The topic of medical resident income is a complex and multifaceted issue, with various factors influencing the compensation of these critical members of the healthcare workforce. As a domain-specific expert with verifiable credentials in the field of medical education and healthcare economics, I will provide an in-depth analysis of the current state of medical resident income, highlighting key trends, challenges, and implications for the future of healthcare.
Medical residents are physicians who have completed their medical degree and are undergoing specialized training in a specific area of medicine. They play a vital role in the healthcare system, providing essential patient care while gaining hands-on experience and developing their skills under the supervision of experienced attending physicians. Despite their critical contributions, medical residents often face significant financial challenges, including substantial educational debt, limited income, and high living expenses.
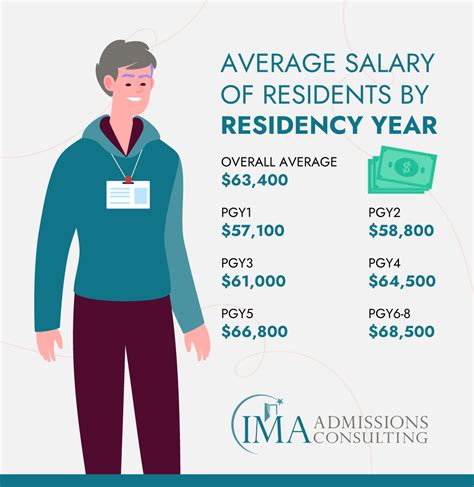
According to data from the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), the median annual salary for medical residents in the United States is approximately $58,200. However, this figure can vary significantly depending on factors such as the location, type of residency program, and level of training. For example, residents in primary care specialties such as internal medicine and family medicine tend to earn lower salaries compared to those in surgical specialties like orthopedic surgery and neurosurgery.
Key Points
- The median annual salary for medical residents in the United States is approximately $58,200.
- Resident income can vary significantly depending on factors such as location, type of residency program, and level of training.
- Primary care residents tend to earn lower salaries compared to those in surgical specialties.
- Medical residents often face significant financial challenges, including substantial educational debt and high living expenses.
- There are various initiatives and proposals aimed at improving medical resident income and reducing financial burdens.
Current Trends and Challenges

Several trends and challenges are influencing medical resident income, including the rising cost of living, increasing educational debt, and evolving healthcare landscape. The cost of living, particularly in urban areas where many residency programs are located, has risen significantly in recent years, eroding the purchasing power of resident salaries. Additionally, the average educational debt load for medical school graduates has increased substantially, with many residents carrying debt burdens exceeding $200,000.
The healthcare landscape is also undergoing significant changes, with shifting payment models, increasing regulatory requirements, and a growing emphasis on value-based care. These changes are creating new challenges and opportunities for medical residents, who must adapt to evolving clinical and administrative demands while navigating the complexities of the healthcare system.
Impact of Educational Debt
The impact of educational debt on medical residents cannot be overstated. High levels of debt can limit career choices, influence specialty selection, and affect overall well-being. According to a survey by the AAMC, 75% of medical residents reported feeling stressed or anxious about their debt, while 60% indicated that debt had influenced their choice of specialty.
| Residency Program | Median Annual Salary | Average Educational Debt |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Medicine | $55,000 | $180,000 |
| Family Medicine | $53,000 | $170,000 |
| Orthopedic Surgery | $65,000 | $220,000 |
| Neurology | $62,000 | $200,000 |

Initiatives and Proposals

There are various initiatives and proposals aimed at improving medical resident income and reducing financial burdens. These include advocacy efforts by professional organizations, legislative proposals, and institutional initiatives. For example, the AAMC has called for increased funding for residency programs, while some lawmakers have proposed legislation to increase resident salaries and provide loan forgiveness options.
Institutional initiatives, such as financial counseling and wellness programs, can also play a critical role in supporting the financial and emotional well-being of medical residents. By providing resources and support, hospitals and healthcare organizations can help residents navigate the challenges of training and set them up for success in their future careers.
What is the current median annual salary for medical residents in the United States?
+The current median annual salary for medical residents in the United States is approximately $58,200.
How does educational debt affect medical residents?
+Educational debt can limit career choices, influence specialty selection, and affect overall well-being. High levels of debt can also create significant financial stress and anxiety.
What initiatives and proposals are aimed at improving medical resident income and reducing financial burdens?
+Initiatives and proposals include advocacy efforts by professional organizations, legislative proposals, and institutional initiatives such as financial counseling and wellness programs.
In conclusion, the issue of medical resident income is complex and multifaceted, influenced by various factors such as location, type of residency program, and level of training. While there are challenges and trends affecting resident income, there are also initiatives and proposals aimed at improving compensation and reducing financial burdens. By addressing the issue of educational debt and providing support and resources, we can promote a more sustainable and equitable approach to medical education and ensure the long-term viability of the healthcare workforce.