The Mean Platelet Volume (MPV) lab test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to measure the average size of platelets in the blood. Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are tiny blood cells that play a vital role in blood clotting. An abnormal MPV result can indicate various health conditions, including bleeding disorders, thrombocytopenia, and thrombocytosis. In this article, we will delve into the details of the MPV lab test, its significance, and the implications of abnormal results.
Key Points
- The MPV test measures the average size of platelets in the blood, which is essential for diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions.
- A normal MPV range is typically between 7.5 and 11.5 femtoliters (fL), but this can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's health status.
- Abnormal MPV results can indicate conditions such as thrombocytopenia, thrombocytosis, and bleeding disorders, among others.
- The MPV test is often used in conjunction with other laboratory tests, such as the complete blood count (CBC) and blood smear, to provide a comprehensive understanding of a patient's blood health.
- Recent studies have shown that MPV can be a valuable biomarker for predicting cardiovascular disease and other conditions, highlighting the importance of monitoring MPV levels in high-risk patients.
What is the MPV Lab Test?
The MPV lab test is a simple and non-invasive procedure that involves collecting a blood sample from a patient’s vein, typically from the arm. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where the MPV is measured using an automated hematology analyzer. The MPV result is usually reported in femtoliters (fL) and is calculated by dividing the total platelet volume by the total number of platelets.
Interpretation of MPV Results
Interpreting MPV results requires a thorough understanding of the normal range and the potential causes of abnormal results. A normal MPV range is typically between 7.5 and 11.5 fL, but this can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual’s health status. Results outside of this range can indicate various health conditions, including:
| MPV Range | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Low MPV (< 7.5 fL) | May indicate thrombocytopenia, platelet dysfunction, or bone marrow disorders |
| High MPV (> 11.5 fL) | May indicate thrombocytosis, platelet activation, or myeloproliferative disorders |
| Normal MPV (7.5-11.5 fL) | Indicates normal platelet size and function |
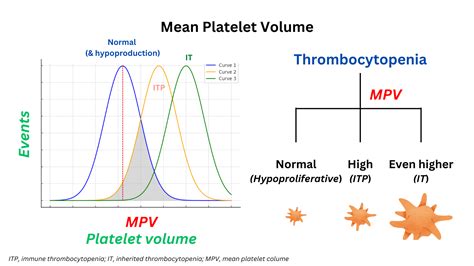
Clinical Significance of MPV
The MPV test has significant clinical implications, as it can help diagnose and monitor various health conditions. For example, a low MPV can indicate thrombocytopenia, a condition characterized by low platelet count, which can increase the risk of bleeding. On the other hand, a high MPV can indicate thrombocytosis, a condition characterized by high platelet count, which can increase the risk of blood clots.
Recent Advances and Future Directions
Recent studies have highlighted the potential of MPV as a biomarker for predicting cardiovascular disease and other conditions. For example, a study published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine found that elevated MPV levels were associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. These findings suggest that monitoring MPV levels may be a valuable tool for identifying high-risk patients and preventing cardiovascular events.
What is the normal range for MPV?
+The normal range for MPV is typically between 7.5 and 11.5 fL, but this can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's health status.
What does a low MPV indicate?
+A low MPV can indicate thrombocytopenia, platelet dysfunction, or bone marrow disorders, among other conditions.
Can MPV be used to predict cardiovascular disease?
+Yes, recent studies have shown that MPV can be a valuable biomarker for predicting cardiovascular disease, particularly in high-risk patients.
In conclusion, the MPV lab test is a valuable diagnostic tool that can provide insights into various health conditions. By understanding the clinical significance of MPV and its interpretation, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about patient care and treatment. As research continues to uncover the potential of MPV as a biomarker for predicting cardiovascular disease and other conditions, its importance in clinical practice is likely to grow.