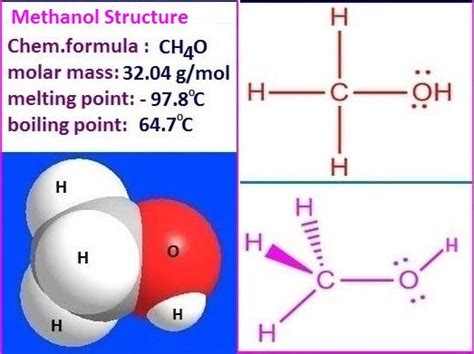
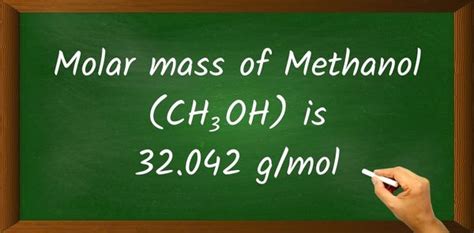Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, is a chemical compound with the molecular formula CH₃OH. Understanding the molar mass of methanol is crucial in various chemical calculations and applications. The molar mass of a substance is the mass of one mole of that substance, expressed in units of grams per mole (g/mol). For methanol, the calculation of its molar mass involves summing the atomic masses of its constituent atoms: carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O).
Calculation of Methanol Molar Mass
To calculate the molar mass of methanol, we use the atomic masses of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The atomic mass of carbon is approximately 12.01 g/mol, hydrogen is about 1.008 g/mol, and oxygen is roughly 16.00 g/mol. Methanol has one carbon atom, four hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom. Thus, the molar mass of methanol can be calculated as follows: (1 * 12.01) for carbon + (4 * 1.008) for hydrogen + (1 * 16.00) for oxygen.
Step-by-Step Calculation
Performing the calculation: - For carbon: 1 * 12.01 = 12.01 g/mol - For hydrogen: 4 * 1.008 = 4.032 g/mol - For oxygen: 1 * 16.00 = 16.00 g/mol Adding these values together gives us the molar mass of methanol: 12.01 + 4.032 + 16.00 = 32.042 g/mol.
| Element | Atomic Mass (g/mol) | Number of Atoms | Total Mass Contribution (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 12.01 | 1 | 12.01 |
| Hydrogen (H) | 1.008 | 4 | 4.032 |
| Oxygen (O) | 16.00 | 1 | 16.00 |
| Total | 32.042 |

Applications of Methanol Molar Mass
The molar mass of methanol is vital in various applications, including the production of formaldehyde, acetic acid, and methyl tertiary-butyl ether (MTBE), a gasoline additive. Understanding the molar mass is also essential in laboratory settings for preparing solutions of known concentration, a process critical in many chemical and biological experiments.
Practical Considerations
In practical terms, knowing the molar mass of methanol allows chemists to calculate the number of moles of methanol in a given mass, or conversely, to find the mass of methanol corresponding to a certain number of moles. This is done using the formula: moles = mass / molar mass. For instance, to find out how many moles are in 100 grams of methanol, one would divide 100 grams by the molar mass of methanol (32.042 g/mol).
Key Points
- The molar mass of methanol is calculated by summing the atomic masses of its constituent atoms: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
- The atomic masses used are approximately 12.01 g/mol for carbon, 1.008 g/mol for hydrogen, and 16.00 g/mol for oxygen.
- Methanol's molecular formula is CH₃OH, indicating one carbon, four hydrogens, and one oxygen atom.
- The calculated molar mass of methanol is 32.042 g/mol.
- Understanding the molar mass of methanol is crucial for various chemical calculations and applications, including the preparation of solutions and the stoichiometry of reactions.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
In conclusion, the molar mass of methanol, calculated to be 32.042 g/mol, is a fundamental constant in chemistry with wide-ranging applications. As research and technology advance, the importance of precise chemical calculations will only continue to grow, underscoring the need for a deep understanding of basic chemical principles, including the determination and application of molar masses.
What is the primary use of knowing the molar mass of methanol?
+The primary use of knowing the molar mass of methanol is for calculations involving the preparation of solutions, stoichiometry of reactions, and determining empirical and molecular formulas.
How is the molar mass of methanol calculated?
+The molar mass of methanol is calculated by summing the atomic masses of its constituent atoms: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, using their respective atomic masses and the number of each atom in the molecule.
What are some industrial applications of methanol?
+Methanol has several industrial applications, including the production of formaldehyde, acetic acid, and methyl tertiary-butyl ether (MTBE), a gasoline additive.