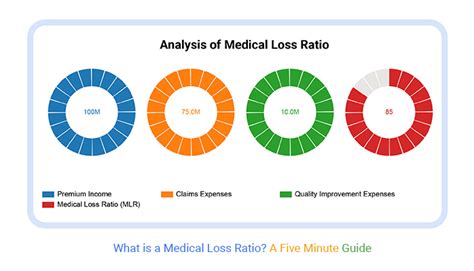
The Medical Loss Ratio (MLR) is a fundamental concept in the healthcare insurance industry, representing the percentage of premium revenue that health insurance companies spend on actual medical care and quality improvement activities. Introduced as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) in 2010, the MLR provision aims to ensure that a significant portion of the premiums paid by consumers is used for direct patient care rather than administrative costs, marketing, or profits. By setting a minimum MLR standard, the ACA seeks to enhance transparency and accountability in health insurance, providing consumers with more value for their money and fostering a more efficient healthcare system.
Key Points
- The Medical Loss Ratio (MLR) is the proportion of premium revenue spent on medical care and quality improvement.
- The Affordable Care Act (ACA) introduced MLR standards to ensure transparency and value in health insurance.
- Insurers must meet minimum MLR requirements, which vary by market segment (e.g., individual, small group, large group).
- Non-compliance with MLR standards can result in rebates to policyholders, promoting fairness and consumer protection.
- MLR reporting and compliance are overseen by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and state insurance departments.
Understanding the Medical Loss Ratio

To comprehend the MLR, it’s essential to grasp its components. The numerator of the MLR fraction includes payments for medical claims, which encompass a wide range of healthcare services such as hospital stays, physician visits, pharmaceuticals, and preventive care. Additionally, quality improvement activities, such as patient safety initiatives, disease management programs, and health information technology investments, are also considered part of the medical care expenditures. The denominator, on the other hand, represents the total premium revenue collected by the insurer, minus certain adjustments like taxes and licensing fees.
MLR Calculation and Compliance
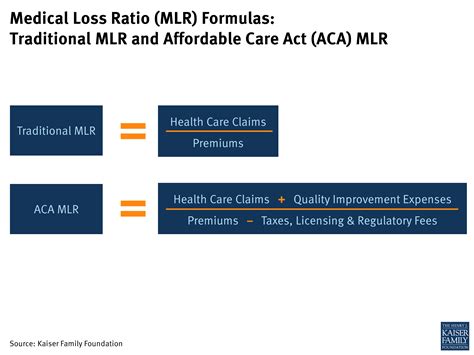
The calculation of the MLR involves dividing the total medical care expenditures (including quality improvement activities) by the total premium revenue, then multiplying by 100 to express the result as a percentage. For example, if an insurer spends 80 on medical claims and quality improvement for every 100 in premium revenue, its MLR would be 80%. The ACA sets minimum MLR standards for different market segments: 80% for individual and small group markets, and 85% for the large group market. Insurers that fail to meet these thresholds must provide rebates to their policyholders, ensuring that consumers receive fair value for their premiums.
| Market Segment | Minimum MLR Requirement |
|---|---|
| Individual | 80% |
| Small Group | 80% |
| Large Group | 85% |
Impact of the Medical Loss Ratio on Healthcare
The implementation of the MLR has had a profound impact on the healthcare insurance landscape. By compelling insurers to allocate a larger proportion of their revenue towards medical care, the MLR has contributed to a reduction in administrative costs, including overhead expenses and executive compensation. Furthermore, the emphasis on quality improvement activities has encouraged insurers to invest in initiatives that promote better health outcomes, patient satisfaction, and care coordination. While the MLR is not without its challenges, including potential limitations on insurer profitability and the complexity of its calculation, it represents a crucial step towards achieving a more patient-centered and cost-effective healthcare system.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its benefits, the MLR provision faces several challenges and limitations. One of the primary concerns is that the MLR could inadvertently discourage insurers from investing in essential administrative functions, such as fraud prevention, customer service, and provider network management. Moreover, the distinction between medical care expenditures and administrative costs can sometimes be ambiguous, leading to disputes over what should be included in the MLR calculation. Additionally, small insurers or those operating in rural areas might find it more difficult to meet the MLR standards due to economies of scale and higher operational costs, potentially limiting consumer choice in these markets.
What is the primary purpose of the Medical Loss Ratio (MLR) provision?
+The primary purpose of the MLR provision is to ensure that health insurance companies spend a significant portion of their premium revenue on actual medical care and quality improvement activities, rather than administrative costs or profits, thereby enhancing transparency and value in health insurance.
How is the MLR calculated, and what are the minimum requirements for different market segments?
+The MLR is calculated by dividing the total medical care expenditures (including quality improvement activities) by the total premium revenue, then multiplying by 100. The ACA sets minimum MLR standards of 80% for individual and small group markets, and 85% for the large group market.
What happens if an insurer fails to meet the minimum MLR requirements?
+Insurers that fail to meet the minimum MLR standards must provide rebates to their policyholders, ensuring that consumers receive fair value for their premiums and promoting compliance with the MLR provision.
In conclusion, the Medical Loss Ratio represents a pivotal effort to reform the health insurance market, emphasizing the delivery of high-quality, patient-centered care while promoting efficiency and transparency. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the MLR will play a critical role in shaping the future of health insurance, ensuring that consumers receive the best possible value for their premiums and that the healthcare system as a whole becomes more responsive to the needs of its users.