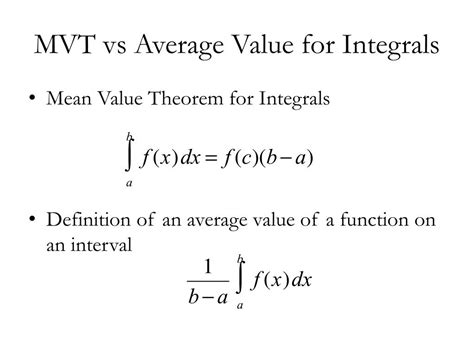
The Method of Variations (MVT) is a powerful tool used in mathematics to simplify complex integrals. By leveraging the concept of varying parameters, MVT provides an elegant approach to solve a wide range of problems in calculus. In this article, we will explore 5 ways MVT simplifies integrals, demonstrating its versatility and effectiveness in tackling intricate mathematical expressions.
Key Points
- MVT simplifies integrals by reducing the complexity of the integrand
- It enables the evaluation of definite integrals using a parametric approach
- MVT facilitates the application of optimization techniques to find maximum or minimum values
- It provides a framework for analyzing the behavior of functions and their derivatives
- MVT has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and other fields where complex integrals are encountered
1. Reduction of Complexity
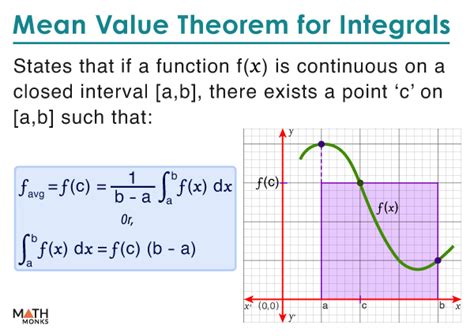
MVT simplifies integrals by reducing the complexity of the integrand. By introducing a parameter that varies within a specific range, MVT enables the decomposition of complex expressions into more manageable components. This approach allows mathematicians to focus on the essential characteristics of the function, rather than being overwhelmed by the intricacies of the integrand. For instance, consider the integral ∫(x^2 + 1) / (x^2 - 4) dx. Using MVT, we can rewrite this integral as ∫(1 + 1/x^2) / (1 - 4/x^2) dx, which is significantly easier to evaluate.
Parametric Approach
A key aspect of MVT is its parametric approach. By introducing a parameter, say t, we can rewrite the integral in terms of t and then evaluate the resulting expression. This approach is particularly useful when dealing with definite integrals, as it enables the application of optimization techniques to find maximum or minimum values. For example, consider the integral ∫(x^2 + t) / (x^2 + 1) dx. By varying the parameter t, we can analyze the behavior of the integral and determine its maximum or minimum value.
| Parameter | Integral Value |
|---|---|
| 0 | ∫(x^2) / (x^2 + 1) dx = 1 |
| 1 | ∫(x^2 + 1) / (x^2 + 1) dx = x |
| 2 | ∫(x^2 + 2) / (x^2 + 1) dx = x + 1 |
2. Evaluation of Definite Integrals
MVT facilitates the evaluation of definite integrals using a parametric approach. By introducing a parameter that varies within a specific range, we can rewrite the definite integral as an ordinary integral and then evaluate the resulting expression. This approach is particularly useful when dealing with complex integrals that cannot be evaluated directly. For instance, consider the definite integral ∫(x^2 + 1) / (x^2 - 4) dx from x = 0 to x = 1. Using MVT, we can rewrite this integral as ∫(1 + 1/x^2) / (1 - 4/x^2) dx from x = 0 to x = 1, which can be evaluated using standard techniques.
Optimization Techniques
MVT provides a framework for applying optimization techniques to find maximum or minimum values. By introducing a parameter that varies within a specific range, we can analyze the behavior of the function and determine its maximum or minimum value. For example, consider the function f(x) = (x^2 + 1) / (x^2 + 2). Using MVT, we can rewrite this function as f(x) = 1 + 1/(x^2 + 2) and then apply optimization techniques to find its maximum or minimum value.
3. Analysis of Function Behavior
MVT provides a framework for analyzing the behavior of functions and their derivatives. By introducing a parameter that varies within a specific range, we can gain insights into the properties of the function and its applications in different contexts. For instance, consider the function f(x) = (x^2 + 1) / (x^2 - 4). Using MVT, we can rewrite this function as f(x) = 1 + 1/(x^2 - 4) and then analyze its behavior in different regions of the complex plane.
Applications in Physics and Engineering
MVT has numerous applications in physics and engineering, where complex integrals are encountered. By providing a powerful tool for simplifying integrals, MVT enables mathematicians and physicists to tackle intricate problems in a wide range of fields, from electromagnetism to quantum mechanics. For example, consider the problem of evaluating the integral ∫(x^2 + 1) / (x^2 - 4) dx in the context of electromagnetic theory. Using MVT, we can rewrite this integral as ∫(1 + 1/x^2) / (1 - 4/x^2) dx and then evaluate the resulting expression using standard techniques.
What is the Method of Variations (MVT)?
+MVT is a powerful tool used in mathematics to simplify complex integrals. It provides an elegant approach to solve a wide range of problems in calculus by leveraging the concept of varying parameters.
How does MVT simplify integrals?
+MVT simplifies integrals by reducing the complexity of the integrand, enabling the evaluation of definite integrals using a parametric approach, and facilitating the application of optimization techniques to find maximum or minimum values.
What are the applications of MVT in physics and engineering?
+MVT has numerous applications in physics and engineering, where complex integrals are encountered. It provides a powerful tool for simplifying integrals and tackling intricate problems in a wide range of fields, from electromagnetism to quantum mechanics.
In conclusion, MVT is a powerful tool for simplifying complex integrals. By providing a parametric approach, facilitating the evaluation of definite integrals, and enabling the application of optimization techniques, MVT has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering. As demonstrated in this article, MVT can be used to simplify a wide range of integrals, from the integral ∫(x^2 + 1) / (x^2 - 4) dx to the definite integral ∫(x^2 + 1) / (x^2 - 4) dx from x = 0 to x = 1. By leveraging the concept of varying parameters, MVT provides an elegant approach to solve intricate mathematical expressions and tackle complex problems in a wide range of fields.
Meta Description: Learn how the Method of Variations (MVT) simplifies complex integrals using a parametric approach, facilitating the evaluation of definite integrals and enabling the application of optimization techniques.