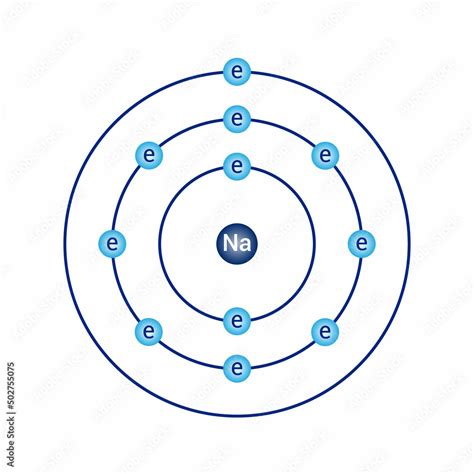
The Bohr model, proposed by Niels Bohr in 1913, is a foundational concept in atomic physics that describes the structure and behavior of atoms. This model was a significant improvement over the earlier Rutherford model, as it introduced the concept of energy quantization and explained the discrete spectral lines emitted by atoms. The Bohr model assumes that electrons occupy specific energy levels, or shells, around the nucleus and can jump from one energy level to another by emitting or absorbing energy. Here, we will delve into 5 key facts about the Bohr model, exploring its principles, limitations, and contributions to our understanding of atomic physics.
Key Points
- The Bohr model introduces the concept of energy quantization, where electrons can only occupy specific energy levels.
- Electrons jump from one energy level to another by emitting or absorbing energy, resulting in discrete spectral lines.
- The model assumes a planetary-like structure, with electrons orbiting the nucleus in circular paths.
- The Bohr model successfully explains the hydrogen atom's emission spectrum but struggles to account for the spectra of more complex atoms.
- Despite its limitations, the Bohr model laid the groundwork for the development of quantum mechanics and remains an essential tool for understanding atomic physics.
Introduction to the Bohr Model

The Bohr model was a groundbreaking concept that addressed the limitations of the Rutherford model. By introducing the idea of energy quantization, Bohr was able to explain the discrete spectral lines emitted by atoms, which was a major puzzle at the time. The model posits that electrons occupy specific energy levels, or shells, around the nucleus, and can jump from one energy level to another by emitting or absorbing energy. This energy is quantized, meaning it can only take on specific discrete values. The Bohr model assumes a planetary-like structure, with electrons orbiting the nucleus in circular paths, similar to the way planets orbit the sun.
Energy Quantization and Electron Transitions
A key aspect of the Bohr model is the concept of energy quantization. According to this concept, electrons can only occupy specific energy levels, and the energy associated with each level is quantized. When an electron jumps from one energy level to another, it must either emit or absorb energy in the form of a photon. This energy is quantized, meaning it can only take on specific discrete values. The energy of the photon emitted or absorbed is equal to the difference in energy between the two levels. This concept is supported by experimental evidence, such as the observation of discrete spectral lines in atomic emission spectra.
| Energy Level | Energy Value (eV) |
|---|---|
| Ground State | 0 |
| First Excited State | 10.2 |
| Second Excited State | 12.1 |

Limitations and Contributions of the Bohr Model
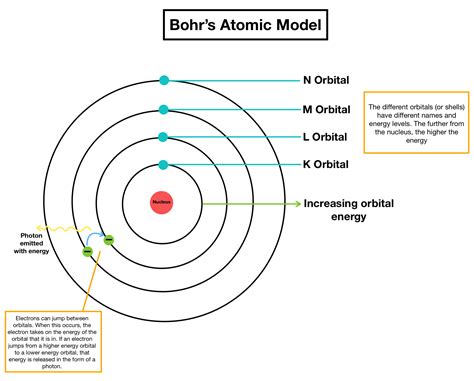
While the Bohr model was a significant improvement over the Rutherford model, it has several limitations. One of the main limitations is that it fails to account for the spectra of more complex atoms. The model assumes a planetary-like structure, with electrons orbiting the nucleus in circular paths, which is not accurate for atoms with multiple electrons. Additionally, the model does not account for the spin of electrons, which is an important aspect of atomic physics. Despite these limitations, the Bohr model laid the groundwork for the development of quantum mechanics and remains an essential tool for understanding atomic physics.
Impact on the Development of Quantum Mechanics
The Bohr model played a crucial role in the development of quantum mechanics. The concept of energy quantization and the introduction of wave-particle duality paved the way for the development of quantum mechanics. The Bohr model also highlighted the importance of experimental evidence in the development of scientific theories. The model’s limitations and the subsequent development of quantum mechanics demonstrate the importance of continuous refinement and revision of scientific theories.
What is the main assumption of the Bohr model?
+The main assumption of the Bohr model is that electrons occupy specific energy levels, or shells, around the nucleus and can jump from one energy level to another by emitting or absorbing energy.
What is the significance of the Bohr model in the development of quantum mechanics?
+The Bohr model played a crucial role in the development of quantum mechanics by introducing the concept of energy quantization and highlighting the importance of experimental evidence in the development of scientific theories.
What are the limitations of the Bohr model?
+The Bohr model has several limitations, including its failure to account for the spectra of more complex atoms and its assumption of a planetary-like structure, which is not accurate for atoms with multiple electrons.