Arizona's monsoon season, which typically runs from June 15 to September 30, is a period of significant weather activity in the state. During this time, the region experiences a dramatic increase in humidity and precipitation, resulting in powerful thunderstorms, heavy rainfall, and flash flooding. The monsoon season is characterized by a shift in wind patterns, which brings moisture from the Gulf of California and the eastern Pacific Ocean into the region. This influx of moisture leads to the formation of thunderstorms, which can be intense and produce large amounts of rainfall in a short period.
The Arizona monsoon season is a complex phenomenon, influenced by a variety of atmospheric and geographical factors. The state's unique geography, with its mountain ranges and desert valleys, plays a significant role in shaping the monsoon season. The Mogollon Rim, a major geographical feature in eastern Arizona, acts as a barrier, forcing moist air to rise and cool, resulting in the formation of thunderstorms. The resulting precipitation can be intense, with some areas receiving over 50% of their annual rainfall during the monsoon season.
Key Points
- The Arizona monsoon season typically runs from June 15 to September 30.
- The monsoon season is characterized by a shift in wind patterns, which brings moisture from the Gulf of California and the eastern Pacific Ocean into the region.
- The state's unique geography, including the Mogollon Rim, plays a significant role in shaping the monsoon season.
- The monsoon season can produce intense thunderstorms, heavy rainfall, and flash flooding.
- Some areas of Arizona receive over 50% of their annual rainfall during the monsoon season.
Causes and Effects of the Arizona Monsoon Season
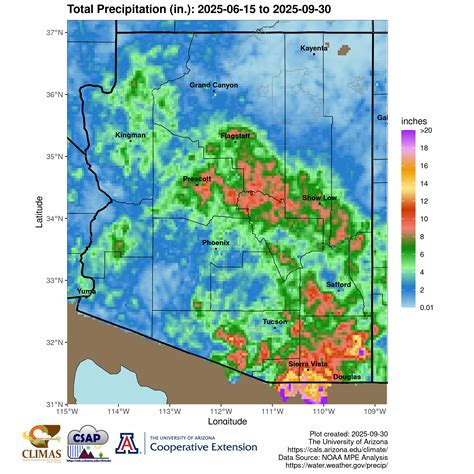
The Arizona monsoon season is caused by a combination of atmospheric and geographical factors. The North American monsoon, a large-scale weather pattern, plays a significant role in shaping the monsoon season. This weather pattern is characterized by a shift in wind patterns, which brings moisture from the Gulf of California and the eastern Pacific Ocean into the region. The resulting precipitation can have a significant impact on the state’s ecosystems, including the replenishment of water sources and the promotion of plant growth.
However, the monsoon season can also have negative effects, including flash flooding, which can be deadly and destructive. The heavy rainfall and flash flooding associated with the monsoon season can also lead to property damage and disruptions to transportation and other services. Additionally, the monsoon season can also lead to an increase in lightning strikes, which can be a significant threat to people and property.
Monsoon Season Safety Tips
During the monsoon season, it is essential to take necessary precautions to stay safe. This includes staying informed about weather conditions, avoiding travel during heavy rainfall, and being aware of the risks associated with flash flooding. It is also essential to have a plan in place in case of an emergency, including a evacuation route and a meeting point. Additionally, it is crucial to stay away from flooded areas, as the water can be contaminated with pollutants and debris.
| Monsoon Season Safety Tips | Description |
|---|---|
| Stay Informed | Stay up-to-date with the latest weather forecast and warnings. |
| Avoid Travel | Avoid traveling during heavy rainfall and flash flooding. |
| Have a Plan | Have a plan in place in case of an emergency, including an evacuation route and a meeting point. |
| Stay Away from Flooded Areas | Stay away from flooded areas, as the water can be contaminated with pollutants and debris. |

Monsoon Season Statistics

The Arizona monsoon season is a significant weather event, with a substantial impact on the state’s climate and ecosystems. According to data from the National Weather Service, the monsoon season typically brings over 50% of the state’s annual rainfall. In some areas, such as the mountains of eastern Arizona, the monsoon season can account for over 70% of the annual rainfall. The monsoon season also plays a crucial role in replenishing the state’s water sources, including reservoirs and groundwater aquifers.
The monsoon season can also have a significant impact on the state's economy, particularly in the agriculture and tourism sectors. The rainfall and flash flooding associated with the monsoon season can damage crops and disrupt transportation, leading to significant economic losses. However, the monsoon season also attracts tourists, who come to experience the state's unique weather patterns and scenic beauty.
Monsoon Season and Climate Change
Climate change is having a significant impact on the Arizona monsoon season, with changes in temperature and precipitation patterns affecting the state’s weather events. According to research, the monsoon season is expected to become more intense and unpredictable, with more frequent and severe flash flooding events. This is due to the warming of the atmosphere, which is leading to an increase in evaporation and precipitation. Additionally, the changing precipitation patterns are also affecting the state’s water sources, including reservoirs and groundwater aquifers.
What is the Arizona monsoon season?
+The Arizona monsoon season is a period of significant weather activity in the state, characterized by a shift in wind patterns, which brings moisture from the Gulf of California and the eastern Pacific Ocean into the region.
When does the Arizona monsoon season typically occur?
+The Arizona monsoon season typically runs from June 15 to September 30.
What are the causes and effects of the Arizona monsoon season?
+The Arizona monsoon season is caused by a combination of atmospheric and geographical factors, and can have a significant impact on the state's ecosystems, including the replenishment of water sources and the promotion of plant growth. However, it can also have negative effects, including flash flooding, which can be deadly and destructive.
Meta description: “Learn about the Arizona monsoon season, including its causes, effects, and safety tips. Understand the impact of climate change on the monsoon season and how to prepare for this significant weather event.”