography is used to evaluate cardiac function, detect cardiovascular disease, and guide interventional procedures such as angioplasty. In radiology, sonography is used to evaluate liver, kidney, and pancreatic function, as well as to detect cancer and other abnormalities.
Clinical Applications
Sonography has several clinical applications, including diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of medical conditions. In diagnosis, sonography is used to detect and characterize abnormalities, such as tumors, cysts, and vascular disorders. In treatment, sonography is used to guide interventional procedures, such as biopsies and drainages. In monitoring, sonography is used to track the progression of medical conditions, such as fetal development and tumor growth.
Sonography also has several advantages over other imaging modalities, including low cost, non-invasiveness, and lack of ionizing radiation. These advantages make sonography an attractive option for patients and healthcare professionals. However, sonography also has several limitations, including operator dependence, limited depth penetration, and artifacts. These limitations must be taken into account when interpreting sonographic images and making diagnostic decisions.
What is the difference between 2D and 3D ultrasound?
+2D ultrasound provides a two-dimensional image of internal structures, while 3D ultrasound provides a three-dimensional image. 3D ultrasound can provide more detailed information about internal structures, but it may not be as widely available as 2D ultrasound.
What are the advantages of sonography over other imaging modalities?
+Sonography has several advantages over other imaging modalities, including low cost, non-invasiveness, and lack of ionizing radiation. These advantages make sonography an attractive option for patients and healthcare professionals.
What are the limitations of sonography?
+Sonography has several limitations, including operator dependence, limited depth penetration, and artifacts. These limitations must be taken into account when interpreting sonographic images and making diagnostic decisions.
In conclusion, medical diagnostic sonography is a valuable diagnostic tool that plays a crucial role in various medical specialties. The technology has evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in equipment, techniques, and applications. Sonography has several advantages over other imaging modalities, including low cost, non-invasiveness, and lack of ionizing radiation. However, sonography also has several limitations, including operator dependence, limited depth penetration, and artifacts. As a medical professional, it is essential to understand the principles and types of sonography to make informed decisions about patient care.