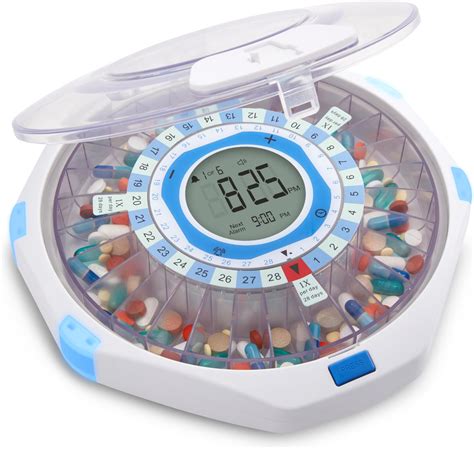
The development and integration of medication dispensers have revolutionized the way patients manage their medication regimens. These devices, which can range from simple pill boxes to complex automated systems, have become increasingly sophisticated, incorporating features such as electronic reminders, automated dispensing, and real-time monitoring. For individuals with chronic conditions, the elderly, and those with complex medication schedules, medication dispensers offer a solution to improve adherence, reduce errors, and enhance overall health outcomes. The evolution of medication dispensers is closely tied to advancements in technology, healthcare policies, and the growing need for patient-centric care models.
Historically, medication management has been a challenging aspect of healthcare, with non-adherence to medication regimens estimated to cost the U.S. healthcare system billions of dollars annually. The introduction of medication dispensers has addressed this issue by providing patients with an organized and systematic way to manage their medications. Early versions of medication dispensers were primarily mechanical, relying on manual setting and dispensing of medications. However, with the advent of digital technology, these devices have transformed into sophisticated tools that not only dispense medication but also monitor and manage the patient's regimen, sending alerts and notifications to both the patient and healthcare providers.
Key Points
- Medication dispensers improve medication adherence and reduce errors.
- They incorporate features such as electronic reminders and real-time monitoring.
- Automated dispensing systems can be integrated with electronic health records (EHRs) for seamless communication.
- These devices support patient-centric care models, enhancing overall health outcomes.
- Technological advancements continue to play a crucial role in the evolution of medication dispensers.
Technical Specifications and Operational Modes
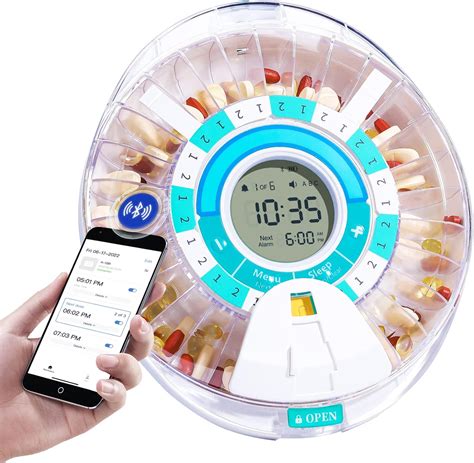

Modern medication dispensers are designed with a range of technical specifications and operational modes to cater to different patient needs. Some devices are equipped with barcode scanning capabilities, allowing patients or caregivers to easily identify and dispense the correct medication. Others may utilize RFID technology to track medications and monitor patient adherence. The operational modes of these devices can vary significantly, from simple timer-based dispensing to complex algorithms that adjust dispensing times based on the patient’s medication history and current health status.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in medication dispensers represents a significant leap forward in personalizing medication management. These advanced systems can analyze patient data, including medication adherence patterns, side effects, and health outcomes, to optimize medication regimens. Furthermore, AI-powered dispensers can predict potential medication interactions and alert healthcare providers to make necessary adjustments, thereby enhancing patient safety.
Benefits and Challenges
The benefits of medication dispensers are multifaceted, including improved medication adherence, reduced medication errors, and enhanced patient safety. By streamlining medication management, these devices also contribute to better health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs. However, the adoption of medication dispensers is not without challenges. High upfront costs, technical difficulties, and the need for continuous maintenance and updates can be barriers to their widespread adoption. Additionally, concerns about data privacy and security, particularly with devices that transmit patient data electronically, must be addressed through robust security measures and compliance with healthcare regulations.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Automated Dispensing | Dispenses medication at pre-set times, reducing the likelihood of missed doses. |
| Electronic Reminders | Sends alerts and notifications to patients and caregivers about upcoming doses. |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Allows healthcare providers to track patient adherence and adjust treatment plans as needed. |
| Integration with EHRs | Facilitates seamless communication between healthcare providers and improves coordination of care. |
Regulatory Framework and Future Directions
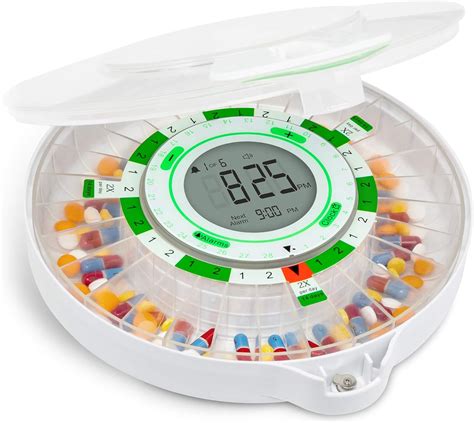
The development and deployment of medication dispensers are subject to a regulatory framework that ensures safety, efficacy, and data security. Regulatory bodies, such as the FDA in the United States, oversee the approval and monitoring of these devices. As medication dispensers become increasingly sophisticated, there will be a growing need for regulatory guidance on issues like data privacy, cybersecurity, and the clinical validation of AI-driven dispensing systems.
Looking ahead, the future of medication dispensers is promising, with potential applications in telehealth, personalized medicine, and population health management. The integration of medication dispensers with wearables, mobile health apps, and other digital health tools will further enhance their utility, offering a holistic approach to medication management and overall patient care. As healthcare continues to evolve towards more patient-centric and technology-driven models, medication dispensers will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in improving adherence, reducing healthcare costs, and enhancing patient outcomes.
What are the primary benefits of using a medication dispenser?
+The primary benefits include improved medication adherence, reduced medication errors, and enhanced patient safety. Medication dispensers also contribute to better health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
How do automated medication dispensers work?
+Automated medication dispensers work by dispensing medication at pre-set times, using mechanisms such as motors or pneumatic systems to release the medication from the device. They are often controlled by electronic timers or computer programs that can be programmed by healthcare providers or patients.
What are some of the challenges associated with the use of medication dispensers?
+Challenges include high upfront costs, technical difficulties, the need for continuous maintenance and updates, and concerns about data privacy and security. Additionally, there may be barriers to adoption among certain patient populations due to lack of familiarity with technology or limited access to these devices.