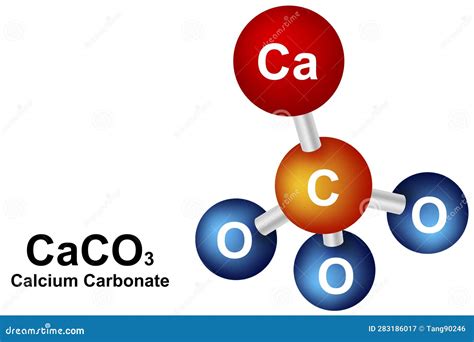
Calcium carbonate, a compound commonly found in rocks, shells, and bones, has been a subject of interest in various fields of science, including chemistry, geology, and biology. Its chemical formula, CaCO3, represents the combination of one calcium (Ca) atom, one carbon (C) atom, and three oxygen (O) atoms. Understanding the molar mass of calcium carbonate is essential for calculating the quantities needed in experiments, manufacturing processes, and environmental studies.
Key Points
- The chemical formula of calcium carbonate is CaCO3.
- Calcium carbonate is composed of one calcium atom, one carbon atom, and three oxygen atoms.
- The atomic masses of calcium, carbon, and oxygen are approximately 40.08 g/mol, 12.01 g/mol, and 16.00 g/mol, respectively.
- The molar mass of calcium carbonate can be calculated by summing the atomic masses of its constituent atoms.
- Calcium carbonate has a wide range of applications, including in construction, manufacturing, and healthcare.
Calculation of Molar Mass
To calculate the molar mass of calcium carbonate, we need to sum the atomic masses of its constituent atoms. The atomic masses of calcium (Ca), carbon ©, and oxygen (O) are approximately 40.08 g/mol, 12.01 g/mol, and 16.00 g/mol, respectively. Given that calcium carbonate has one calcium atom, one carbon atom, and three oxygen atoms, the calculation is as follows:
Molar mass of CaCO3 = (1 * atomic mass of Ca) + (1 * atomic mass of C) + (3 * atomic mass of O)
Molar mass of CaCO3 = (1 * 40.08 g/mol) + (1 * 12.01 g/mol) + (3 * 16.00 g/mol)
Molar mass of CaCO3 = 40.08 g/mol + 12.01 g/mol + 48.00 g/mol
Molar mass of CaCO3 = 100.09 g/mol
Significance of Calcium Carbonate’s Molar Mass
The molar mass of calcium carbonate, approximately 100.09 g/mol, is a critical piece of information for various applications. In chemistry, knowing the molar mass allows for the calculation of the number of moles of a substance, which is essential for stoichiometric calculations in chemical reactions. In construction and manufacturing, the molar mass of calcium carbonate is important for determining the quantities needed for production processes, such as in the manufacture of cement, glass, and paper.
| Element | Atomic Mass (g/mol) | Number of Atoms in CaCO3 | Total Mass Contribution (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium (Ca) | 40.08 | 1 | 40.08 |
| Carbon (C) | 12.01 | 1 | 12.01 |
| Oxygen (O) | 16.00 | 3 | 48.00 |
| Total | 100.09 |
Applications of Calcium Carbonate
Calcium carbonate has a wide range of applications due to its abundance, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. In the construction industry, it is used as a building material in the form of limestone, marble, and chalk. It is also a key component in the production of cement. In manufacturing, calcium carbonate is used in the production of glass, paper, and plastics. Additionally, it is used in healthcare as an antacid and as a source of calcium for dietary supplements.
Environmental Considerations
Calcium carbonate plays a significant role in the Earth’s carbon cycle and is a key component of many marine organisms’ shells and skeletons. The molar mass of calcium carbonate is essential for understanding the geochemical processes that affect the Earth’s climate and ecosystems. For instance, the dissolution and precipitation of calcium carbonate in the oceans influence the pH of seawater and the availability of carbon dioxide, a critical greenhouse gas.
What is the chemical formula of calcium carbonate?
+The chemical formula of calcium carbonate is CaCO3.
How is the molar mass of calcium carbonate calculated?
+The molar mass of calcium carbonate is calculated by summing the atomic masses of its constituent atoms: calcium, carbon, and oxygen.
What are some of the applications of calcium carbonate?
+Calcium carbonate has a wide range of applications, including in construction, manufacturing, and healthcare. It is used as a building material, in the production of cement, glass, paper, and plastics, and as an antacid and dietary supplement.
In conclusion, the molar mass of calcium carbonate, approximately 100.09 g/mol, is a fundamental property that underlies its chemical and physical behaviors. Its calculation and significance are essential for understanding the compound’s role in various scientific, industrial, and environmental contexts. As a naturally occurring substance with diverse applications, calcium carbonate continues to be a subject of interest and importance across multiple disciplines.