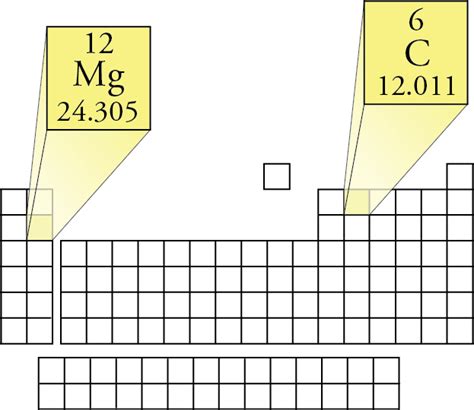
The magnesium molar mass value is a fundamental concept in chemistry, particularly in the fields of inorganic chemistry and materials science. Magnesium, with the atomic symbol Mg, is an alkaline earth metal that plays a crucial role in various biological and industrial processes. To understand the molar mass of magnesium, it's essential to delve into the atomic structure and the definition of molar mass itself.
Molar mass is defined as the mass of one mole of a substance, which is equal to 6.022 x 10^23 particles (atoms or molecules) of that substance. The molar mass of an element is calculated by summing the masses of its naturally occurring isotopes, each multiplied by its abundance. For magnesium, the primary isotopes and their masses are magnesium-24 (23.985042 u), magnesium-25 (24.985837 u), and magnesium-26 (25.982593 u), with abundances of approximately 78.99%, 10.00%, and 11.01%, respectively.
Calculation of Magnesium Molar Mass
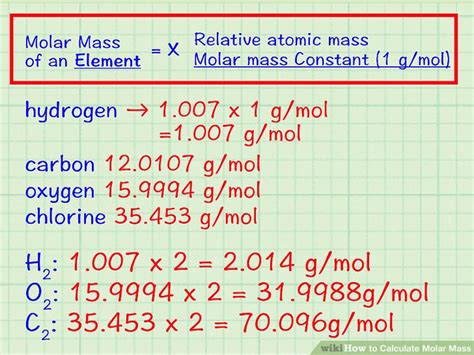
The calculation of the magnesium molar mass involves taking the weighted average of the masses of its isotopes based on their natural abundances. The formula for this calculation is: (Mass of Mg-24 * Abundance of Mg-24) + (Mass of Mg-25 * Abundance of Mg-25) + (Mass of Mg-26 * Abundance of Mg-26). Substituting the known values: (23.985042 u * 0.7899) + (24.985837 u * 0.1000) + (25.982593 u * 0.1101).
Performing the calculation: (23.985042 u * 0.7899) = 18.950411 + (24.985837 u * 0.1000) = 2.4985837 + (25.982593 u * 0.1101) = 2.848147, which sums to approximately 24.2971 u. However, for the purpose of calculating molar mass in grams per mole (g/mol), the unified atomic mass unit (u) is used, where 1 u = 1 g/mol. Therefore, the molar mass of magnesium is approximately 24.305 g/mol, considering the standard atomic weight and rounding for practical purposes.
Significance of Magnesium Molar Mass
The molar mass of magnesium is significant in various chemical and biological applications. In chemistry, knowing the molar mass of magnesium is crucial for calculating the amounts of substances needed for reactions, determining the composition of compounds, and understanding the properties of materials. For instance, in the production of magnesium alloys, which are used in aerospace and automotive industries due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, accurate calculations of reactants and products are necessary, relying on the molar mass of magnesium.
In biological contexts, magnesium plays a vital role as a cofactor for many enzymes and is involved in muscle and nerve function, among other physiological processes. Understanding its molar mass can help in the formulation of dietary supplements and in the study of magnesium deficiency or toxicity in clinical settings.
| Isotope | Mass (u) | Abundance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Mg-24 | 23.985042 | 78.99 |
| Mg-25 | 24.985837 | 10.00 |
| Mg-26 | 25.982593 | 11.01 |

Key Points
- The molar mass of magnesium is approximately 24.305 g/mol, which is calculated based on the masses and abundances of its naturally occurring isotopes.
- Understanding the molar mass of magnesium is crucial for various chemical and biological applications, including the production of magnesium alloys and the study of magnesium's role in biological processes.
- The calculation of molar mass involves taking the weighted average of the masses of isotopes based on their natural abundances.
- Magnesium's primary isotopes are Mg-24, Mg-25, and Mg-26, with masses of approximately 23.985042 u, 24.985837 u, and 25.982593 u, respectively.
- The molar mass of an element is essential for determining the amounts of substances needed for reactions and for understanding the properties of materials.
The molar mass of magnesium, like that of other elements, is a foundational piece of information that underpins a wide range of scientific inquiries and applications. Its calculation and significance underscore the importance of detailed knowledge of atomic structure and isotopic composition in understanding the properties and behaviors of elements.
What is the molar mass of magnesium and how is it calculated?
+The molar mass of magnesium is approximately 24.305 g/mol, calculated by taking the weighted average of the masses of its naturally occurring isotopes based on their abundances.
Why is the molar mass of magnesium important in chemical and biological applications?
+The molar mass of magnesium is crucial for calculating the amounts of substances needed for reactions, determining the composition of compounds, and understanding the properties of materials, as well as for its role in biological processes as a cofactor for enzymes and in physiological functions.
How does the isotopic composition of magnesium affect its molar mass?
+The isotopic composition of magnesium, including the masses and abundances of Mg-24, Mg-25, and Mg-26, directly affects its molar mass, as the molar mass is calculated based on the weighted average of these isotopes.