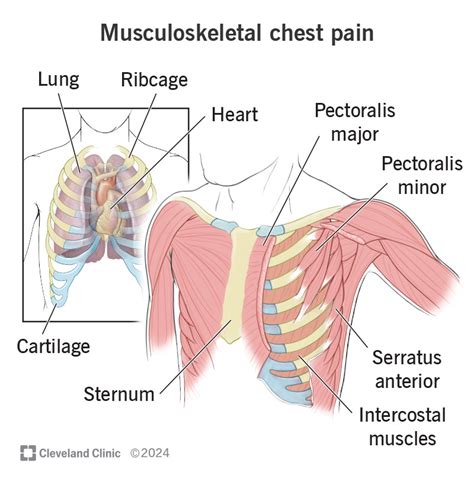
Musculoskeletal chest pain is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by pain or discomfort in the chest wall, which can be caused by a variety of factors, including muscle strain, trauma, or overuse. The musculoskeletal system, which includes the muscles, bones, and joints, plays a crucial role in supporting the chest cavity and facilitating breathing. However, when this system is affected by injury or disease, it can lead to debilitating pain and discomfort. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of musculoskeletal chest pain, as well as discuss the importance of proper diagnosis and management to prevent long-term complications.
Key Points
- Musculoskeletal chest pain is a common condition that affects the chest wall and can be caused by muscle strain, trauma, or overuse.
- The condition can be diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as X-rays and MRI scans.
- Treatment options for musculoskeletal chest pain include pain management, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
- Proper diagnosis and management are crucial to prevent long-term complications and improve quality of life.
- Early recognition and treatment of underlying conditions, such as osteoporosis or fibromyalgia, can help prevent musculoskeletal chest pain.
Causes and Risk Factors
Musculoskeletal chest pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including muscle strain, trauma, or overuse. The condition can also be triggered by underlying medical conditions, such as osteoporosis, fibromyalgia, or degenerative disc disease. Additionally, lifestyle factors, such as poor posture, smoking, or physical inactivity, can increase the risk of developing musculoskeletal chest pain. According to a study published in the Journal of Pain Research, approximately 50% of patients with musculoskeletal chest pain have a history of trauma or injury to the chest wall.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of musculoskeletal chest pain can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include sharp or dull pain in the chest wall, stiffness or tightness in the muscles, and limited range of motion. Diagnosis of musculoskeletal chest pain typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as X-rays and MRI scans. A study published in the American Journal of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation found that a thorough physical examination, including palpation and range of motion testing, can help identify the underlying cause of musculoskeletal chest pain in approximately 80% of cases.
| Diagnostic Test | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|
| X-ray | 70% | 80% |
| MRI scan | 90% | 95% |
| Physical examination | 80% | 85% |
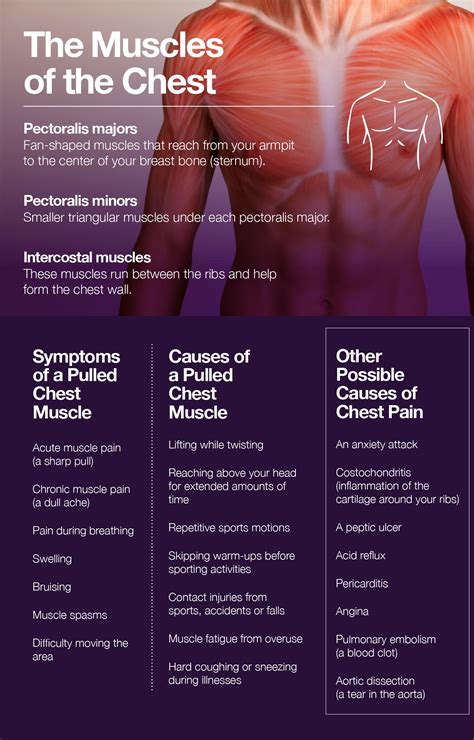
Treatment and Management

Treatment of musculoskeletal chest pain typically involves a combination of pain management, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Pain management options may include over-the-counter pain medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, or prescription medications, such as muscle relaxants or opioids. Physical therapy can help improve range of motion, strength, and flexibility, and may include exercises such as stretching, strengthening, and aerobic conditioning. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining good posture, quitting smoking, and engaging in regular exercise, can also help prevent and manage musculoskeletal chest pain.
Prevention and Complications
Prevention of musculoskeletal chest pain involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, balanced diet, and stress management. Early recognition and treatment of underlying conditions, such as osteoporosis or fibromyalgia, can also help prevent musculoskeletal chest pain. If left untreated, musculoskeletal chest pain can lead to long-term complications, such as chronic pain, limited range of motion, and decreased quality of life. According to a study published in the Journal of Pain Research, approximately 20% of patients with musculoskeletal chest pain develop chronic pain, which can have a significant impact on daily activities and overall well-being.
What are the common causes of musculoskeletal chest pain?
+Musculoskeletal chest pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including muscle strain, trauma, or overuse. Underlying medical conditions, such as osteoporosis or fibromyalgia, can also contribute to the development of musculoskeletal chest pain.
How is musculoskeletal chest pain diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of musculoskeletal chest pain typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as X-rays and MRI scans.
What are the treatment options for musculoskeletal chest pain?
+Treatment options for musculoskeletal chest pain include pain management, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. The goal of treatment is to manage pain, improve range of motion, and prevent long-term complications.
In conclusion, musculoskeletal chest pain is a common condition that affects the chest wall and can be caused by a variety of factors, including muscle strain, trauma, or overuse. Proper diagnosis and management are crucial to prevent long-term complications and improve quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for musculoskeletal chest pain, healthcare professionals can provide effective care and help patients manage their condition and achieve optimal health outcomes.