The European continent is home to some of the most breathtaking and diverse mountain ranges in the world. From the snow-capped peaks of the Alps to the rugged landscapes of the Carpathians, each range has its unique charm and characteristics. In this article, we will delve into the five major European mountain ranges, exploring their geography, climate, and cultural significance.
Introduction to European Mountain Ranges
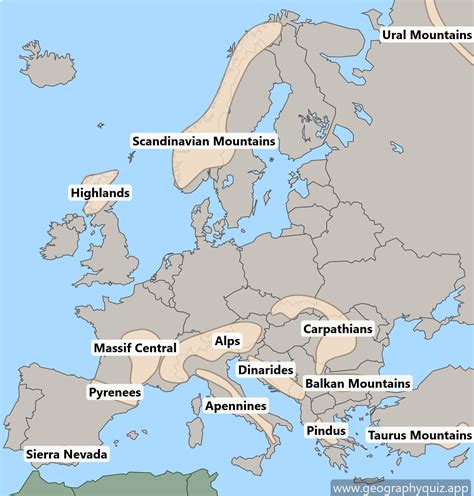
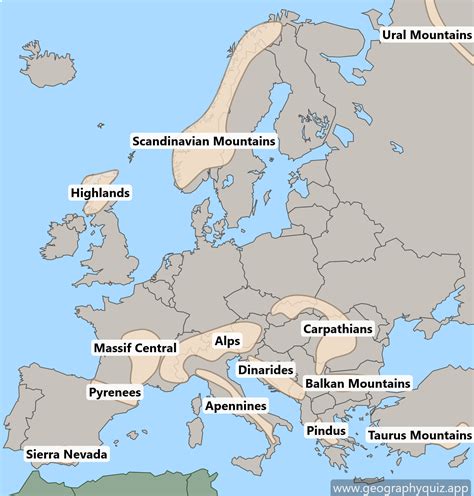
European mountain ranges stretch across the continent, forming the backbone of Europe’s landscape. These ranges have been shaped by millions of years of tectonic activity, weathering, and erosion, resulting in a diverse array of peaks, valleys, and plateaus. The five major European mountain ranges are the Alps, the Carpathians, the Apennines, the Pyrenees, and the Scandinavian Mountains. Each range has its distinct geology, climate, and ecosystem, supporting a wide range of flora and fauna.
Key Points
- The Alps are the highest and most extensive mountain range in Europe, stretching across eight countries.
- The Carpathians are the second-longest mountain range in Europe, covering an area of approximately 210,000 square kilometers.
- The Apennines are a mountain range that runs along the eastern coast of Italy, forming the backbone of the Italian Peninsula.
- The Pyrenees are a mountain range that separates France from Spain, stretching for approximately 435 kilometers.
- The Scandinavian Mountains are a mountain range that stretches across northern Scandinavia, covering an area of approximately 300,000 square kilometers.
The Alps: The Highest and Most Extensive Range
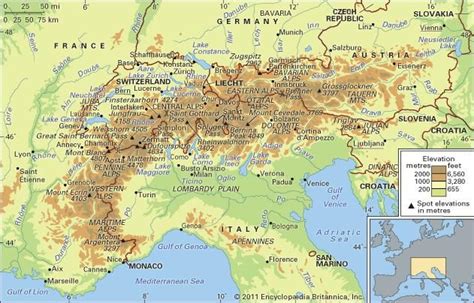
The Alps are the highest and most extensive mountain range in Europe, stretching across eight countries, including France, Switzerland, Italy, Germany, Austria, Slovenia, Monaco, and Liechtenstein. The range is approximately 1,200 kilometers long and 250-300 kilometers wide, covering an area of around 190,000 square kilometers. The Alps are home to some of the highest peaks in Europe, including Mont Blanc, the Matterhorn, and the Eiger. The range is also known for its picturesque valleys, alpine lakes, and diverse ecosystems, supporting a wide range of flora and fauna.
Geology and Climate of the Alps
The Alps are a relatively young mountain range, formed as a result of the collision between the African and Eurasian tectonic plates. The range is composed of a variety of rocks, including granite, gneiss, and limestone, which have been shaped by millions of years of weathering and erosion. The climate of the Alps varies greatly depending on the altitude and location, ranging from subtropical to polar. The higher peaks are covered in snow and ice year-round, while the lower valleys have a more temperate climate, with warm summers and cold winters.
| Mountain Range | Length (km) | Width (km) | Area (km²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alps | 1,200 | 250-300 | 190,000 |
| Carpathians | 1,500 | 100-200 | 210,000 |
| Apennines | 1,000 | 50-100 | 30,000 |
| Pyrenees | 435 | 20-50 | 10,000 |
| Scandinavian Mountains | 1,800 | 100-300 | 300,000 |
The Carpathians: A Range of Contrasts
The Carpathians are the second-longest mountain range in Europe, covering an area of approximately 210,000 square kilometers. The range stretches across seven countries, including Romania, Ukraine, Slovakia, Poland, Hungary, Serbia, and Austria. The Carpathians are a range of contrasts, with steep peaks and deep valleys, as well as rolling hills and plateaus. The range is home to a diverse range of ecosystems, including forests, grasslands, and wetlands, supporting a wide range of flora and fauna.
