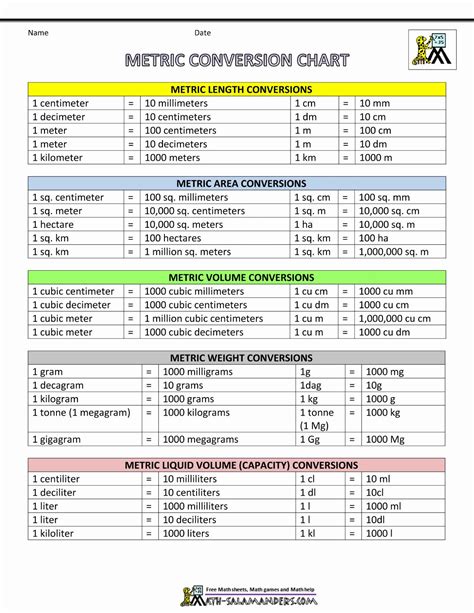
The metric system, also known as the International System of Units (SI), is the global standard for measurement. It's used in most countries and is an essential tool for scientists, engineers, and everyday people. Mastering the metric system can seem daunting, but with the right approach, it can become second nature. In this article, we'll explore five key tips to help you understand and work with the metric system like a pro.
Key Points
- Understanding the basic units of the metric system, including meters, liters, and grams
- Learning the prefixes that denote different scales, such as kilo-, centi-, and milli-
- Converting between units using multiplication and division
- Applying the metric system to real-world problems, such as calculating volume and density
- Practicing with sample problems to build confidence and fluency
Tip 1: Learn the Basic Units
The metric system is based on seven fundamental units, including the meter (length), liter (volume), and gram (mass). Understanding these basic units is crucial for working with the metric system. For example, the meter is defined as the distance traveled by light in a vacuum in 1⁄299,792,458 of a second. The liter is equal to 1,000 milliliters or 1 cubic decimeter. The gram is defined as the mass of a cubic centimeter of water at 4°C.
Understanding the Meter
The meter is a fundamental unit of length in the metric system. It’s used to measure distances, heights, and widths. To get a sense of the meter, consider that it’s approximately equal to 3.28 feet or 1.09 yards. The meter is also divided into smaller units, such as the centimeter (1⁄100 of a meter) and the millimeter (1⁄1,000 of a meter).
| Unit | Definition |
|---|---|
| Meter | Distance traveled by light in a vacuum in 1/299,792,458 of a second |
| Liter | 1,000 milliliters or 1 cubic decimeter |
| Gram | Mass of a cubic centimeter of water at 4°C |

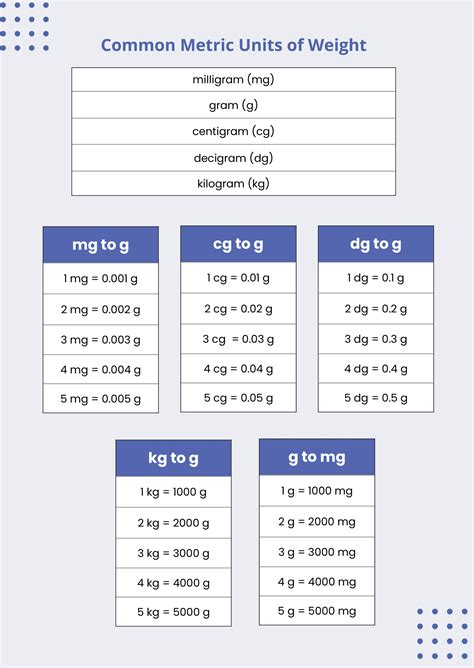
Tip 2: Master the Prefixes
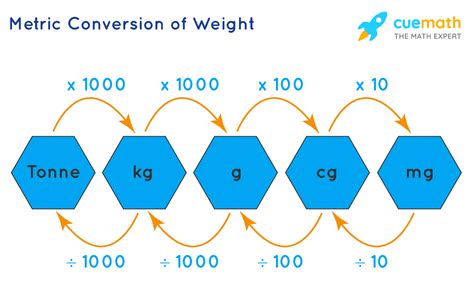
The metric system uses prefixes to denote different scales. These prefixes include kilo- (1,000), centi- (1⁄100), and milli- (1⁄1,000). Understanding these prefixes is essential for converting between units and working with the metric system. For example, a kilometer is equal to 1,000 meters, while a centimeter is equal to 1⁄100 of a meter.
Common Prefixes
Here are some common prefixes used in the metric system:
- Kilo- (1,000)
- Centi- (1/100)
- Milli- (1/1,000)
- Mega- (1,000,000)
- Giga- (1,000,000,000)
Tip 3: Convert Between Units
Converting between units is a critical skill for working with the metric system. To convert between units, you need to multiply or divide by a conversion factor. For example, to convert from meters to kilometers, you would divide by 1,000, since there are 1,000 meters in a kilometer.
Conversion Examples
Here are some examples of converting between units:
- Meters to kilometers: 1,000 meters ÷ 1,000 = 1 kilometer
- Grams to kilograms: 1,000 grams ÷ 1,000 = 1 kilogram
- Liters to milliliters: 1 liter × 1,000 = 1,000 milliliters
Tip 4: Apply the Metric System to Real-World Problems
The metric system is used in a wide range of real-world applications, from science and engineering to cooking and construction. To apply the metric system to real-world problems, you need to understand the units and conversion factors involved. For example, if you’re building a deck, you might need to calculate the volume of lumber required, using units such as cubic meters or board feet.
Real-World Example
Suppose you’re a chef, and you need to convert a recipe from US customary units to metric units. The recipe calls for 2 cups of flour, which is equivalent to approximately 250 grams. To convert the recipe, you would need to multiply the volume of flour in cups by the conversion factor, which is approximately 120 grams per cup.
Tip 5: Practice with Sample Problems
Practicing with sample problems is an excellent way to build your skills and confidence with the metric system. Try working through problems that involve converting between units, calculating volumes and densities, and applying the metric system to real-world scenarios. The more you practice, the more comfortable you’ll become with the metric system, and the easier it will be to work with it in your daily life.
What is the difference between the metric system and the US customary system?
+The metric system is based on the International System of Units (SI), while the US customary system is based on traditional units such as inches, feet, and pounds. The metric system is used in most countries and is the global standard for measurement.
How do I convert between units in the metric system?
+To convert between units, you need to multiply or divide by a conversion factor. For example, to convert from meters to kilometers, you would divide by 1,000, since there are 1,000 meters in a kilometer.
What are some common prefixes used in the metric system?
+Some common prefixes used in the metric system include kilo- (1,000), centi- (1⁄100), and milli- (1⁄1,000). These prefixes are used to denote different scales and are essential for converting between units.