The debate between micro and macro evolution has been a longstanding topic of discussion in the scientific community, with some arguing that these two concepts are distinct and separate, while others view them as part of a continuum. To understand the differences and similarities between micro and macro evolution, it's essential to delve into the definitions, mechanisms, and evidence supporting each concept. In this article, we'll explore the intricacies of micro and macro evolution, providing a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge in the field.
Introduction to Micro Evolution
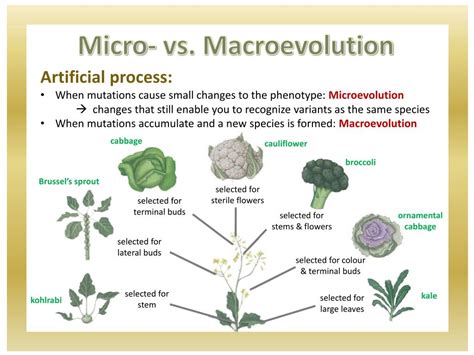
Micro evolution refers to the small-scale changes that occur within a population over a relatively short period. These changes can result from various factors, including genetic drift, mutation, and gene flow, which can lead to the adaptation of a population to its environment. Micro evolution is often observed in laboratory experiments, where scientists can control and manipulate the conditions to study the evolutionary process. For example, the development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria is a classic example of micro evolution, where the population adapts to the selective pressure of antibiotics through genetic mutations.
Mechanisms of Micro Evolution
Several mechanisms contribute to micro evolution, including genetic drift, which is the random change in the frequency of a gene or trait in a population over time. Mutation is another key factor, where errors in DNA replication or repair can lead to changes in the genetic code. Gene flow also plays a crucial role, as the movement of individuals with different genotypes into a population can introduce new genetic variants. These mechanisms can lead to the adaptation of a population to its environment, resulting in the evolution of new traits or the loss of existing ones.
| Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Genetic Drift | Random change in gene frequency |
| Mutation | Errors in DNA replication or repair |
| Gene Flow | Movement of individuals with different genotypes |

Introduction to Macro Evolution

Macro evolution, on the other hand, refers to the large-scale changes that occur over long periods, resulting in the formation of new species, genera, or even higher taxonomic ranks. Macro evolution is often observed in the fossil record, where the transition from one species to another can be traced over millions of years. The evolution of whales from land-dwelling mammals is a classic example of macro evolution, where a series of adaptations led to the emergence of a new species.
Mechanisms of Macro Evolution
Macro evolution is thought to result from the cumulative effect of micro evolutionary changes over time, combined with other factors such as speciation, where a new species emerges from an existing one. Phylogenetic analysis also plays a crucial role, as it allows scientists to reconstruct the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. Geological events, such as changes in sea levels or the formation of mountain ranges, can also drive macro evolution by creating new habitats and selective pressures.
Key Points
- Micro evolution refers to small-scale changes within a population
- Macro evolution refers to large-scale changes resulting in new species or higher taxonomic ranks
- Mechanisms of micro evolution include genetic drift, mutation, and gene flow
- Mechanisms of macro evolution include speciation, phylogenetic analysis, and geological events
- The study of micro and macro evolution has significant implications for our understanding of the evolutionary process
The distinction between micro and macro evolution is not always clear-cut, and some scientists argue that these two concepts are part of a continuum. However, understanding the differences and similarities between micro and macro evolution can provide valuable insights into the evolutionary process and the diversity of life on Earth.
Comparing Micro and Macro Evolution
While micro and macro evolution differ in terms of their scope and timescale, they share some commonalities. Both micro and macro evolution involve the adaptation of populations to their environment, resulting in the emergence of new traits or the loss of existing ones. However, the mechanisms driving micro and macro evolution differ, with micro evolution being driven by genetic drift, mutation, and gene flow, and macro evolution being driven by speciation, phylogenetic analysis, and geological events.
Similarities and Differences
One of the key similarities between micro and macro evolution is the role of selection, where the environment acts as a filter, favoring individuals with certain traits over others. However, the timescale and scope of micro and macro evolution differ significantly, with micro evolution occurring over relatively short periods and macro evolution occurring over millions of years. The complexity of the traits evolving also differs, with micro evolution often resulting in the evolution of simple traits, such as antibiotic resistance, and macro evolution resulting in the evolution of complex traits, such as the emergence of new body plans.
| Characteristic | Micro Evolution | Macro Evolution |
|---|---|---|
| Timescale | Relatively short | Millions of years |
| Scope | Small-scale changes | Large-scale changes |
| Mechanisms | Genetic drift, mutation, gene flow | Speciation, phylogenetic analysis, geological events |
Conclusion
In conclusion, micro and macro evolution are two distinct but interconnected concepts that have been the subject of much debate and discussion in the scientific community. While micro evolution refers to the small-scale changes that occur within a population over a relatively short period, macro evolution refers to the large-scale changes that occur over long periods, resulting in the formation of new species, genera, or even higher taxonomic ranks. Understanding the differences and similarities between micro and macro evolution can provide valuable insights into the evolutionary process and the diversity of life on Earth.
What is the main difference between micro and macro evolution?
+The main difference between micro and macro evolution is the scope and timescale of the changes. Micro evolution refers to small-scale changes within a population over a relatively short period, while macro evolution refers to large-scale changes resulting in new species or higher taxonomic ranks over millions of years.
What are the mechanisms driving micro evolution?
+The mechanisms driving micro evolution include genetic drift, mutation, and gene flow. These mechanisms can lead to the adaptation of a population to its environment, resulting in the evolution of new traits or the loss of existing ones.
What are the implications of micro and macro evolution for our understanding of the evolutionary process?
+The study of micro and macro evolution has significant implications for our understanding of the evolutionary process, and can inform fields such as conservation biology, ecology, and medicine. Understanding the mechanisms driving micro and macro evolution can provide valuable insights into the diversity of life on Earth and the emergence of new traits and species.
Meta description: “Explore the differences and similarities between micro and macro evolution, and discover the mechanisms driving these two concepts. Learn about the implications of micro and macro evolution for our understanding of the evolutionary process.” (149 characters)



