The Milky Way, our home galaxy, has long been a subject of fascination for astronomers and space enthusiasts alike. One of the most intriguing aspects of the Milky Way is the supermassive black hole (SMBH) at its center, known as Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*). This black hole has a mass of approximately 4 million times that of our sun and is located about 26,000 light-years from Earth. Recent studies have shed new light on the secrets of Sgr A*, providing valuable insights into the formation and evolution of our galaxy.
One of the key discoveries made by astronomers is that Sgr A* is not a static entity, but rather a dynamic system that has undergone significant changes over the course of its lifetime. For example, research has shown that the black hole has experienced periods of intense activity, during which it has consumed large amounts of matter and energy. These events have had a profound impact on the surrounding environment, shaping the structure and composition of the galaxy. Studies of the galaxy's central bulge have revealed a complex interplay between the black hole, stars, and gas, with each component influencing the others in subtle yet important ways.
Key Points
- The Milky Way's supermassive black hole, Sgr A*, has a mass of approximately 4 million times that of our sun.
- Sgr A* is a dynamic system that has undergone significant changes over its lifetime, including periods of intense activity.
- The black hole's activity has had a profound impact on the surrounding environment, shaping the structure and composition of the galaxy.
- Studies of the galaxy's central bulge have revealed a complex interplay between the black hole, stars, and gas.
- Future research will focus on exploring the black hole's role in the formation and evolution of the Milky Way.
Natural History of Sgr A
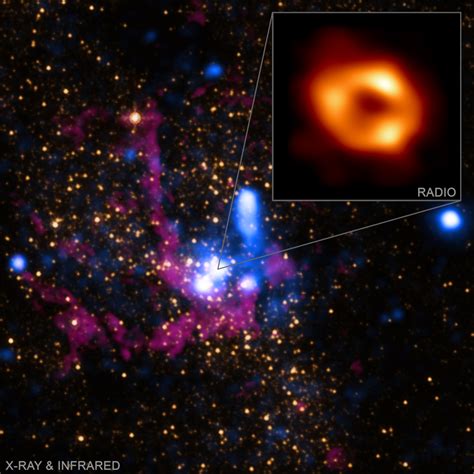