Culture and History of the Carpathians
The Carpathians have a rich cultural and historical heritage, with many traditional villages and towns scattered throughout the range. The range has been home to many different ethnic groups, including Romanians, Ukrainians, Slovaks, Poles, Hungarians, Serbs, and Austrians, each with their own unique customs and traditions. The Carpathians have also played a significant role in European history, with many important trade routes and battles taking place within the range.
The Apennines: A Mountain Range of Italy
The Apennines are a mountain range that runs along the eastern coast of Italy, forming the backbone of the Italian Peninsula. The range stretches for approximately 1,000 kilometers, covering an area of around 30,000 square kilometers. The Apennines are a relatively narrow range, with steep peaks and deep valleys, as well as rolling hills and plateaus. The range is home to a diverse range of ecosystems, including forests, grasslands, and wetlands, supporting a wide range of flora and fauna.
Geology and Climate of the Apennines
The Apennines are a relatively young mountain range, formed as a result of the collision between the African and Eurasian tectonic plates. The range is composed of a variety of rocks, including limestone, dolomite, and granite, which have been shaped by millions of years of weathering and erosion. The climate of the Apennines varies greatly depending on the altitude and location, ranging from subtropical to temperate. The higher peaks are covered in snow and ice year-round, while the lower valleys have a more temperate climate, with warm summers and cold winters.
The Pyrenees: A Range of Natural Beauty
The Pyrenees are a mountain range that separates France from Spain, stretching for approximately 435 kilometers. The range covers an area of around 10,000 square kilometers, with steep peaks and deep valleys, as well as rolling hills and plateaus. The Pyrenees are home to a diverse range of ecosystems, including forests, grasslands, and wetlands, supporting a wide range of flora and fauna. The range is also known for its natural beauty, with many picturesque villages and towns scattered throughout the range.
Culture and History of the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees have a rich cultural and historical heritage, with many traditional villages and towns scattered throughout the range. The range has been home to many different ethnic groups, including French, Spanish, and Catalan, each with their own unique customs and traditions. The Pyrenees have also played a significant role in European history, with many important trade routes and battles taking place within the range.
The Scandinavian Mountains: A Range of Northern Europe
The Scandinavian Mountains are a mountain range that stretches across northern Scandinavia, covering an area of approximately 300,000 square kilometers. The range stretches across three countries, including Norway, Sweden, and Finland. The Scandinavian Mountains are a relatively flat range, with rolling hills and plateaus, as well as steep peaks and deep valleys. The range is home to a diverse range of ecosystems, including forests, grasslands, and wetlands, supporting a wide range of flora and fauna.
Geology and Climate of the Scandinavian Mountains
The Scandinavian Mountains are a relatively old mountain range, formed as a result of the collision between the Baltic and Scandinavian tectonic plates. The range is composed of a variety of rocks, including granite, gneiss, and limestone, which have been shaped by millions of years of weathering and erosion. The climate of the Scandinavian Mountains varies greatly depending on the altitude and location, ranging from subarctic to temperate. The higher peaks are covered in snow and ice year-round, while the lower valleys have a more temperate climate, with warm summers and cold winters.
What are the five major European mountain ranges?
+The five major European mountain ranges are the Alps, the Carpathians, the Apennines, the Pyrenees, and the Scandinavian Mountains.
Which mountain range is the highest and most extensive in Europe?
+The Alps are the highest and most extensive mountain range in Europe, stretching across eight countries and covering an area of approximately 190,000 square kilometers.
What is the cultural significance of the Carpathian Mountains?
+The Carpathian Mountains have a rich cultural and historical heritage, with many traditional villages and towns scattered throughout the range. The range has been home to many different ethnic groups, each with their own unique customs and traditions.
What is the geology of the Apennine Mountains?
+The Apennine Mountains are a relatively young mountain range, formed as a result of the collision between the African and Eurasian tectonic plates. The range is composed of a variety of rocks, including limestone, dolomite, and granite, which have been shaped by millions of years of weathering and erosion.
What is the climate of the Scandinavian Mountains?
+The climate of the Scandinavian Mountains varies greatly depending on the altitude and location, ranging from subarctic to temperate. The higher peaks are covered in snow and ice year-round, while the lower valleys have a more temperate climate, with warm summers and cold winters.
Meta Description: Explore the five major European mountain ranges, including the Alps, Carpathians, Apennines, Pyrenees, and Scandinavian Mountains, and discover their unique geography, climate, and cultural significance.