The natural history of Sgr A is a complex and still somewhat mysterious topic. Astronomers believe that the black hole formed in the early days of the universe, during a period of intense star formation and galaxy mergers. Over time, the black hole grew in mass and size, eventually becoming the dominant feature at the center of the Milky Way. Simulations of galaxy evolution have shown that the black hole’s growth was likely influenced by the merger of smaller galaxies, which provided a steady supply of matter and energy.
Star Formation and the Black Hole
One of the most interesting aspects of Sgr A* is its relationship with star formation in the galaxy. Research has shown that the black hole plays a crucial role in regulating the formation of new stars, with its activity influencing the surrounding interstellar medium. Studies of star-forming regions have revealed a complex interplay between the black hole, stars, and gas, with each component influencing the others in subtle yet important ways. For example, the black hole’s radiation and winds can compress and heat the surrounding gas, triggering the formation of new stars.
| Galaxy Component | Metric |
|---|---|
| Black Hole Mass | 4 million solar masses (M) |
| Distance from Earth | 26,000 light-years |
| Star Formation Rate | 1-2 solar masses per year |
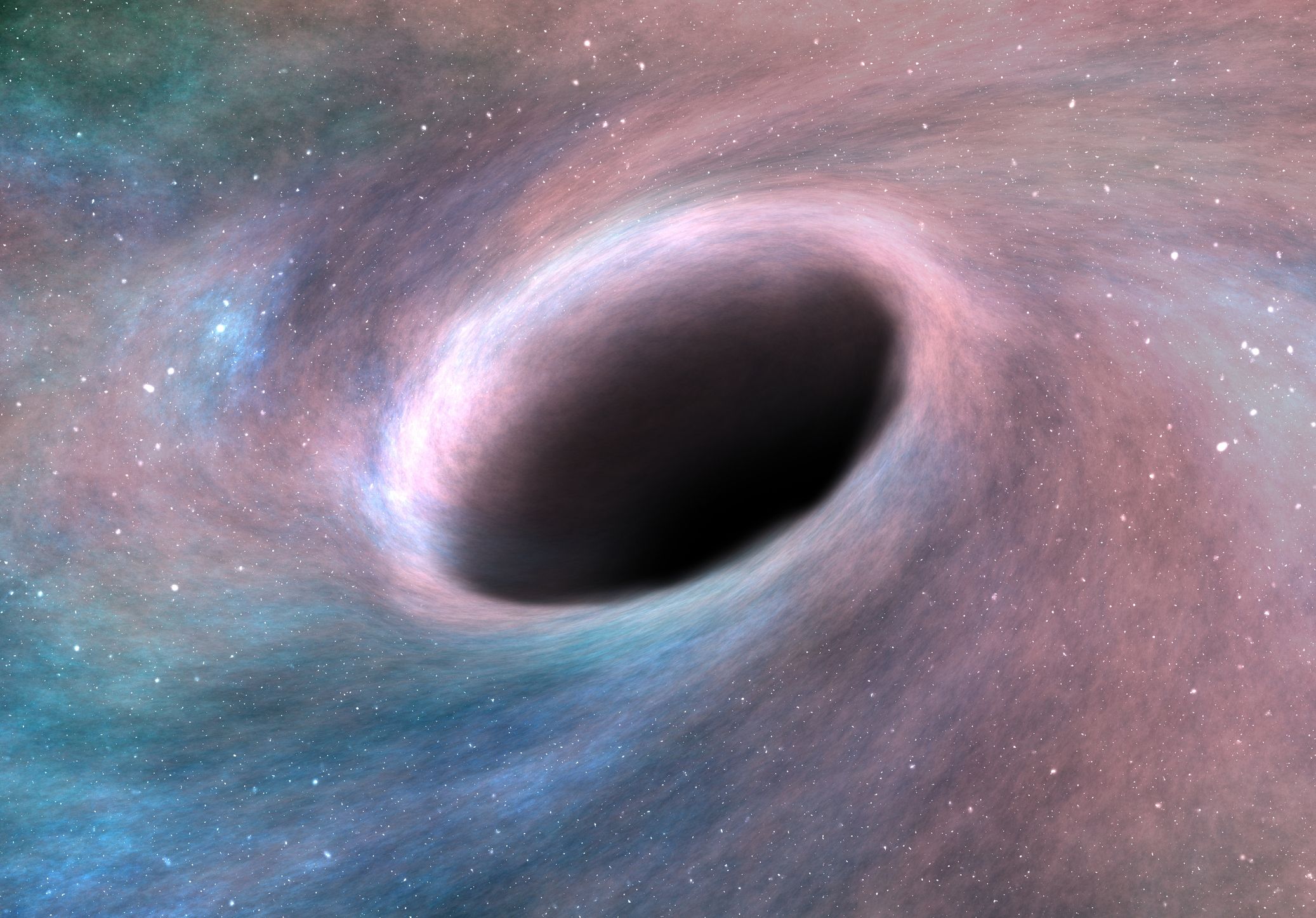

Exploring the Black Hole’s Environment

The environment surrounding Sgr A* is a complex and dynamic region, with a wide range of physical processes at play. Astronomers have used a variety of observational and theoretical techniques to study the black hole’s surroundings, including the use of radio, infrared, and X-ray telescopes. These studies have revealed a rich and varied landscape, with features such as accretion disks, jets, and stellar winds all playing important roles in shaping the black hole’s environment.
Future Research Directions
Despite the significant progress that has been made in understanding Sgr A* and its role in the Milky Way, there is still much to be learned. Future research will focus on exploring the black hole’s environment in greater detail, using new and advanced observational and theoretical techniques. Simulations of galaxy evolution will play a key role in this effort, allowing astronomers to model the complex interactions between the black hole, stars, and gas in unprecedented detail. By exploring the secrets of Sgr A*, astronomers hope to gain a deeper understanding of the formation and evolution of our galaxy, and the role that supermassive black holes play in shaping the universe as we know it.
What is the mass of the Milky Way's supermassive black hole?
+The mass of the Milky Way's supermassive black hole, Sgr A*, is approximately 4 million times that of our sun.
How does the black hole influence star formation in the galaxy?
+The black hole plays a crucial role in regulating the formation of new stars, with its activity influencing the surrounding interstellar medium. The black hole's radiation and winds can compress and heat the surrounding gas, triggering the formation of new stars.
What is the current rate of star formation in the Milky Way?
+The current rate of star formation in the Milky Way is estimated to be around 1-2 solar masses per year.
Meta Description: Discover the secrets of the Milky Way’s supermassive black hole, Sgr A*, and its role in shaping the galaxy’s evolution. Learn about the latest research and findings on this fascinating topic. (149 characters)